![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
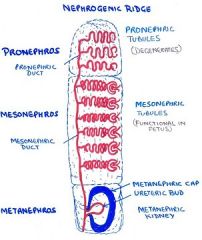
what germ layer and embryonic structure do kidneys develop from?
|
intermediate mesoderm - nephrogenic ridge
|
|
|
intermediate mesoderm, which lies between the______ and the _____.
|
1. lateral plate mesoderm
2. somites (paraxial mesoderm) |
|
|
intermediate mesoderm later loses its connection with the somites and forms longitudinal elevation of mesoderm called the _______.
|
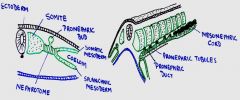
nephrogenic ridge
|
|
|
nephrogenic ridge forms three systems
|
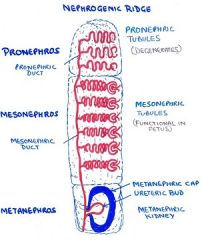
1. Pronephros
2. Mesonephros 3. Metanephros |
|
|
mesonephros is smallest in ?
type of placenta ? |
carnivores (endotheliochorial),
endotheliochorial: type of placenta in which the maternal blood is separated from the chorion by the maternal capillary endothelium; occurs in dogs. |
|
|
Name 3 parts of Urogenital sinus (formed below urorectal septum)
And what they form? |
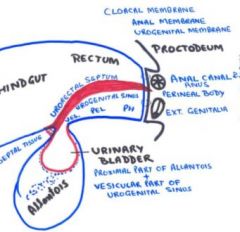
1. vesicle part (cranial) : forms urinary bladder
2. pelvic part (middle): Pelvic urethra, Prostate in males Pelvic urethra and Vagina (caudal) in females 3. phallic part (phallic) - forms Penile urethra and Bulbourethral gland in male - Vestibule and Vestibular gland in female |
|
|
how does intermediate mesoderm emerge? how created?
how is nephrogenic ridge created from interm.mesoderm? |
- emerges as individual segments, 1 associated with each somite
(on both sides of notocord, b/c there are somites on each side also) segments of interm.mesoderm fuse to form ridge - |
|
|
What is fate of each "system" (3) of nephrogenic ridge in mammals?
|
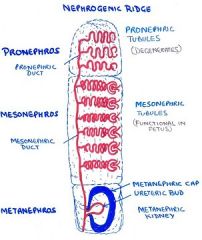
pronephros - forms first but regresses (except in fish)
- only main duct persists as duct of mesonephros mesonephros - 2nd to form. Functional only in fetus, dev. little farther than pronephr. b/c each meson.tubule actually forms a fetal glomerulus - later regresses except duct part which forms male genital duct and also to form metanephric diverticulum metanphros - last to grow. It dev. all the way and becomes adult kidney |
|
|
Mesophrose is largest in ____?
Intermediate size in ____? Smallest in ____? Bonus: also name type of placenta |
Pig - largest (epitheliochorial)
Ruminant Carnivores - smallest (endotheliochial) for whatever reason, it is associated with type of placenta and size of connection to mother |
|
|
parts of metanephros (metanephric kidney)?
|
duct actually called (1) mesonephric duct, b/c it is remnant from mesonephros
(2) UTERIC BUD aka metanephritic diverticulum develops as loop from meson.duct (3) metanephritic. cap (outside part) kind of forms bubble around uterine bud. |
|
|
1. WHAT is metanephric diverticulum a diverticulum of? (in other words what structure does it come from?
2. -Ureteric bud (metanephric diverticulum) forms? |
1. WHAT is metanephric diverticulum a diverticulum of?
>MESOnephric duct (which is only part of mesonephros that persisted) 2. Ureteric bud (metanephric diverticulum) forms? >collecting system and URETER |
|
|
1. Metanephric cap develops from induction of surrounding tissue and develops INTO what structure?
2. Metanephric diverticulum develops into what structures? |
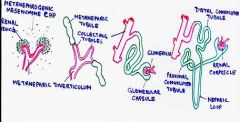
1. M. cap forms Bowman’s capsule, PCT, loop of henle, and DCT.
2. Metanephric diverticulum (aka ureteric bud) develops into collecting system -collecting tubules, major and minor calyces, renal pelvis and URETER |
|
|
How is developing urinary system and external genitalia seperated from developing rectum?
(in dork talk: partitiion of cloaca & development of bladder) |
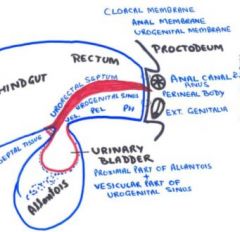
Formed when urorectal septum moves caudally
|
|
|
Urinary bladder is formed from
|
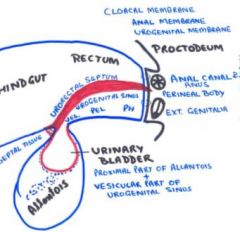
left over proximal part of allantois (and vesicular part of urogenital sinus)
|
|
|
Identity compartments created by urorectal partition? (2)
note: 1 of them has 3 parts |
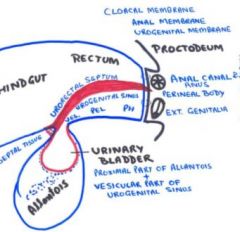
Dorsally: rectum and anal canal
Ventrally: urogenital sinus 3 parts of urogenital sinus? 1. vesicle part (cranial) 2. pelvic part (middle) 3. phallic part (phallic) |
|
|
1. splanchnic mesoderm is closer to
2. somatic mesoderm is closer to |
endoderm
remember splanchnic means "visceral" 2. ectoderm |
|
Urachus forms from?
What does it become? (don't think about it, just memorize) |
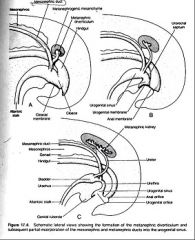
Regressed part of allantois (not bladder; see image)
Medial ligament of the bladder |
|
|
Renal agenesis
|
absence of one or both kidney
|
|
|
Horse-shoe kidney
|
two kidneys may fuse
|
|
|
Cystic kidney
|
failure of union between the developing nephron and collecting tubules.
|
|
|
In males, the ductus deferens and epididymis develop from the ?
|
mesonephric duct
After mesophric (fetal) kidney regresses, mesen.duct hooks up with testes. Meanwhile, paramesonephric duct regresses in males. |
|
|
In female, uterine tube, uterus, and part of vagina originate from?
|
paramesonephric duct
After mesonephric (fetal) kidney and mesen.duct regress, paramesonephric duct extends caudally - forming uterus/vagina in the process. |
|
|
fate of mesonephric duct in female?
fate of mesonephric duct in male? |
regresses
ductus deferens, epididymis, vesicular gland |
|
|
condition where ureter opens into the urethra (instead of bladder)? Common in female dogs.
|
Ectopic ureter
|
|
|
Medial ligament of the bladder known as?
|
Urachus
|
|
|
Urinary bladder is derivative of ?
|
ventral urogenital sinus: (edit)
Vesicle part |
|
|
Pelvic urethra is derivative of ?
|
ventral urogenital sinus: (edit)
Pelvic part |
|
|
Glomerulus develops from what structures?
|
Glomerulus is derived from a series of branches of dorsal aorta invaginated in the bowman’s capsule BUT all blood vessels come from SPLANCHNIC MESODERM (lateral mesoderm)
So Bowman's capsule and tubular system is from INTERMEDIATE MESODERM |
|
|
another name for paramesonephric duct?
|
Mullerian Duct
|
|
|
another name for mesonephric duct?
|
Wolffian ducts
|
|
|
Testes and ovaries derived from?
|
Intermediate mesoderm - gonadal ridges
|
|
|
primordial germ cells originate from the ____ ;
they migrate to and induce the _____ to form ______. |
primordial germ cells originate from YOLK SAC (yolk sac endoderm);
they migrate/induce the GENITAL RIDGE to form primitive sex cords in mesenchyme (future sex cells e.g. sperm&egg). |
|
|
Which chromosome contains the testis determining factor (TDF) genes?
|
Y chromosome contains the testis determining factor (TDF) genes
So in absence of this factor, female development is established (by default) |
|
|
Mullerian inhibitory substance (MIS) produced by _____, and causes ________.
|
Mullerian inhibitory substance (MIS) produced by the SERTOLI cells, and causes the regression of the Mullerian (paramesonephric) duct .
Remember Mullerian duct becomes the uterus,etc. |
|
|
Testosterone produced by ?
Stimulates the development of ? |
Testosterone, produced by LEYDIG cells,
- stimulates the development of the Wolffian (mesonephros) duct and causes the regression of the Mullerian duct. mesonephros = male |
|
|
What do the primordial germ cell develop into in the male?
|
gonocytes, later spermatogonia
|
|
|
What do the testis (gonadal) cords develop into?
|
Seminiferous tubules Rete testis
|
|
|
What is the term for accumulation of the fluid within the two layers of the tunica vaginalis?
|
Hydrocoele
|
|
|
How many pairs of pronephric tubules form at the nephrogenic ridge?
|
7-8 pairs
|
|
|
What does the remainder of the allantois degenerate into?
|
Urachus
|
|
|
What is the indifferent stage during development?
|
When you can not determine the sex of the embryo
|
|
|
What induces the genital ridge to form the primitive sex cords in the mesenchyme?
|
primordial germ cells
|
|
|
What do the gonadal cords in females break up into?
|
Follicles which contain primordial germ cells to develop oogonia
|
|
|
What do some of the persisting mesonephric tubules develop into in the male?
|
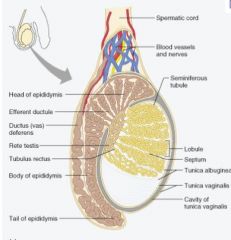
efferent ductules
|
|
|
What does the paramesonephric duct develop into in the male?
|
Uterus masculinus
|
|
|
What does the pelvic part of the urogenital sinus become in the male adult?
What does the pelvic part of the urogenital sinus become in the female adult? |
Pelvic urethra
Prostate Urethra Vagina (caudal) |
|
|
What does the phallic part of the urogenital sinus become in the male adult?
|
Penile urethra
Bulbourethal gland |
|
|
What does the phallic part of the urogenital sinus become in the female adult?
|
Vestibule
Vestibular gland |
|
|
What does the gebernaculum become in the adult male?
|
Ligament of the testis and epididymis
|
|
|
What does the gebernaculum become in the adult male?
|
Ligament of the testis and epididymis
|
|
|
What does the gebernaculum become in the adult female?
|
Round ligament of the uterus
|
|
|
What does the urogenital fold in the adult male become?
|
urethral fold of the penile urethra
|
|
|
What does the genital swelling in the adult male become?
|
STROTUM
note: also (like other parts of urogenital system) originates from intermediate mesoderm |
|
|
What does the genital swelling in the adult female become?
|
Labia
|
|
|
What does the genital tubercle in the adult male become?
|
Penis
|
|
|
What does the genital tubercle in the adult female become?
|
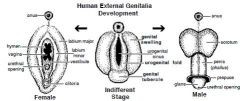
CLITORIS
|
|
|
What animals have the smallest mesonephros? Type of placenta?
|
Carnivores, endotheliochorial
|
|
|
What does the pronephric duct continue as later?
|
mesonephric duct
|
|
|
What animals have the largest mesonephros? type of placenta?
|
Pigs, Epitheliochorial
|
|
|
What cells in the testis are derived from mesenchyme?
|
Sertoli and Leydig cells
|
|
|
What do the gonadal cords in females break up into?
|
Follicles which contain primordial germ cells to develop oogonia
|
|
|
Which cells in the ovary are of mesenchymal origin?
|
follicular cells
|
|
|
What does the urogenital fold in the adult female become?
|
Labia minora
|
|
|
What does external genitalia originate from?
|
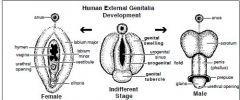
External genitalia are derived from three different swellings (mesoderm proliferations) that appear in the perineal region
|

