![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What event marks the determination of sex?
|
Fertilization
|
|
|
What is the genetic factor that determines sex?
|
Presence or absence of the Y-chromosome
|
|
|
When does the male/female morphology start?
|
7th week
|
|
|
What forms the genital (gonadal) ridges?
|
From the proliferation of epithelium and condensation of the underlying mesenchyme.
|
|
|
When do germ cells start to appear?
|
6th week
|
|
|
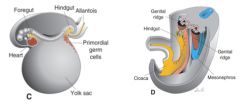
Where are primordial germs cells INITIALLY found?
|
In the wall of the yolk sac close to the allatois
|
|
|
Describe primordial germ cell migration?
|
1. migrate via ameboid movement along the dorsal mensentery of the hindgut
2. Arrive at the primitive gonads at the beginning of the 5th week 3. Invade gonadal ridges in the 6th week |
|
|
What cells induce the development of the testis or ovaries?
|
Primordial Germ Cells
|
|
|
The absence of primordial germ cells would cause the absence of what structures?
|
Testis and ovaries
|
|
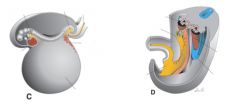
Identify all tagged structures
|
|
|
|
What Y-chromosome segment is responsible for the formation of the testis?
|
SRY-TDF
Sex-determination Region of the Y Chromosome-- Testis Determining Factor |
|
|
In the 4th month, what cells make up the testis?
|
Primordial germ cells
Sertoli cells |
|
|
What is the somatic cell component of the testis? Where does it come from?
|
Sertoli cells from the surface epithelium
|
|
|
What cells lie in between the testis cords? Where did they come from?
|
Interstatial Leydig cells from the original mesenchyme of the gonadal ridge
|
|
|
When does testosterone production start?
|
week 8
|
|
|
In the male, what structure forms the ductus deferens?
|
Mesonephric duct
|
|
|
What structures are formed by the mesonephric duct in the male?
|
The rete testis
The efferent ducts The epididymis The vas deferens The seminal vesicle |
|
|
What structure forms the prostate?
|
UG sinus
|
|
|
When will the testis undergo canalization?
|
Puberty
|
|
|
What happens if the primordial germ cells do not carry a Y-chromosome?
|
The sex cords will dissociate into irregular cell clusters.
Degeneration of medullary cords. |
|
|
What will form the oogonia and the follicular cells?
|
Cords split into cell clusters surrounding PGCs.
PGCs become oogonia and surrounding cells become follicular cells |
|
|
Unspecialized gonads and two sets of ducts exist until week ___.
|
6
|
|
|
The Mullerian duct will form which sex's reproductive organs?
|
female
paramesonephric |
|
|
Thw Wolffian duct will form which sex's reproductive organs?
|
male
mesonephric |
|
|
Which cells are responsible for the production of the Anti-Mullerian hormone?
|
Sertoli (sustentacular) cells
|
|
|
What hormone is responsible for the development of the external male structures?
|
DHT
|
|
|
What hormone is responsible for the development of the internal male structures?
|
Testosterone
|
|
|
What cells are responsible for the increase in testosterone in males?
|
Interstitial (Leydig) cell
|
|
|
The genital tubercle and the UG sinus for what two structures?
|
The prostate and the penis
|
|
|
What is the remnant of the mesonephric duct in the female?
|
Epoopheron and paroopheron
|
|
|
THe mesenchyme of the uterus will form which tissue layer?
|
Myometrium
|
|
|
What are the two origins of the vagina?
|
Paramesonephric duct
UG sinus |
|
|
What is uterus didelphys?
|
double uterus (double cervix)
|
|
|
What is uterus arcuatus?
|
indented uterus (middle)
|
|
|
What is uterus bicornis?
|
Cranial portion of the uterus is bifurcated. Caudal portion is normal.
|
|
|
In the male the urethral folds fuse to form the ____.
|
urethra
|
|
|
In the female the urethral folds do not fuse and for the _____.
|
Labia minora
|
|
|
What structures are formed by the genital swelling in the male and female?
|
Fused to form scrotum
Labia majora |
|
|
What is hypospadias?
|
Incomplete fusion of the urethral fold. Abnormal opening to the urethra.
|
|
|
What is epispadias?
|
Urethra opens on the dorsum of penis.
|
|
|
What causes epispadias?
|
lack of migration of the mesoderm between the umbilicus and the genital tubercle.
|
|
|
What causes insufficient androgen production?
|
hypogonadonism
hypothalamic or pituitary dysfunction |
|
|
What is a micropenis?
|
2.5 standard deviations below normal
|
|
|
Excessive androgen in an XX female can cause what syndrome?
|
pseudohermaphroditism
|
|
|
If tissues are insensitive to testosterone, what is the outcome of an XY individual?
|
Testicular feminization
No testosterone +estrogen = female |
|
|
What is cryptorchidism?
|
one or both testes do not descend
|

