![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What flies pose the most problems for dogs and cats?
|
Cuterebra, the bot fly, and Stomoxys, the stable fly.
|
|
|
What is fly strike or myiasis?
|
Fly larvae may develop in the subcutaneous tissues of the skin of domestic and wild animals. The hatched eggs feed on the dead blood cells and secretions and may migrate through healthy tissue.
|
|
|
What types of lice infect dogs and why must you be concerned with them?
|
Both biting and sucking lice infect dogs and large numbers can cause anemia.
|
|
|
What is a fomite?
|
objects or materials that are likely to carry infection, such as clothes, utensils, and furniture.
|
|
|
What is the intermediate host for dipylidium (canine tapeworm)?
|
Lice or fleas.
|
|
|
How do you treat lice?
|
Use powders or shampoos containing insecticides and treat again within two weeks (kill the hatching nits)
|
|
|
When is the flea parasitic?
|
When it is an adult.
|
|
|
What complications can arise with flea infestations of dogs and cats?
|
Severe infestations can cause anemia, which may result in death for young animals. Some dogs and cats can become allergic to flea's saliva.
|
|
|
How do you control fleas?
|
Powders/shampoos with insecticides kill adult fleas. Drugs are available that kill adults and prevent eggs from hatching. Surrounding may require extermination.
|
|
|
When is the tick parasitic?
|
As a larva, nymph, and adult.
|
|
|
How do you treat ticks?
|
Small numbers of ticks can be removed with tweezers. Be careful to remove without squeezing the head. Larger infestations require application of topical pesticide.
|
|
|
What is an acaricide?
|
Substance poisonous to mites or ticks.
|
|
|
Can dogs get Lyme disease and, if so, what is the vector?
|
Yes, they can get Lyme disease. It is spread from mice to dogs by Ixodes scapularis, the blacklegged or deer tick.
|
|
|
What diseases does the American dog tick (dermacentor) carry?
|
Rocky Mountain spotted fever and canine piroplasmosis (babesiosis), a protozoan disease.
|
|
|
What mange mites infect dogs?
|
Demodex canis and sarcoptes scabei.
|
|

|
Dog Flea Ctenocephalides canis
|
|

|
Cat flea
|
|

|
Biting louse Trichodectes canis intermediate host for Dipylidium (tapeworm)
|
|

|
Brown dog tick Rhipicephalus
|
|
|
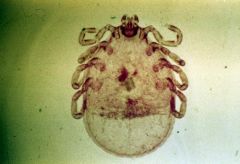
American dog tick Dermacentor
|
|
|
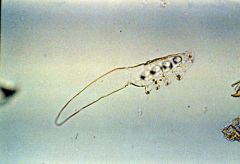
Demodex canis
|
|
|
Notoedres cati; infests ears and neck - may go to the face and feet.
|
|
|
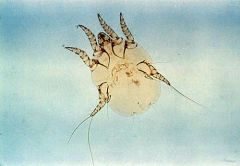
Otodectes cyanotis
|
|
|
How do you diagnose demodetic mange?
|
By scraping the skin in the area of the lesions and finding larval, nymphal and adult mites. You must scrape in the direction of the hair until capillary bleeding is observed.
|
|
|
How do you treat demodetic mange?
|
Amitraz dips are done every 2 weeks for 4-6 weeks. Antibiotics may be given to prevent secondary infections.
|
|
|
What type of mange is zoonotic?
|
Scabies from sarcoptes scabei.
|
|
|
Is sarcoptes common in cats?
|
No, it is rare.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose sarcoptes?
|
With a skin scraping of the host's lesions.
|
|
|
How do you treat sarcoptic mange?
|
Amitraz dips can be used every 2 weeks for 4-6 weeks. Ivermectin is also effective (do not give to herding dogs. Selamectin is also effective.
|
|
|
What mite causes mange in cats?
|
Notoedres cati.
|
|
|
How do you treat cat mange?
|
Amitraz or lime/sulfur dips, weekly injections of Ivermectin, and selamectin.
|
|
|
How are ear mites diagnoses?
|
Using an otoscope and looking at ear debris under a microscope.
|
|
|
What is the scientific name for ear mites?
|
Otodectes cynotis.
|
|
|
How do you treat ear mites?
|
selamectin (topical), fipronil (drops), and Ivermectin (applied to ear canal).
|
|

|
sucking louse, Linognathus setosus, has a head that is more slender than the thorax, with mouthparts
designed to suck the host’s tissue, body fluids, and blood. |

