![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Conductors |
Materials that let electrons pass through them |
|
|
Insulators |
Are materials that conduct hardly at all. Insulators are easy to charge. |
|
|
Good conductor |
Metals - the electrons are free making them good thermal conductors |
|
|
Good Insulator |
Plastics
|
|
|
Bad conductors |
Water |
|
|
Bad insulator |
Glass |
|
|
Semi conductor |
Poor conductors when cold better conductors when warm |
|
|
Electricity |
A flow of elctrons |
|
|
earthing |
Where objects are connected to the ground by a conducting material so that unwanted charge flows away |
|
|
Charge (C) |
Current x time |
|
|
How can you charge objects |
Friction because electrons are transferred leaving one with less and one with more electrons |
|
|
Dangers of static electricity |
Refuelling aircrafts you can get sparks which lead to explosion |
|
|
Uses of static electricity |

Inkjet printers photocopiers |
|
|
If resistance goes up in a circuit |
Current goes down |
|
|
Volt meters always have to be connected in.. |
Parallel |
|
|
Ammeters are always connected in.. |
series |
|
|
Resistance= |
Voltage \ current |
|
|
Conventional current |
+ to - |
|
|
Electrons |
- to + |
|
|
Voltage= |
Current x resistance |
|
|
Diode symbol |
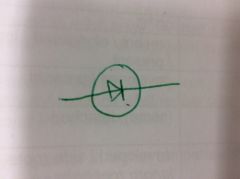
|
|
|
Charge = |
Current x time Q = I x t |
|
|
The more components in a circuit |
The lower the current the electrons have to fight their way through all of it |
|
|
Ldr |
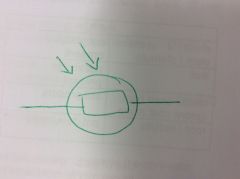
|
|
|
Thermistor |
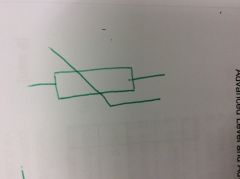
|

