![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the cells of the islets of langerhans in the pancreas? 4
|
1. alpha cells
2. beta cells 3. delta cells 4. F cells (one of these is not like the others...) |
|
|
What do the alpha cells in the islet of langerhans produce? 3
|
1. glucagon- like peptides
2. glucagon 3. proglucagon |
|
|
What do the beta cells in the islet of langerhans produce? 4
|
1. insulin
2. proinsulin 3. C peptide 4. amylin |
|
|
What do the delta cells in the islet of langerhans produce? 1
|
1. somatostatin
|
|
|
What do the F cells in the islet of langerhans produce?1
|
pancreatic polypeptide
|
|
|
A little look at the pancreas just for shats and giggles...
|
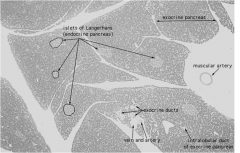
|
|
|
Why do scientists use Laser Scanning Cytometry to study the physiology of the pancreas?
|
to access their viability before transplantation
|
|
|
Summarize insulin production. 7
|
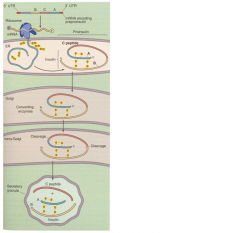
1. mRNA from the insulin gene contains: 5’ untranslated region,B, C, and A peptide domains; and a 3’UTR.
2. The leader plus the B, C, and A domains make the preproinsulin. 3. During translation of the mRNA, the leader sequence is cleaved in the lumen of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. 4. What remains is the proinsulin, which consists of the B, C, and A domains. 5. In the trans-Golgi, proteases cleave the proinsulin at two sites, releasing the C peptide as well as the mature insulin molecule, which consists of the B and A chains that are connected by two disulfide bonds. 6. The secretory granule contains insulin and the C peptide, as well as proinsulin. 7. These components all are released into the extracellular space during secretion. |
|
|
How is insulin secreted? Oh look another graph... yippee.
|
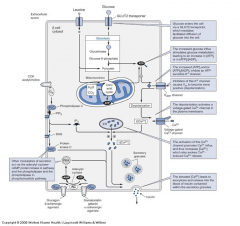
|
|
|
Is more insulin secreted in response to oral or IV glucose?
|
More insulin is secreted with oral glucose b/c of GI hormones released which facilitate beta cell function and insulin secretion. This is called an incretin effect.
|
|
|
What happens when glucose is given by IV?
|
Glucose delivered via IV stimulates a biphasic release in insulin. The initial increase is believed to be the secretion of preformed insulin present in beta cells. Then secretion increases again as the cells synthesizes ‘new’ insulin.
|
|
|
What is the incretin effect?
|
When glucose is given orally and the GI hormones facilitate beta cell function and insulin secretion
|
|
|
What happens when insulin signals? and what determines the cellular response that will happen? (2)
|
- the binding of insulin to its receptor can result in the activation of multiple second messenger systems.
- The amount of insulin that binds and the second messenger systems that are activated dictate the cellular responses that will ensue. |
|
|
Where are the effects of insulin felt the most? 3
|
1. muscles
2. adipocytes 3. liver |
|
|
What does insulin do to muscle tissue? 3
|
1. inc glucose uptake
2. inc protein synthesis 3. dec the breakdown of proteins |
|
|
What effect does insulin have on adipocytes? 3
|
1. inc glucose uptake
2. inc free fatty acid uptake 3. inc triglyceride production |
|
|
What effect down insulin have on the liver? 4
|
1. inc glucose conversion to glycogen
2. dec glycogenolysis 3. inc glycolysis and triglycerie prouction 4. dec gluconeogenesis |
|
|
What is amylin?
|
a 37 amino acid peptide co-secreted with insulin in response to nutrient load
|
|
|
What does amylin inhibit? 3
|
1. gastric emptying and gastric acid secretion (area = postrema hindbrain)
2. glucagon secretion 3. food intake - satiety factor (area = postrema) |
|
|
What peptide hormone's receptor is bound to G alpha s?
|
Glucagon
|
|
|
What stimulated the secretion of glucagon? 2
|
1. hypoglycemia
2. amino acids |
|
|
What inhibits the secretion of glucagon? 3
|
1. hyperglycemia
2. somatostatin 3. insulin |
|
|
Hypoglycemia and amino acids stimulate what?
|
the secretion glucagon
|
|
|
Hyperglycemia, Somatostatin, and insulin inhibit the secretion of..?
|
glucagon.
|
|
|
What effects does glucagon have? and where?
|
1. the liver
2. dec glycolysis 3. inc gluconeogenesis 4. inc glycogenolysis 5. inc lipolysis |
|
|
The physiology in normal ppl and pathophysiology in diabetes.
|
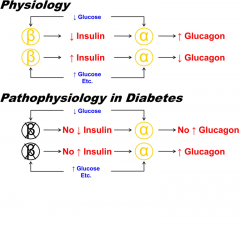
Normally a decrease in plasma glucose causes a decrease in β-cell insulin secretion that signals an increase in α-cell glucagon secretion during hypoglycemia. An increase in plasma glucose, among other nutrients, causes an increase in β-cell insulin secretion that prevents an increase in α-cell glucagon secretion in response to those nutrients after a mixed meal. On the other hand, in the setting of β-cell failure in type 1 diabetes and advanced type 2 diabetes, a decrease in plasma glucose cannot cause a decrease in β-cell insulin secretion, and the absence of that signal results in no increase in pancreatic α-cell glucagon secretion during hypoglycemia. Conversely, in the setting of β-cell failure, an increase in plasma glucose, among other nutrients, cannot cause an increase in β-cell insulin secretion, and the absence of that restraining signal results in an increase in pancreatic α-cell glucagon secretion after a mixed meal.
|
|
|
What secretes somatostatin and what stimulates its secretion? (3)
|
1. delta cells
1. Glucose 2. Arginine 3. GI hormones |
|
|
What are the somatostatin receptors?
|
- SSTR 1-5, G-protein coupled receptors
- SSTR 5 responsible for dec insulin secretion - SSTR 2 responsible for neg glucagon and GH |
|
|
What are the 3 effects of somatostatin?
|
1. Slows gastric emptying
2. Decreases gastric secretions 3. Inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion (and GH |
|
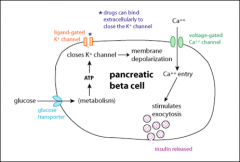
|
Same graph as earlier but less confusing...
|

