![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hypothalamus |
*then stimulates the anterior pituitary TRH --> TSH CRH --> ACTH PRH/PIH --> Prolactin GHRH --> GH GnRH --> LH & FSH |
|
|
Anterior pituitary gland |
FSH: ovaries, estrogen
LH: progesterone & testosterone TSH: thyroid gland (metabolic rate) GH: growth of body ACTH: adrenal glands (cortisol & aldosterone) Prolactin: lactation & milk production |
|
|
Posterior pituitary gland |
vasopressin (ADH) & oxytocin *ADH increases BP |
|
|
Parathyroid gland |
PTH --> responsible for calcium balance
Hypercalcemia - overactive PTH - inc Ca2+ - tx: surgery remove parathyroid gland
Primary hyperparathyroidism - ddx hypercalcemia, adenoma, carcinoma or hyperplasia
Hypocalcemia - chvostek's & trousseau's sign (brisk reflexes, numbness, twitching of face --> ER) - cause: post-surgery, vit D deficient
Osteoporosis - low bone mass & bone quality - DEXA: >2.5 SD
Osteopenia - menopause, dec estrogen @ risk - DEXA: 1-2.5 SD |
|
|
Thyroid gland |
T4 & T3 Calcitonin (inc Ca2+ levels, opposed of PTH) |
|
|
TSH |
Normal: 0.4-4.0 If abnormal: order full thyroid panel |
|
|
American thyroid association |
>35yo screened q5yrs *euthyroid = normal range |
|
|
Hyperthyroidism |
LOW TSH HIGH free T4 & T3 |
|
|
Hyperthyroidism sx |
Goiter Fine tremors, sweaty palms, smooth ski Exophthalmos in later stages tachy, afib, CHF Weight loss, can't sleep Oligomenorrhea Heat intolerance Hyperreflexia Freq stools (loose) |
|
|
Grave's disease |
autoimmune dz causing production of excess thyroid hormones (T3 & T4) also at risk for RA, pernicious anemia & osteoporosis |
|
|
Labs/tests |
1. TSH, serum free T4, T3 2. Antibody test for grave's dz (thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulin) 3. Thyroid u/s: if mass or nodule 4. 24hr RAIU: cold spot (worrisome -- fine needle aspiration), hot spot (benign -- radioiodine ablation or surgery) *subtotal thyroidectomy --> monitor laryngeal nerve (speaking ability) |
|
|
Hyperthyroidism meds/tx |
1. Propylthiouracil (PTU)* -- preferred tx 2. Methimazole (Tapazole) - Shrinks thyroid gland/dec hormone production - Monitor CBCs, LFTs 3. Adjunctive tx: BB to alleviate sx of anxiety, tachy, etc. 4. Radioactive Iodine: permanent destruction of thyroid gland -- hypothyroidism for life (contra: preg) |
|
|
Thyroid storm |
aka thyrotoxicosis - hyperthyroidism left untreated - acute worsening of sx d/t stress or infxn - sx: dec LOC, fever, abd pain - ER ASAP - tx: high doses BB, methimazole or PTU |
|
|
Hypothyroidism |
HIGH TSH LOW free T4 - classic case: hashimoto's thyroiditis (test = animicrosomal antibodies elevated) |
|
|
Hypothyroidism sx |
Skin thick, dry Reflexes: hyporeflexia Depression Weight gain Constipation Menorrhagia Cold intolerance Can cause dyslipidemia *can also have a goiter |
|
|
Hypothyroidism tx |
Levothyroxine (Synthroid): 25-50mcg/day *recheck TSH q6-8wks until normalized - if >4: increase synthroid by 12.5-25 - If <0.5: decrease by 12.5-25 |
|
|
Subclinical hypothyroidism |
HIGH TSH w/ NORMAL serum free T4 |
|
|
Myxedema coma |
*untreated hypothyroidism - dec mental status, hypotension, dec BG - ER! |
|
|
Pancreatic islets |
Glucagon (low blood glucose conc) Insulin (increases blood glucose conc) Somatostatin (digestive system) |
|
|
Type I DM |
Destruction of beta cells --> abrupt cessation of insulin production - uncorrected = body fat will be used for fuel, ketones build up in body --> DKA, coma |
|
|
DKA |
- extreme hyperglycemia w/ DMI - BG 300-800 - quick onset! - s/s: hypokalemia, acidosis, rapid breathing, +ketones (>200), FVD & electrolyte loss |
|
|
Type II DM |
Progressive decreased secretion of insulin (w/ peripheral insulin resistance) - strong genetic component |
|
|
Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) |
- extreme hyperglycemia w/ DMII - BG >1000 - slow onset - s/s: tachy, CNS changes, -ketones, hypotension, |
|
|
Diabetes type II risk factors |
- overweight (BMI>30) - abdominal obesity, sedentary lifestyle - metabolic syndrome - hispanic, AA, asian, indian - positive fam hx - hx gestational DM or infant wt >9lbs @ birth - impaired fasting BS or glucose tolerance |
|
|
Metabolic syndrome |
- Obesity, HTN, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia |
|
|
Diagnostic criteria for DM |
A1c: >6.5% Fasting glucose: >126 Sx hyperglycemia + random BG >200 2hr plasma glucose >200 *must have >2 & test repeated Goal: BP <130/80 LDL <100 A1c <7% (<8% if comorbidities, elderly) Peak postprandial glucose: <180 Extra: HDL >50, total cholesterol <200, TG <150 |
|
|
Normal serum glucose levels |
Fasting glucose: 70-100 Peak postprandial glucose: <180 A1c: <6% |
|
|
Newly diagnosed |
- Check A1c q3mo until controlled, then q6mo - Lipid profile at least 1x/yr - Microalbuminuria at least 1x/yr (if type II & at time of dx!) - Electrolytes (K, Mg, Na), liver fxn panel, TSH Every visit: check BP, feet, weight, BMI, blood sugar Preventative care: - Flu shot/yr - Pneumococcal vaccine - ASA 81mg if high risk MI, stroke - Ophthalmologist yearly (type II time of dx!, type I first exam at 5yrs) - Podiatrist: 1-2x/year - Dental |
|
|
Management |
*Lifestyle changes 1st line! along w/ oral meds - Wt loss improves metabolic control in type II - Exercise: Increases glucose utilization by the muscles At high risk: - encourage wt loss (7% body wt) - regular physical activity (150min/wk) - increase dietary fiber & foods w/ whole grains |
|
|
Type II DM tx algorithm |
Metformin + SU, TZD, DPP-4, SGLT2, GLP, or insulin (if A1c NOT at target after 3mo of monotherapy) + (A1c not achieved 3mo) same meds + (not achieved) basal insulin + mealtime insulin OR GLP-1 |
|
|
Diabetes tx algorithm picture |
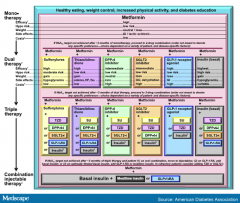
|
|
|
Dietary recomm |
- Alcohol: 1x/day for women, 2x/day for men - Monitor carbs - Saturated fat <7% total calories - Reduce intake trans fat |
|
|
Hypoglycemia |
High risk: <50 Sx: sweaty palms, tired, dizzy, tachy, confusion, weak *BB can mask sx! Tx: Glucose (15-20g) for conscious pts; glucagon for sig risk |
|
|
Hyperglycemia |
*BS >126 - polydipsia, polyphagia (inc hunger), polyuria (>200), blurred vision, tired, dry skin |
|
|
DI |
- Pituitary disorder (lack of ADH) - s/s: polyuria, polydipsia |
|
|
Illness & surgery |
- Do not stop taking anti diabetic meds - Contact HCP: dehydrated, vomiting, diarrhea, BG >300, changes LOC |
|
|
Dawn phenomenon |
- Elevation in glucose early in AM d/t inc insual resistance btwn 4&8am caused by physiologic spike in growth hormone, glucagon, epinephrine & cortisol |
|
|
Somogyi effect |
*rebound hyperglycemia, common type I - severe nocturnal hypoglycemia stimulates counterregulary hormones (glucagon) to be released in liver - high levels glucagon --> high fasting BG by 7am - Due to over treatment w/ the evening &/or bedtime insulin Tx: check BG very early in am (3:00am) for 1-2wks - Snack before bedtime, or eliminate dinner time NPH dose or lower bedtime dose for both NPH & regular insulin |
|
|
Diabetic retinopathy |
- Microaneurysms (cotton wool exudates) - Neovascularization (small arterioles in retina rupture easily) |
|
|
Types of insulin |
Rapid acting (lispro/humalog; aspart/novolog;) 1 meal at a time - Onset: 15min - Peak: 30min-2.5hrs - Duration: 4.5hrs Short acting (regular insulin/novolin; pump) meal to meal - Onset: 30min - Peak: 1-5hrs - Duration: 6-8hrs Intermediate (NPH) covers bfast to dinner - Onset: 1hr - Peak: 6-14hrs - Duration: 18-24hrs Basal insulin (glargine/lantus; detemir/levemir) *once a day - Onset: 1hr - NO PEAK - Duration: 24hrs Mixture (humulin 70/30) - Onset: 30min - Peak: 4hrs - Duration: 24hrs *Do NOT use oral antidiabetic drugs for type I DM! *always initiate therapy w/ daily glargine or detemir or bedtime NPH |
|
|
Biguanides (Metformin) |
*1st line - decreases glucogenesis & peipheral insulin resistance - INSULIN SENSITIZER, REDUCES HEPATIC GLUCOSE PRODUCTION, REDUCES INTESTINAL GLUCOSE ABSORPTION - promotes wt loss - monitor serum creatinine, GFR, UA & LFTs - IV contrast: HOLD on day procedure & 48hrs after
Risks: - increased risk lactic acidosis - can inc vit B12 def --> causing parasthesias - Do NOT give if GFR <30
*can use w/ peds >8yo |
|
|
Sulfonylureas |
Glipizide, Glyburide, Glimepiride* - stimulates beta cells to secrete more insulin - BOOSTS INSULIN RELEASE in pancreas - not commonly used (high risk severe hypogly) ADE: - wt gain - photosensitivity - inc w/ kidney dz - Last option before insulin* |
|
|
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) |
Avandia, Actos* (a/w bladder CA?) - INSULIN SENSITIZER - enhances insulin sensitivity in muscle tisse - avoid: CHF, heart dz (causes water retention, edema!) - monitor ALT ADE: - wt gain |
|
|
DPP-4 Inhibitors |
-gliptin - BOOSTS INSULIN RELEASE IN RESPONSE TO RISE IN BS Warning: - Avoid saxagliptin & alogliptin in CHF - Linagliptin CAN use w/ kidney dz - Do NOT use sitagliptin (januvia) w/ kidney dz |
|
|
SGLT2 inhibitior |
-gliflozin - INCREASES EXCRETION OF GLUCOSE IN URINE IN RESPONSE TO HIGH BS - glucose co-transporters - GFR must be >60 ADE: - UTI, increased urination - urosepsis, DKA |
|
|
Bile-acid sequestrants |
Cholestyramine (questran) - redue hepatic glucose production - also lowers LDL* ADE: - GI sx (take w/ meals) |
|
|
Meglitinide |
Repaglinide (prandin) - stimulates pancreatic secretion of insulin - type II w/ post-prandial hyperglycemia - NOT recomm as monotherapy |
|
|
GLP-1 agonist |
Exenatide (byetta) - stimulates GLP-1 causing inc insulin production & inhibits postprandial glucagon release - SLOWS GASTRIC EMPTYING, BOOSTS INSULIN RELEASE IN RESPONSE TO RISE IN BS - monitor: amylase/lipase - use 1x/day ADE: - wt gain - pancreatitis *injection only |
|
|
Acanthosis nigricans |
- marker of insulin resistance |
|
|
HgbA1c |
Decreases as TG decreases (want <150) |
|
|
Adrenal gland |
Adrenal medulla - Epinephrine & Norepinephrine - increases HR & BP (sympathetic NS) Adrenal cortex - Aldosterone (kidneys, preserve Na+&H20, excrete K+) - Cortisol - Adrenal androgens |
|
|
Adrenal insufficiency |
Primary (Addison's Disease) - excess ACTH - glucocorticoid & mineralcorticoid replacement - hyperpigmentation, hyperkalemia, met acidosis - fever, n/v, abd pain --> send to ER (addison's crisis) - after tx will NEVER get cortisol production Secondary - long term steroids - glucocorticoid replacement only - ACTH deficient - after tx cortisol production comes back Labs: - dec Na+, dec glucose, hypotension |
|
|
Adrenal excess |
Cushing's disease - inc cortisol - s/s: moon facies, buffalo hump, HTN, DM Primary aldosteronism - inc aldosterone - cause: adrenal adenoma |
|
|
Adrenal medulla |
Pheochromocytoma - hormone secreting tumor - classic triad: HA, sweating, palpitations - alpha blockers FIRST then BB or CCB |
|
|
Pituitary disease |
Acromegaly - inc GH & IGF-1 - children = inc long bone (gigantism) - s/s: facial changes, HTN, hyperhydrosis *GH remains inc when inc glucose Hypopituitarism - cause: hypothalamic or pituitary tumor |
|
|
Cushing's triad |
Nervous system response to ICP: 1. HTN 2. Irregular breathing 3. bradycardia |

