![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

What are the 3 main reasons we use patch panels?
|
1. Ease of upgrading
2. Reducing cable damage 3. Troubleshooting |
|

What are the types of wiring an RJ 45?
|
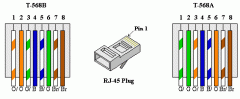
1. 568a
2. 568 b 3. Rollover |
|
|
When creating an Ethernet cable, why do we split the green cable with the blue cable?
|
It prevents cross talk.
|
|
|
What is crosstalk?
|
A signal traveling down one wire that will generate an electrical magnetic field that can disrupt or induce a false signal with another cable.
|
|

What are the only wires used in an Ethernet cable for a 10/100 network?
|
1,2,3,6
are the only cables used |
|
|
What is attenuation?
|
Weakening of the signal.
|
|
|
What is the minimum length an Ethernet cable must reach before the attenuation starts degrading?
|
100 meters
|
|
|
What does a repeater do?
|
It restores the signal to the signals original strength
|
|
|
What is needed to ping?
|
1. Source MAC address
2. IP address |
|
|
What is the MAC broadcast address?
|
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF
otherwise known as the "all F" address. |
|
|
What is anding
|
- The mathematical process where if all locations = 1, the output will be 1; if any number is 0 the output will be 0
-- Any number anded with itself is going to be itself -- Any number with all 1s is going to give you the number you started with -- Any number anded with all 0's is going to be 0 |
|
|
What happens with an ARP request if the destination is local?
|
Address Resolution Protocol
The address is sent |
|
|
What is ASIC?
|
Application Specific Integrated Circuit
It is used in switches |
|
|
What is the command to show the MAC address in a Cisco router?
|
Show Mac-address-table
|
|
|
What is IEEE 802.2?
|
Ethernet Standard
|
|
|
What is IEEE 802.3?
|
Novel standard
|
|
|
802.2 and 802.3 ___________________
are or are not compatible with each other |
802.2 and 802.3 are not compatible with each other
|
|
|
What is the preamble?
|
The signal sent to the node warning the node that a transmission is about to begin.
|
|
|
What is SFD stand for?
|
Start of Frame Delimiters
|
|
|
What is an SFD?
|
Start of Frame Delimiters
This identifies where the data begins during transmission |
|
|
How many bits is an Ethernet frame header?
|

14-bytes
|
|
|
What does the Ethernet Frame Header Contain?
|

- MAC destination address
- MAC source address - Other various fields |
|
|
The encapsulation header for layer 3 includes?
|
- IP destination address
- IP Source address |
|
|
What is propagation delay?
|
In general it is the length of time taken for the quantity of interest to reach its destination.
In other words - Data Gets lost |
|
|
When do switches broadcast?
|
When they do not have the MAC address in their MAC-address table.
|
|
|
How many ports can bridges have?
|
up to 16
|
|
|
How many ports can switches have?
|
hundreds
|
|
|
Are bridges hardware or software based?
|
Hardware
|
|
|
Are switches hardware or software based?
|
Software
|
|
|
What does STP stand for?
|
Spanning Tree Protocol
|
|
|
What are the key points of STP?
|
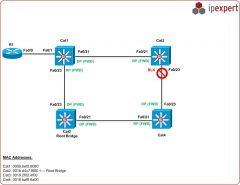
Spanning Tree Protocol
- Eliminates redundancy - Shuts off unneeded cables until they are needed |
|
|
What does CIDR stand for?
|
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
|
|
|
What is CIDR?
|
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR)
1. This is a way of subdividing a network 2. The number of bits turned on beyond the default mask, is going to determine the total number of subnets * Ex) class A subnet mask, with an ending subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 * CLASS A: 11111111.00000000.00000000.00000000 * NEW SM: 11111111.11111111.11111111.1111.0000 o This is 20 bits in addition to the starting mask n^20 determines how many host addresses there are |
|
|
What is the host formula for usable addresses
|
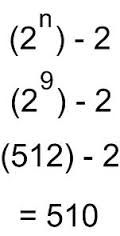
2^n -2
|

