![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why are emotions important? |
They are important for survival. - Fight/flight responses to dangerous situations - Reproduction (attraction)/upbringing (attachment) - Quick decisions to complex problems - Learning (avoidance/approach) |
|
|
What are the two components of emotion? |
Emotional response (changes in body sensations)
Subjective emotional feeling |
|
|
What controls change in the ANS? |
When one nervous system is active, the other is not. There is no voluntary control of the ANS, it is controlled by the hypothalamus
|
|
|
What happens in the flight or fight response? |
It is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). The symptoms of it work short-term to get it out of danger (i.e. fear, arousal) Causes accelerated HR, slow digestive system, perspiration and increase glucose availability. |
|
|
How does emotion response result in hormonal changes? |
The adrenal glands produce hormones such as cortisol (stress hormone) adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (nor-epinephrine). This increases production in case of stress and gives supply of oxygen and glucose to the brain and muscles. |
|
|
What is the route required to hypothalamus to stimulate the release of cortisol? |
Hypothalamus - Releasing factor - Pituitary Gland - ACTH - Adrenal Glands (cortex) - Cortisol |
|
|
What are typical actions? |
Body postures and gestures |
|
|
What are believed to be innate facial expressions and why? |
Some are innate and universal. Paul Ekman's work believed in 6 primary emotions; happiness sadness, fear, anger, surprise and disgust. Found that they are universal due to a blind boy laughing, despite never seeing happiness |
|
|
What is involved in voluntary facial expressions? |
Involves the corticospinal system and the pyramidal tract (motor cortex) |
|
|
What is involved in involuntary facial expressions? |
Involves the subcortical system and the extrapyramidal tract (insula, basal ganglia) |
|
|
What is Damasio's view of emotions as subjective feelings? |
Awareness of feelings results from the integration of what happens in the outside world and what happens in the body |
|
|
What is the James Lange theory? |
Believes that if a person saw an emotional stimulus, they first experience a physiological change in the body (e.g. HR), resulting in a body sensation. This information then goes from the spinal cord to the brain resulting in the feeling of fear. (Response then feeling) |
|
|
What are the weaknesses of the JL theory? |
1. The autonomic responses are quite crude and not diversified enough to produce all the range of emotions we can feel 2. Patients with spinal cord injuries can still feel emotions |
|
|
What is the Cannon Bard Theory? |
Once a person saw an emotional stimulus, this creates the feeling of fear which then causes information to go from the brain to the spinal cord and cause physiological changes. |
|
|
What are the weaknesses of the CB theory? |
1. It can't explain why forcing yourself to smile makes you more happy 2. Drugs influencing HR reduce the subjective feeling of anxiety 3. Automatic responses to angry faces despite the fact the ppt were not aware of seeing the faces 4. There is no need for conscious feeling to have an emotional response. |
|
|
Historically, how were emotions seen in the brain? |
There was a search for a single emotion centre of the brain. Focused on the limbic system which James Papez highlighted a circuit of brain structures involved in emotion. |
|
|
What is the Papez Circuit? |
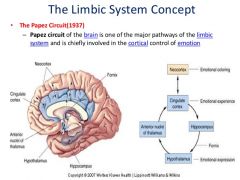
Neocortex involved in subjective feelings, underneath = emotional response |
|
|
How are emotions in the brain viewed nowadays? |
There is no evidence that not all structures of the limbic system are involved in emotion More evidence there is no single emotion system Instead, there are difference brain networks for different emotions Structures involved in emotion processing are no exclusively involved in emotion processing |
|
|
What is Damasio's study? |
He did numerous PET scans while ppt recalled emotional/neutral episodes and found different parts of the brain were highlighted for each emotion (anger, fear, sadness, and happiness) compared to neutral |
|
|
What brain stuctures are important for emotion? |
Hypothalamus Amygdala Ventromedial prefrontal cortex Insula |
|
|
What is the function of the Hypothalamus? |
Important in generating the emotional response (hormonal changes and changes in the ANS). It have been associated with aggressive behaviour |
|
|
What is the function of the amygdala? |
Important for fear and aggression |
|
|
How does it interact with fear? |
First discovered via the Kluver-Bucy Syndrome, as lesions on the amygdala nuclei resulted in docility. Monkeys with their temporal lobe removed showed an absence of fear and aggression It appeared that the amgydala lesion was critical for changes in emotional state |
|
|
What are the two routes from the stimulus to the amygdala? |
1. Thalamus to Amygdala, quick but only for simple stimuli 2. Thalamus - Cortex - Amgydala Results in emotional response as the central nucleus in the amygdala foes to the hypothalamus, periaqueductal gray matter, and cerebral cortex |
|
|
What is the ventromedial prefrontal cortex? |
Important for emotional feeling, social interactions and decision making First described in the case of Phineas Gage, where a iron rod went through his head but survived. Changes in his social behaviour such as impatience, distracted, lack of decision making VPC is important in decision making |
|
|
What is the IOWA gambling task, in concern to the VPC? |
Ppt were given cards A-D, turn a card from one of the decks, the back of the card will tell you if you win or lose money. Decks A and B had a greater gain, but a greater long-term loss than C and D Patients with ventromedial lesions continued to use bad decks due to their immediate greater gain |
|
|
What are the functions of the insula? |
Important for the experience of pain and several basic emotions It translates visceral states into subjective feelings |

