![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
65 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Negotitation
|
Joint examination to resolve conflict by reaching solution acceptable to both parties
|
|
|
|
Importance of negotiation
|
-Relevant for everyone
-helps receive a workin resolution -preserve relationships -reduces stress and potential conflicts |
|
|
|
Aspects of negotiation
|
-setting objectives
-formal/informal or collective/individual -occurs at all levels |
|
|
|
Why negotiate
|
Managers-enhance performance
Employees- work life/balance |
|
|
|
Forms of negotiation
|
Distributive - win lose
Integrative - win win |
|
|
|
Impacts of negotiation
|
Competing- you lose, I win
Collaborating- I win, you win Compromising- I win some, you win some, I lose some, you lose some Avoiding- I lose, you lose Accommodating- I lose, you win |
|
|
|
Stages of negotiation
|
1. Preparation and planning
2. Definition of ground rules 3. Clarification and justification 4. Bargaining and problem solving 5. Closure and implementation |
|
|
|
Successful negation
|
Requires serious thought and preparation
Communication skills Look forward not backwards Adopt a win win attitude |
|
|
|
Staffing - HRM
|
HRM- effective use of human resources in order to enhance organisational performance
|
|
|
|
HRM 3 key elements
|
1.Attracting - planning, recruitment, selection
2.developing - training, learning and development, career planning and development 3. Maintaining - retention, performance review and remuneration |
|
|
|
HR planning
|
-Having right person at the right time with the right skills in the right place
-important to anticipate changes |
|
|
|
Planning process
|
1. Identify staff requirements
2. Assess demand for human resources - gap analysis 3. Forecasting - assess future demand 4. Assessing internal and external supply of human resources 5. Creating an action plan to staff organisation. Long term and short term |
|
|
|
Cost of getting it wrong
|
Loss of other key staff
Burnout Further recruitment costs Training and orientation investment loss Reduced profits Impaired reputation and image |
|
|
|
Learning and development
|
The people develop
Team and groups work better The organisation improves |
|
|
|
Learning theories
|
Behaviourist approach
Cognitive approach Social learning Experiential learning |
|
|
|
Behaviourist approach
|
Classical - behaviours are shaped by the pairing of stimulus eg. Certain smell or song brings on certain emotion
Operant conditioning - behaviours as a result of consequences eg. Repeat behaviours that are rewarded positively |
|
|
|
Cognitive approach
|
Linking ideas with experiences and situations - link theory and practice
|
|
|
|
Social learning
|
Learning by observation and imitation
|
|
|
|
Experiential learning
|
Requires personal involvement
Responsibility for learning rests with learner 4 learning styles - activists (concrete experience), reflectors (reflective observation), theorists (understand underlying concepts), pragmatists (active experimentation) |
|
|
|
Training
|
Link to business strategy
Assess needs Design and deliver activities Evaluate effectiveness |
|
|
|
Evaluate effectiveness
|
4 levels
Reaction - at conclusion of activity Immediate - assessment of learning outcomes Intermediate - impact on performance Ultimate - impact on organisational performance |
|
|
|
Performance management
|
|
|
|
|
Staffing
|
-Planning, acquiring and retaining a work force
- determine who will work for organisation |
|
|
|
Staffing process - matching people with jobs
|
1. Job design
2. Job analysis 3. Job description 4. Person specification 5. Recruitment 6. Selection 7. Appointment |
|
|
|
Job design
|
How tasks to be performed are combined to form job
|
|
|
|
Job analysis
|
Collecting and analysing information about tasks and responsibilities of job
Methods- computer systems, questionNaires, interviews Outcomes- job description and person specification |
|
|
|
Job description
|
Describes activities to be done, identifies tasks, duties and responsibilities
Key elements 1. Job title 2. Location 3. Purpose of job 4. Hours 5. Responsibilities/duties 6. Salary conditions and incentives |
|
|
|
Person specification
|
Attributes specific to the person like knowledge and skills, abilities needed to perform job satisfactorily
Includes - training and qualifications, experience |
|
|
|
Recruitment
|
Process of attracting a pool of qualified and experienced candidates to apply for position.
Internal and external recruitment |
W
|
|
|
Selection
|
Most suitable applicant for position
Common to use more than one data method Techniques - reference checks interviews and personality tests Choice - practicability, sensitivity, reliability l, validity |
|
|
|
Performance management
|
Everything in HR - attraction, development & maintenance
Aims to improve performance |
|
|
|
4 key elements of pm
|
Induction and socialisation
Reviewing and appraising performance Reinforcing performance standards Counselling and support |
|
|
|
1.Induction & socialisation
|
Begins after commencement of employment, induction is te process of the socialisation of individuals into the organisation
|
|
|
|
2.Reviewing and appraising performance
|
Performance appraisal
- development - coach - administrative - judge - determines pay and promotions, transfers and demotions 5 Step MBO process 1. Set objectives 2. Cascade objectives to employees 3. Monitor 4. Evaluate performance 5. Reward performance |
|
|
|
Problems/issues with pm appraisals
|
Validity - behavioral traits difficult to measure
Conflicting aims of pm mgt process Inadequate line manager skills and training No pm system is perfect because of the bureaucratic nature Biases such as -halo effect - one good aspect clouds all others - horn effect - one negative aspects clouds all others - crony - appraiser and appraiser to close |
|
|
|
Managing poor performance
|
Should identify shortcomings in performance don't leave until review time
Identify possible causes and solutions Implement performance imrovement program - document all procedures |
|
|
|
Managing review outcomes
|
Initiate dismissal process is performance remains unsatisfactory
If no cases of theft or assault, dismiss with notice after procedural fairness which is escalated system of warnings e. 3 strikes your out |
|
|
|
3. Reinforcing performance standards
|
Standards and objectives need to be SMART
Quality of outcomes maybe more important than quantity Use of formal and informal methods to clarify standards |
|
|
|
4. Counselling and support
|
Utilise listening skills
Counselling provided Alleviate absenteeism and health and well being problems |
|
|
|
Managing ansence
|
Reasons - poor health, job related stress
Define problem and set up appropriate mgt systems Approaches - informal chats, interviews, counselling, hard approach disciplinary action |
|
|
|
Reward management
|
Process by which organisations distribute financial or other rewards to employees
- attract motivate and retain employees |
|
|
|
Motivation and rewards
|
Extrinsic
Intrinsic |
|
|
|
Modern content theories
|

|
|
|
|
Mcgregor
|

|
|
|
|
Maslow
|
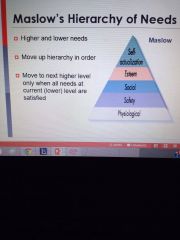
|
|
|
|
Herzberg
|

|

|
|
|
Process theories
|
Concerned with how motivation occurs
Focus on extrinsic needs Main theories Lockes goal setting theory Adams equity theory Vrooms expectancy theory |
|
|
|
Lockes theory
|
Specific and difficult goals with self generated feedback leading to higher performance
Relation ship between goals and performance depend on Self efficacy Goal commitment Task characteristics |
|
|
|
G
|
H
|
|
|
|
Adams theory
|
|
|
|
|
N
|
B
|
|
|
|
V
|
V
|
|
|
|
Adams theory
|
|
|
|
|
N
|
B
|
|
|
|
V
|
V
|
|
|
|
Adams theory
|

|
|
|
|
Vrooms expectancy theory
|
Tendency to act in a certain way depending on expectation that the act will be followed by given outcomes
1. Effort 2. Performance 3. Reward |
|
|
|
V
|
V
|
|
|
|
G
|
C
|
|
|
|
Adams theory
|
|
|
|
|
Vrooms expectancy theory
|
Tendency to act in a certain way depending on expectation that the act will be followed by given outcomes
1. Effort 2. Performance 3. Reward |
|
|
|
V
|
V
|
|
|
|
Bases for pay systems
|
Time - easily understood and administered
Results - provide strong incentive Enterprise - employee effort and achievement Performance - objectives and indicators eg customer satisfaction levels Skills |
|
|
|
Don't forget pat on back
|
Intrinsic (non monetary) factors more effective motivators than extrinsic d
|
|
|
|
The end
|
Bye
|
|

