![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
embryo gets completely implanted on
|
11th day post fertilisation
|
|
|
|
Definitive palcenta is formed on |
4th month POG |
|
|
|
tirlaminar Germ disc is formed at
|
by 21d (3rd week)
|
|
|
|
prochordal plate and primitive streak
|
Day 14
|
|
|
|
In what week does the bilaminar disk (epiblast:hypoblast form)?
|
Week 2 - day 8
also - Cyto and trophoblast differentiates |
|
|
|
In what week do we see the Gastrulation, formation of the primitive streak, notochord, and neural plate?
|
Week 3
|
|
|
|
In what time frame is the fetus most susceptible to teratogens?
|
Weeks 3-8
|
|
|
|
Thyroid gland reaches its defintive position on
|
7th week
|
|
|
|
In what week does the heart begin to beat?
|
Week 4
|
|
|
|
In what week do the limb buds form?
|
Week 4
|
|
|
|
Platal process and the nasal septum fuses with each other
|
10th week
|
|
|
|
formation of neural tube begins
|
3rd week
|
|
|
|
Closure of anterior neuropore
|
25th day
|
|
|
|
Closure of post neuropore
|
27th day
|
|
|
|
Eye and |
22nd day |
|
|
|
coronary circulation is established
|
6th week
|
|
|
|
Kidneys become functional in
|
12th week
|
|
|
|
Vagina gets canalised
|
5th month
|
|
|
|
From what embryologic layer do the adenohypophysis and lens of eye develop?
|
Surface ectoderm
|
|
|
|
From what embryologic layer do the neurohypophysis and CNS neurons develop?
|
Neuroectoderm
|
|
|
|
From what embryologic layer do the ANS and cranial nerves develop?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
|
From what embryologic layer does the gut tube epithelium develop?
|
Endoderm
|
|
|
|
What induces the ectoderm to form neuroectoderm and what is its postnatal derivative?
|
Notochord; develops into nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disk
|
|
|
|
What embryologic layer forms the connective tissue, muscle,, bone, CV and various other visceral structures?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
|
What are the common mesodermal defects?
|
VACTERL: Vertebral defect, anal atresia, cardiac defects, tracheo-esophageal fistula, renal defects, and limb defects
|
|
|
|
What is the leading cause of birth defects and mental retardation in the U.S.?
|
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
|
|
|
|
What teratogen causes renal damage?
|
ACE inhibitors
|
|
|
|
What teratogen predisposes to vaginal clear cell adenocarcinoma?
|
Diethylstilbestrol (DES)
|
|
|
|
What teratogen causes congenital goiter or hypothyroidism?
|
Iodide
|
|
|
|
What teratogen causes limb defects?
|
Thalidomide; sedative and used to treat multiple myeloma
|
|
|
|
What teratogen is believed to be related to ADHD?
|
tobacco
|
|
|
|
Teratogenic anticoagulant?
|
Warfarin
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 major components of the umbilical cord and their functions? |
Umbilical arteries (2) carry deoxygenated bloodd from fetus to placenta; |
|
|
|
This embryonic structure gives rise to the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk?
|
Truncus arteriosus
|
|
|
|
Forms smooth portions of left and righ ventricle?
|
Bulbus cordis
|
https://o.quizlet.com/fzeh49koNLr67ris2wFR-A_m.jpg
|
|
|
Forms trabeculated portions of ventricles?
|
Primitive ventricle
|
https://o.quizlet.com/fzeh49koNLr67ris2wFR-A_m.jpg
|
|
|
Forms trabeculated portions of atria?
|
Primitive atria
|
https://o.quizlet.com/fzeh49koNLr67ris2wFR-A_m.jpg
|
|
|
Forms coronary sinus and smooth part of right atrium? |
*sinus venosus* . |
https://o.quizlet.com/fzeh49koNLr67ris2wFR-A_m.jpg |
|
|
Forms superior vena cava?
|
right common cardianl vein and right anterior cardinal vein
|
|
|
|
Which organs are responsible for fetal erythropoiesis? |
Yolk sac (3-8 wks) Liver(6-30 wks) Spleen (9-28 wks) Bone marrow (28 wks on) |
|
|
|
Describe fetal circulation?
|
Umbilical vein -> ductus venosus -> IVC -> foramen ovale -> Aorta -> abdominal aorta -> umbilical arteris off internal iliac; Deoxygenated blood from SVC -> pulmonary artery -> ductus arteriosus -> joins oxygenated blood in descending aorta
|
https://o.quizlet.com/i/yxEEpF-qiTKxXFB-WQhGXg_m.jpg
|
|
|
This becomes the ligamentum teres hepatis?
|
umbilical vein
|
|
|
|
This becomes ligamentum arteriosum?
|
ductus arteriosum
|
|
|
|
This becomes the ligamentum venosum?
|
ductus venosum
|
|
|
|
This becomes the fossa ovalis?
|
foramen ovale
|
|
|
|
this becomes the median umbilical ligament?
|
Urachus (allantois)
|
|
|
|
Part of the allantoic duct between the bladder and umblicus?
|
urachas
|
|
|
|
Common carotid artery arises from what aortic arch?
|
3rd
|
|
|
|
Subclavian arteries arise from this aortic arch?
|
4thh
|
|
|
|
Major derivatives of branchial arch 1? |
*Meckel's cartilage* (mandible, malleus, incus); |
|
|
|
Major derivatives of branchial arch 2?
|
Reicherts cartialge (stapes, styloid process); muscles of facial expression; CN VII
|
|
|
|
Major derivatives of branchial arch 3?
|
Greater horn of hyoid; stylopharyngeus; CN IX
|
https://o.quizlet.com/i/Uc9XkZ7lZiQPqWjZiXj5Bw_m.jpg
|
|
|
Major derivatives of branchial arches 4? |
thyroid, cricoid, arytenoids (with 6); most pharyngeal constrictors, cricothyroid; CN X (superior laryngeal branch) |
|
|
|
Major derivatives of branchial arches 6? |
thyroid, cricoid, arytenoids (with 4); all intrinsic muscles of larynx except cricothyroid; CN X (recurrent laryngeal branch) |
|
|
|
What nerves control the tongue? (taste, sensation, and motor?) |
*ant 2/3 : * Taste - Chroda tympani ; sense : V2, V3 |
|
|
|
What develops into the external auditory meatus?
|
1st branchial cleft
|
|
|
|
What branchial pouches contribute to the parathyroids?
|
3rd pouch (inferior parathyroids) and 4th pouch (superior parathyroids)
|
|
|
|
What branchial pouch develops into the thymus?
|
3rd pouch
|
|
|
|
What is the result of aberrant 3rd and 4th pouch development? |
DiGeorge syndrome; |
|
|
|
What is the foramen cecum?
|
Normal remant of thyroglossal duct
|
|
|
|
What causes cleft lip?
|
falure of fusion of maxillary and medial nasal processes
|
|
|
|
What causes cleft palate?
|
failure of fusion of lateral palatine processes, nasal septum, and/or median palatine processes
|
|
|
|
What are the 3 embryologic kidneys and when do they function? |
Pronephros (week 4), |
|
|
|
What inhbits paramesonephric development and what secretes it?
|
Mullerian inhibiting substance, excreted by the testes
|
|
|
|
What are the genital homologues developed from the genital tubercle?
|
Glans penis and glans clitoris
|
|
|
|
What are the genital homologues developed from the urogenital sinus? |
Men: corpus spongiosum, bulbourethral glands, and prostate gland; |
|
|
|
Intermediate mesoderm (male testes)
|
Leydig cells - secrete testosterone
|
|
|
|
Proctodeum
|
Anal canal (lower part)
|
|
|
|
Neural tube (downgrowth)
|
Neurohypophysis (posterior lobe of pituitary)
|
|
|
|
Rathke's pouch
|
Adenohypophysis (anterior lobe of pituitary)
|
|
|
|
Foregut
|
Mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum to bile duct, respiratory airways, lungs, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
|
|
|
|
Midgut
|
Duodenum after bile duct, jejunum, ileum, cecum, ascending colon, proximal part of transverse colon
|
|
|
|
Hindgut
|
Distal part of transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, upper part of anal canal, bladder, urethra
|
|
|
|
primitive streak is initiated and maintained by
|
Nodal gene
|
|
|
|
Diaphragm is formed by |
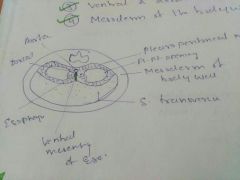
1. Septum tranversum 2. Pleuriperitoneal membrane 3. Ventral and Dorsal mesentry of the esophagus 4. Mesoderm of the body wall
|
|
|
|
The sptum transversum gives rise to |
Diaphragm Falciform ligament Messentry of the lesser sac |
|

