![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
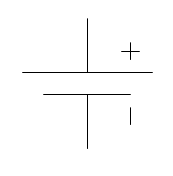
|
Battery: Stores DC voltage |
|
|
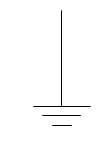
Earth Ground: Electrical grounding connection to earth. Also used as a chassis ground on EMD locomotives |
|
|
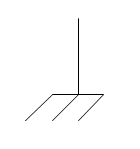
Chassis Ground: Electrical grounding connection to the chassis or frame of a piece of equipment |
|
|
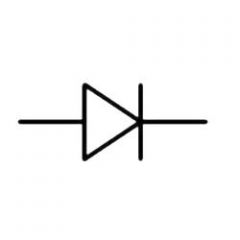
Diode: Allows current flow in one direction only |
|

|
Zener Diode: AZener diode is a diode which allows current to flow in the forward direction inthe same manner as an ideal diode, but will also permit it to flow in thereverse direction when the voltage is above a certain value known as thebreakdown voltage |
|
|
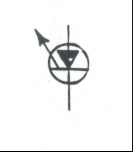
Light Emitting Diode (LED): Indicates applied voltage when illuminated |
|

|
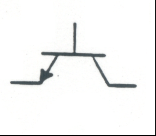
Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR): A gated diode. Only conducts electricity when a voltage is applied to the gate wire |
|
|
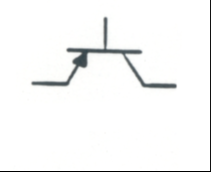
NPN Transistor: High speed switching device |
|
|
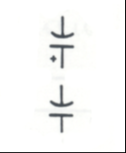
PNP Transistor: High speed switching device |
|
|
Capacitor: Temporarily stores an electrical charge. May be polarized. |
|
|
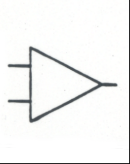
Operational Amplifier: Producesan output voltage that is typically hundreds of thousands of times larger thanthe voltage difference between its input terminals |
|
|
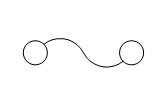
Transistorized Circuit: Representative of amore in depth circuit.May include diodes, transistors, capacitors,Zeners, resistors, etc. |
|
|
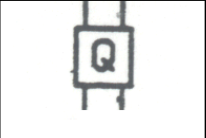
Fuse: A protective device which must be replaced when it fails |
|
|
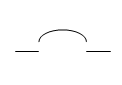
Instant Trip Circuit Breaker: Circuit protection device that can be reset after it has tripped |
|
|
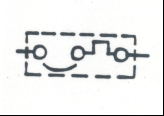
Thermal Trip Circuit Breaker: Circuit protection device that can be reset after it is tripped |
|
|
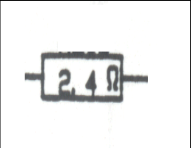
Resistor: Limits current flow, has a fixed value |
|
|
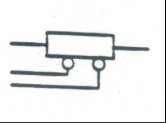
Tapped Resistor: Resistance cannot be adjusted |
|
|
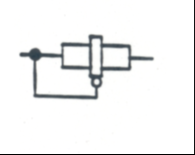
Slider Resistor: Resistance can vary when manually adjusted |
|
|
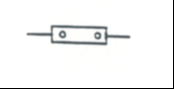
Shunt: Low value resistor |
|
|
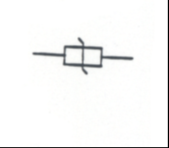
Varistor: A resistor whose value changes due to applied voltage change |
|
|
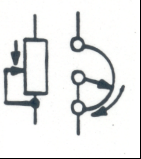
Rheostat: Resistance will varyas arm rotates |
|
|
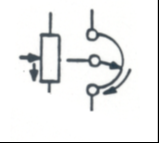
Potentiometer: Resistance will vary as arm rotates |
|
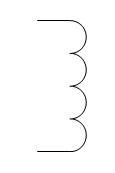
|
Field Winding: Partof the excitation circuit for traction motors and alternators. When voltage isapplied a magnetic field is created that then induces a voltage into the outputwindings of the motor or alternator. Windings are also found in transformers |
|
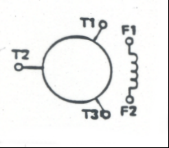
|
Three Phase Alternator: Generates AC voltagewhen its field windings are excited. Used to supply high voltage for the tractionmotors |
|
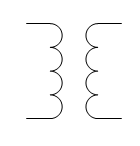
|
Transformer: Steps AC voltage up or down |
|
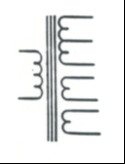
|
Multiple Winding Transformer: Steps AC voltage up or down |
|
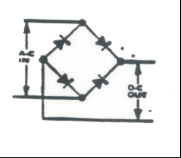
|
Full Wave Bridge Rectifier: Converts AC voltage to DC voltage |
|

|
Relay Coil: Magneticdevice that opens or closes sets of contacts in a relay or contactor. May alsobe used with air or fluid valves |
|
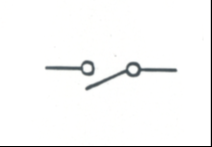
|
Normally Open Contact or Interlock - Single Break (NO): Opens or closes a circuit based on the condition of it's associated relay coil |
|

|
NormallyClosed Contact or Interlock – Single Break (NC): Opens or closes a circuit base on the condition of its associated relay coil
|
|
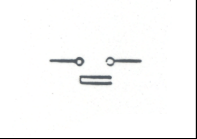
|
NormallyOpen Contact or Interlock – Double Break (NO): Opensor closes a circuit base on the condition of its associated relay coil
|
|
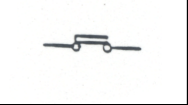
|
NormallyClosed Contact or Interlock – Double Break (NC): Opensor closes a circuit base on the condition of its associated relay coil
|
|
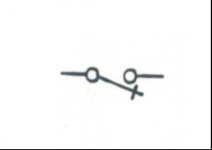
|
Single Pole Single Throw Switch: Manually operated switch to open or close a circuit |
|
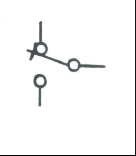
|
Single Pole Double Throw Switch: Manually operated switch to open or close a circuit
|
|
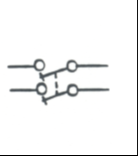
|
Double Pole Single Throw Switch: Manually operated switch to open or close a circuit
|
|
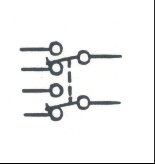
|
Double Pole Double Throw Switch: Manually operated switch to open or close a circuit
|
|
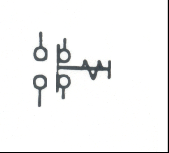
|
Push Button Switch: Manually operated, momentary contact switch to open or close a circuit |
|
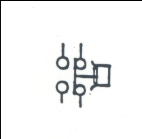
|
Pressure Switch: Opens or closes a circuit based on applied pressure. Can be operated by air, water, fuel, etc. |
|
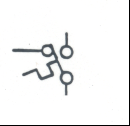
|
Thermal Switch: Opens or closes a circuit based on applied temperature. Can be used in air, water, fuel, etc. systems |
|
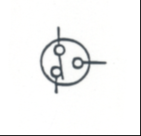
|
Cam Operated Switch: Rotationalswitch that opens or closes a circuit "air or electrically operated" |
|
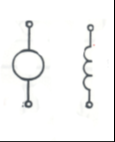
|
Traction Motor: Drives axles to movelocomotive.Shown in two parts, the armature and the field |
|
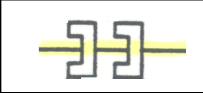
|
Transducer: Senses current flowin cables or wires passing through their center.These do not emit a current. Their resistancevalue changes based on applied EMF |
|
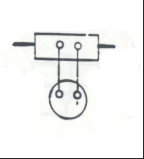
|
Load Ammeter: Measurescurrent going to the traction motors |
|
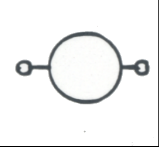
|
Axle Alternator: Mounted to tractionmotor axle.Supplies current for operation of the speedindicator |
|
|
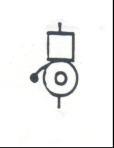
Bell: Mounted in the cab. Supplies warning to the crew of a trouble |

