![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
12-lead ECG |
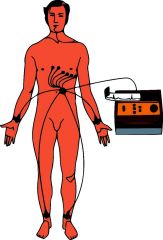
An ECG that uses 12 leads attached to the patient's skin; these include the limb leads and chest leads. |
|
|
4-lead ECG |
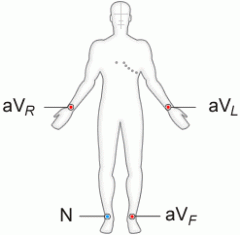
An ECG that uses 4 leads attached to the patient's skin; these include the limb leads. |
|
|
abandonment |
Unilateral termination of care by the EMT without the patient's consent and without making provisions for transferring care to another medical professional with the skills and training necessary to meet the needs of the patient. |
|
|
abdomen |
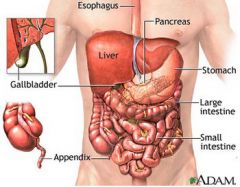
The body cavity that contains the major organs of digestion and excretion. It is located below the diaphragm and above the pelvis. |
|
|
abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) |
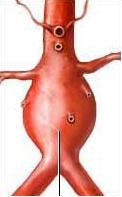
A condition in which the walls of the aorta in the abdomen weaken and blood leaks into the layers of the vessel, causing it to bulge. |
|
|
abdominal-thrust maneuver |
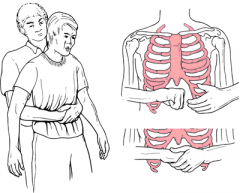
The preferred method to dislodge a severe airway obstruction in adults and children; also called the Heimlich maneuver. |
|
|
abduction |
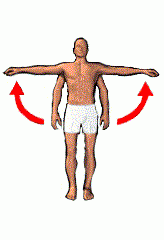
Motion of a limb away from the midline. |
|
|
abrasion |
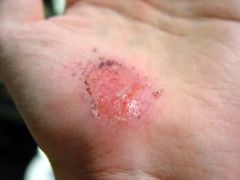
Loss or damage of the superficial layer of skin as a result of a body part rubbing or scraping across a rough or hard surface. |
|
|
abruptio placenta |
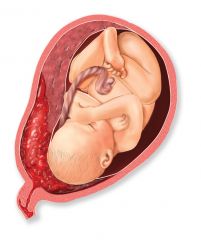
A premature separation of the placenta from the wall of the uterus. |
|
|
absorption |
The process by which medications travel through body tissues until they reach the bloodstream. |
|
|
access |
Gaining entry to an enclosed area and reaching a patient. |
|
|
access port |
A sealed hub on an administration set designed for sterile access to the intravenous fluid. |
|
|
accessory muscles |
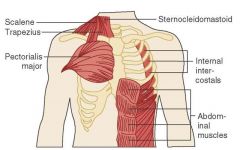
The secondary muscles of respiration. They include the neck muscles (sternocleidomastoids), the chest pectoralis major muscles, and the abdominal muscles. |
|
|
acetabulum |
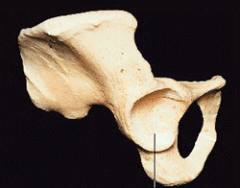
The depression on the lateral pelvis where its three component bones join in, in which the femoral head fits snuggly. |
|
|
acidosis |
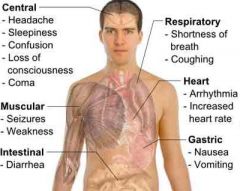
A pathologic condition that results from the accumulation of acids in the body. |
|
|
acromioclavicular (AC) joint |
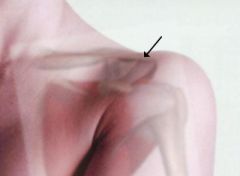
A simple joint where the bony projections of the scapula and the clavicle meet at the top of the shoulder. |
|
|
action |
The therapeutic effect of a medication on the body. |
|
|
activated charcoal |

An oral medication that binds and absorbs ingested toxins in the gastrointestinal tract for treatment of some poisoning and medication overdoses. Charcoal is ground into a very fine powder that provides the greatest possible surface area for binding medications that have been taken by mouth; it is carried on the EMS unit. |
|
|
activities of daily living |
The basic activities a person usually accomplishes during a normal day, such as eating, dressing, and bathing. |
|
|
acute abdomen |
A condition of sudden onset of pain within the abdomen, usually indicating peritonitis; immediate medical or surgical treatment is necessary. |
|
|
acute coronary syndrome |
A term used to describe a group of symptoms caused by myocardial ischemia; includes angina and myocardial infarction. |
|
|
acute myocardial infarction (AMI) |
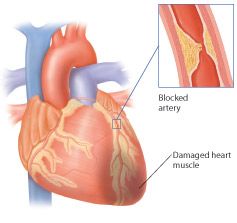
A heart attack; death of heart muscle following obstruction of blood flow to it. Acute in this context means "new" or "happening right now." |
|
|
acute stress reactions |
Reaction to stress that occurs during a stressful situation. |
|
|
Adam's apple |
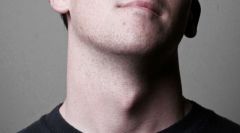
The firm prominence in the upper part of the larynx formed by the thyroid cartilage. It is more prominent in men than in women. |
|
|
addiction |
A state of overwhelming obsession or physical need to continue the use of a drug or agent. |
|
|
adduction |
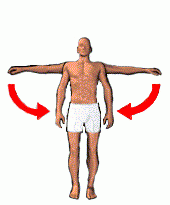
Motion of a limb toward the midline. |
|
|
adenosine triphosphate (ATP) |
The nucleotide involved in energy metabolism; used to store energy. |
|
|
adolescents |
Persons who are 12 to 18 years of age. |
|
|
adrenal glands |
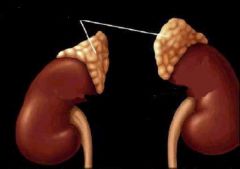
Endocrine glands located on top of the kidneys that release adrenaline when stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. |
|
|
adrenergic |
Pertaining to nerves that release the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, or noradrenaline (such as adrenergic nerves, adrenergic response). The term also pertains to the receptors acted on by norepinephrine, that is, the adrenergic receptors. |
|
|
adsorption |
The process of binding or sticking to a surface. |
|
|
advance directive |
Written documentation that specifies medical treatment for a competent patient should the patient become unable to make decisions; also called a living will or health care directive. |
|
|
advanced EMT (AEMT) |
An individual who has training in specific aspects of advanced life support, such as intravenous therapy, and the administration of certain emergency medications. |
|
|
advanced life support (ALS) |
Advanced lifesaving procedures, some of which are now being provided by the EMT. |
|
|
adventitious breath sounds |
Abnormal breath sounds such as wheezes, rhonchi, and rales. |
|
|
aerobic metabolism |
Metabolism that can proceed only in the presence of oxygen. |
|
|
afterload |
The force or resistance against which the heart pumps. |
|
|
aging |
The process by which the temporary bond between the organophosphate and acetylcholinesterase undergoes hydrolysis, resulting in a permanent covalent bond. |
|
|
agitated delirium |
A condition of disorientation, confusion, and possible hallucinations coupled with purposeless, restless physical activity. |
|
|
agonal respirations |
Slow, shallow, irregular respirations or occasional gasping breaths; sometimes seen in dying patients. |
|
|
agonist |
A medication that causes stimulation of receptors. |
|
|
air ambulances |
Fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters that have been modified for medical care; used to evacuate and transport patients with life threatening injuries to treatment facilities. |
|
|
air embolism |
The presence of air in the veins, which can lead to cardiac arrest if it enter the heart. |
|
|
airborne transmission |
The spread of an organism in aerosol form. |
|
|
airway |
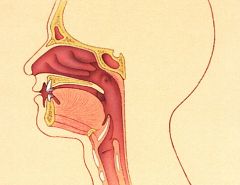
The upper airway tract or the passage above the larynx, which includes the nose, mouth, and throat. |
|
|
alkalosis |
The buildup of excess base (lack of acids) in the body fluids. |
|
|
allergen |
A substance that causes an allergic reaction |
|
|
allergic reaction |
The body's exaggerated immune response to an internal or surface agent. |
|
|
alpha |
A type of energy that is emitted from a strong radiologic source; it is the least harmful penetrating type of radiation and cannot travel fast or through most objects. |
|
|
alpha-adrenergic receptors |
Portions of the nervous system that, when stimulated, can cause constriction of blood vessels. |
|
|
altered mental status |
A change in the way a person thinks and behaves that may signal disease in the central nervous system or elsewhere in the body. |
|
|
alveolar ventilation |
The volume of air that reaches the alveoli. It is determined by subtracting the amount of dead space air from the tidal volume. |

