![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CSF Protein Electrophoresis, MS patient |
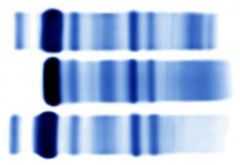
1) CSF, MS patient. Oligoclonal bands. Increased gamma globulins. 2)Serum, MS patient. No banding. 3) CSF, normal. |
|
|
CSF Isoelectric focusing, MS patient |
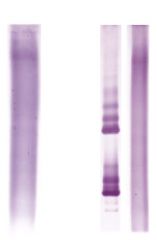
On left: normal CSF. On right: CSF with oligoclonal banding. Serum with no banding. |
|
|
Alpha-1 |
Thyroxine-binding globulin alpha-1-antitrypsin alpha-1-lipoprotein (HDL) |
|
|
Alpha-2 |
Alpha-2-macroglobulin Haptoglobin Ceruloplasmin |
|
|
Beta |
Transferrin, Complement, beta-lipoprotein (LDL) |
|
|
Gamma |
IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, IgE, and CRP |
|

1) intravascular hemolysis (decreased alpha-2) 2) Normal patient 3) In vitro hemolysis Hemoglobin/haptoglobin complex band |
On protein electrophoresis, depressed serum haptoglobin as occurs with hemolysis in vivo results in a depressed alpha-2 band.When hemolysis occurs in vitro during specimen handling, the released hemoglobin binds to haptoglobin and alters its migration. On protein electrophoresis, this appears as a band between the alpha-2 and beta-1 bands. |
|

1) plasma (large fibrinogen band) 2) normal 3) small clot in serum (light band) |
Plasma is not recommended for electrophoresis because the large fibrinogen band may obscure a monoclonal gammopathy. Serum samples will occasionally not clot completely. When this happens, a small fibrinogen band appears near the point of application. A monoclonal gammopathy is ruled out by immunofixation or by thrombin treatment. Thrombin removes the fibrinogen without affecting the monoclonal gammopathy. |
|

Alpha-1-antitrypsin Deficiency. 1) lack of alpha-1 band 2) normal |
Inhibition ofprotease neutrophil elastase. Mutation in SERPINA1 gene cause deficiency. APRincreased in inflammatory response, pregnancy and contraceptive use. Can result in emphysema and chronic liver disease. |
|
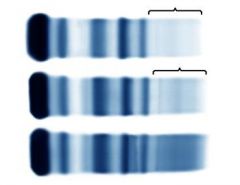
Hypogammaglobulinemia 1)Severe 2)Moderate 3)Normal |
A broad suppression or absence (acquired or genetic) of immunoglobulins places the patient at risk of recurrent infections. There is a wide spectrum of acquired and genetic disorders affecting immunoglobulin concentration.
|
|

Bisalbumin |
Albumin variants are uncommon; however, occasionally a double albumin band (bisalbumin) is detected on serum electrophoresis. One allele produces normal albumin and the other allele produces the variant, which migrates slightly differently
|
|
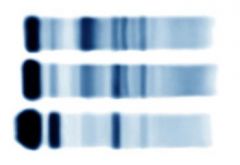
Nephrotic syndrome 1) Serum, renal loss. Albumin decreased. Alpha-2-macroglobulin increased. Beta-lipoprotein increased. 2)Normal serum 3) Urine, renal loss. Increased albumin, increased alpha-1-antitrypsin, no alpha-2 |
Markedlydecreased albumin and increased alpha-2 band due to increasedalpha-2-macroglobulin. Beta-lipoprotein increased. Smaller proteins are lostinto urine.
|
|
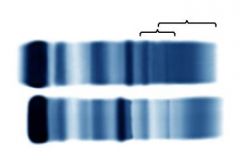
Liver Disease 1) beta-gamma bridging, gamma increased, albumin (anodal slurring) 2) Normal |
Bilirubinalters migration of albumin band. Albumin bind not completely migrated, anodalslurring, beta gamma bridging, gamma (broadly increased) |
|

Acute inflammation 1) Albumin decreased, alpha-1 increased, alpha-2 increased, beta-1 decreased, beta-3 increased 2) normal |
Acute inflammation.Alpha-1,2 increased. Albumin and beta-1 (transferrin) decreased.Beta-3 (complement) increased. |
|
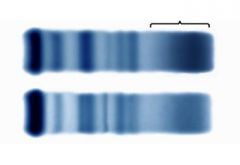
Chronic inflammation 1) gamma increased 2) normal |
Elevation in gammaregion along with same findings as acute inflammation. |
|

Monoclonal protein |
1/3 have malignancy(multiple myeloma, waldenstrom’s). 2/3 will not have diagnosis related toM-protein (MGUS). M spike. Large M protein.dFrauL: |
|
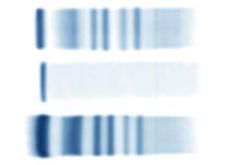
Urine, tubular proteinuria 1) alpha-2-microglobulin and beta-2 microglobulin seen 2) normal |
Increase alpha-2microglobulin, beta-2 microglobulin and free light chains |
|
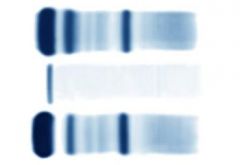
Glomerular Proteinuria 1) Increased albumin, increased alpha-1, increased beta-1 |
Albumin increased,alpha-1-antitrypsin increased, no alpha-2-macroglobulin in urine. |

