![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Electric current |
The rate of flow of charges |
|
|
|
A switch |
A conducting link between the cell and the bulb |
|
|
|
Electric circuit |
A continuous and closed path of an electric current |
|
|
|
Direction of electronic current |
From negative to positive |
|
|
|
Direction of conventional current |
From positive to negative |
|
|
|
Coulomb |
The SI unit of electric Charge And 1 charge of coulomb contains 6×10^18 electrons |
|
|
|
Ampere |
The electric current is expressed by a unit called ampere |
Named after French scientist Andre Marie ampere( 1775 to 1836) |
|
|
1ampere=? |
1A=1C/1s 1 ampere is constituted by the flow of 1 coulomb of charge per second |
|
|
|
Ammeter |
An instrument used to measure the electric current in a electric circuit It is always connected in series |
|
|
|
Potential difference |
The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is defined as the amount of work done in moving a unit charge from one point to the other Point Pd=Volt |
The SI unit of potential difference is volt A battery or a cell how to maintain the potential difference across a conductor |
|
|
1VOLT=? |
1volt=1JOULE/1coulomb (Potential difference = work done upon unit charge) |
it is named after Alessandra Volta (from 1745 to 1827) an Italian physicist |
|
|
Voltmeter |
Voltmeter is an instrument used to measure the potential difference in the circuit |
The voltmeter is always connected in parallel across the points between which the potential difference is to be measured |
|
|
Ohm's law |
The potential difference between the two point in an electric circuit is defined as work done to move a unit charge from one place to another |
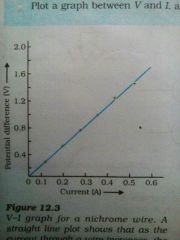
R=V/I where R is ohm (Resistance) |
|
|
Resistance |
The property of a conductor due to which it opposes the flow of current through it is called resistance |
The s i unit of resistance is Ohm |
|
|
Proportionality |
The current is directly proportional to potential difference and the current is inversely proportional to resistance |
|
|
|
1ohm=? |
If the potential difference across the two ends of a conductor is 1 volt and the current through it is 1 ampere then the resistance of the conductor is 1 Ohm |
R=V/I I=V/R V=IR |
|
|
Variable resistance |
A component used to regulate current without changing the voltage source |
In an electric circuit a device called the rheostat is often used to change the resistance in the circuit |
|
|
Resistor |
A conductor having some appreciable resistance is called a resistor |
A component of a given site that offers a low resistance is called a good conductor |
|
|
Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends |
Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends r on its length and area of cross section and the nature of the material |
|
|
|
Resistivity |

|
S i unit of Resistivity is ohm metre |
|
|
Resistors in series |
When a number of resistance are connected in series and the sum of the potential difference across all the resistances is equal to the voltage of the battery applied |
They have different potential difference(volt) but same current |
|
|
Resistor in series |
Rs=R1+R2+R3 |
|
|
|
Resistors in parallel |
The potential difference(volt) is same but the current is different |
Rp=1/R1+1/R2+1/R3 |

