![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Compare adrenal cortex and medullar in the following aspects:
- embryonic origin - when does it migrate - extra-adrenal tissue or not |
Adrenal cortex
- embryonic origin: mesoderm - migrate at 4-6 wks - no extra-adrenal tissue adrenal medulla - embryonic origin: ectoderm - migrate at 5th wks - extra-adrenal tissue: paravertebral and para-aortic, organ of Zuckerkandl |
|
|
Where are ectopic adrenal cortical tissue usually found?
|
- near kidney
- in pelvis along the path of migration from urogenital ridge - vaginsa and coccyx |
|
|
What is the clinical significance of ectopic adrenal cortical tissue?
|
if ACTH is elevated, ectopic tissue may get hyperplastic and hypertrophic
|
|
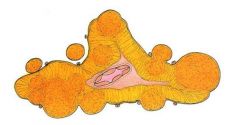
What is this adrenal disease?
|
cortical nodule
- not associated with cortical hyperfunction - risk factors: age, HTN, diabetes - associated with cushings(excess ACTH) or paraneoplastic ACTH by small cell carcinoma of lung |
|
|
What is the difference between cortical nodule and diffuse nodular hyperplasia?
|
diffuse nodular hyperplasia: entire cortex is thickened
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
|
- autosomal recessive biochemical defect affecting any of the 5 steps in synthesizing cortisol cholesterol. 95% exhibit absent 21-hydroxylase.
- diffuse cortical hyperplasia (especially zona reticularis) - adrenogenital syndrome (pure virilization, salt losing disorder) |
|
|
What enzyme defect is often present in most cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
|
21-hydroxylase
- convert progesterone to 11- deoxycorticostone - convert 17-hydroxyprogesterone to 11-deoxycortisol |
|
|
How to treat congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
|
- replace cortisol
- early surgical correction of external sex organs for genetic females |
|
|
What are some etiology of acquired cortical hyperplasia?
|
secondary cause
- pituitary hyperfunction: cushing syndrome (hypercortisolism) - ectopic ACTH from small cell lung carcinoma primary cause - primary hyperaldolsteronism |
|
|
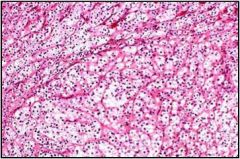
What is this adrenal disease?
gross: - cortical hyperplasia: yellow cortex, diffusely thickened, multinodular micro: rich cells in zonba fasculata and reticularis - bilateral |
acquired cortical hyperplasia
|
|
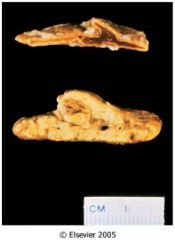
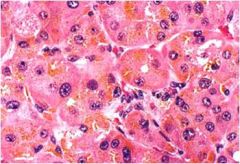
What is this congenital adrenal disease?
|
acquired cortical hyperplasia
- diffusely thickened and multinodular cortex. - rich cells in zona fasciculata and reticularis |
|
|
What is this adrenal disease?
- weakness - GI disturbances - gradual skin hyperpigmentation - hyperkalemia - hyponatremia - volume depletion, hypotension |
Addison disease
- low cortisol - low aldosterone - high ACTH |
|
|
List the 3 autoimmune adrenalitis.
|
- Addison disease
- autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome 1 (APS1): mutation in AIRE gene 21q22. candidiasis, ectodermal dystrophy, parathyroid hypofunction - autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome 2: adrenalitis with thyroiditis or type 1 diabetes |
|
|
What is this disease?
- candidiasis - ectodermal dystrophy - parathyroid hypofunction |
APS 1 (antoimmune polyendocrine syndrome 1)
- mutation in AIRE gene 21q22 |
|
|
What is this disease?
- adrenalitis - thyroiditis |
APS2 (antoimmune polyendocrine syndrome 2)
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- adrenalitis - type 1 diabetes |
APS2 (antoimmune polyendocrine syndrome 2)
- autoimmunity against islet cells of pancreas -> type 1 diabetes |
|
|
What is the function of AIRE protein? What happens when there is a genetic mutation?
|
- promotes self antigen in the thymus which lead to apoptosis of self-reactive T cells
- mutation leads to autoimmunity against adrenal gland (APS1) |
|
|
What does the skin look like in someone with Addison disease?
|
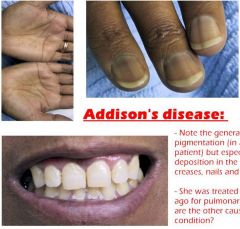
- generalized hyperpigmentation: skin, palmar creases, nail beds, gingivae
|
|
|
What disease is this?
- septic shock in newborns due to Nisseria meningitidis - DIC with widespread purpura |
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome: see adrenal homorrhage
|
|
|
List the types of neoplasms of the adrenal cortex.
|
- adenoma
- carcinoma - myelolipoma - metastatic carcinoma from lung and breast |
|
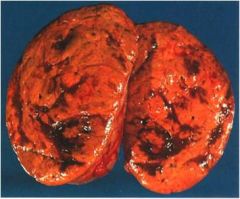
What is this tumor of the adrenal cortex?
gross: - solitary nodule, encapsulated - small: <50gm, <5cm |
cortical adenoma
- yellow (lipid laden) - balck (lipofuscin laiden) |
|
What cortical tumor is this?
|
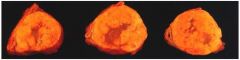
cortical adenoma
- yellow (lipid laiden) |
|
What cortical tumor is this?
|

cortical adenoma
- black (lipofuscin laiden) |
|
|
Name 2 causes of primary hyperaldosteronism.
|
- acquired cortical hyperplasia
- cortical adenoma |
|
|
What is this cortical tumor?
- large mass: 900 gm - invade central vein - wide range of differentiation - atypical mitoses |
cortical carcinoma
- gross: large, hemorrhage, necrosis, invasion of central vein - mean age 50yrs. |
|
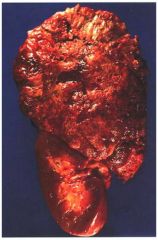
What is this cortical tumor?
|
cortical carcinoma
|
|
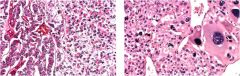
What is this cortical tumor?
|
cortical carcinoma
- high mitotic rate - atypical mitoses |
|
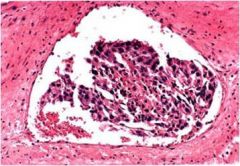
What is this cortical tumor?
|
cortical carcinoma
- invasion of veins - 50% show endocrine dysfunction |
|
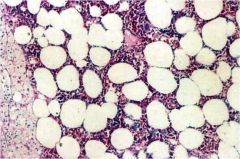
What is this cortical tumor?
|
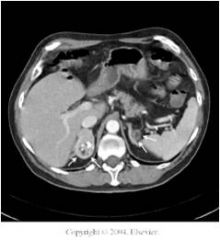
myelolipoma
- mixed fat and hematopoietic cells - CT: hypodense area of fat, focal bright calcifications |
|
|
What are some common place to find myelolipoma?
|
- adrenal gland
- spleen - most are solitary and unilateral |
|
|
List the tumors associated with adrenal medulla.
|
- medullary hyperplasia
- neurooblastoma - pheochromocytoma |
|
|
What is this adrenal tumor?
- bilateral, grossly nodular or diffuse - associated with MEN 2 - symptoms similar to pheochromocytoma |
adrenal medullary hyperplasia
|
|
|
What is the most common solid organ malignancy in children? 2nd most common?
|
- most common: brain tumor
- 2nd most common: neuroblastoma |
|
|
What is the most common malignancy in children overall?
|
acute leukemia
|
|
|
Tumor genetics of neuroblastoma.
|
- 17q gain
- 1p deletion - MYC amplification |
|
|
What are some sites of origin of neuroblastoma?
|
- adrenal medulla: 40%
- paravertebral region in abdomen: 25% - midline alomg sympathetic chain: 20% - posterior mediastinum: 15% |
|
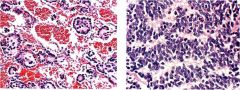
What is this tumor?
- homer-wright rosettes - palisading rosettes |
neuroblastoma
|
|
|
What are some common locations you find pheochromacytoma?
|
think midline
- intra-adrenal - extra-adrenal: abdominal paragnaglia, organ of Zuckerkandl |
|
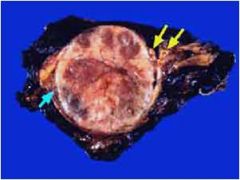
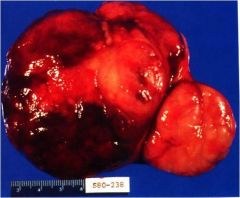
What is this tumor?
- soft, tan-red - encapsulated - highly vascular |
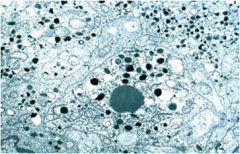
pheochromocytoma
- picture: dense core granules |
|
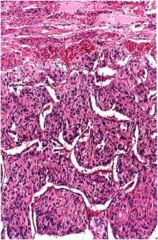
What is this adrenal tumor?
|
pheochromocytoma
- zellballen arrrangement: ball of cells |
|
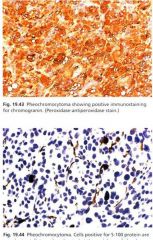
What is this adrenal tumor?
- staining of chromogranin |
pheochromocytoma
|
|
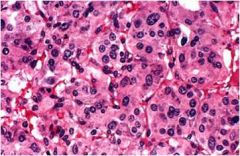
What is this adrenal tumor?
- gross: soft, tan-red, capsulated, highly vascular |
pheochromocytoma
- nuclear pleomorphism |
|
|
Compare tumor genetics of MEN2 and MEN3.
|
MEN2: germline mutation in RET protooncogene resulting in gain of function.
MEN3: mutation in RET affecting single AA of RET protein, altering tyrosine kinase domain. |
|
|
MEN2 or MEN3?
germline mutation in RET protooncogene resulting in gain of function |
MEN2
|
|
|
MEN2 or MEN3?
mutation in RET affecting single AA of RET protein, altering tyrosine kinase domain. |
MEN3
|
|
|
MEN2 or MEN3?
- pheochromocytoma - paratyroid hyperplasia - medullary carcinoma of thyroid - indolent |
MEN2
|
|
|
MEN2 or MEN3?
- pheochromocytoma - medullary carcinoma of thyroid - mucosal neuromas - marfanoid habitus - aggressive |
MEN3
|
|
|
What is this tumor?
- gross: 225 gm tumor in retroperitoneum near right kidney - histo: similar to pheochromocytoma |
extra-adrenal paraganglioma
|
|
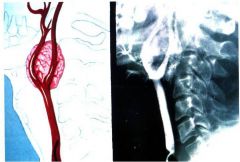
What is this?
|
carotid body paraganglioma
|
|
|
Name some adrenal-based causes of glucocorticoid excess. (3)
|
- cortical adenoma
- cortical carcinoma - micronodular hyperplasia |
|
|
Name some extra-adrenal-based causes of glucocorticoid excess. (3)
|
- pituitary ACTH-adenoma
- ectopic ACTH syndrome - iatrogenic steroid therapy |
|
|
Name some adrenal-based causes of glucocorticoid deficiency (Addison's). (3)
|
- TB
- antoimmune adrenalitis - adrenal hemorrhage |
|
|
Name some extra-adrenal-based causes of glucocorticoid deficiency (Addison's). (2)
|
- exogenous suppression of ACTH after steroid therapy
- lesions destroying pituitary gland |
|
|
Name some adrenal-based causes of mineralocorticoid excess.
|
- corical adenoma
- cortical carcinoma - congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
|
|
Name some extra-adrenal-based causes of mineralocorticoid excess.
|
- licorice intoxication: competively inhibits 11-beta-HSD
|
|
|
Name some adrenal-based causes of mineralocorticoid deficiency.
|
- TB
- autoimmune afrenalitis - adrenal hemorrhage - 18-hydroxylase deficiency |

