![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name two natural barriers to entry |
Economies of scale High sunk costs |
|
|
3 Artificial Barriers to Entry |
Copyright Health and safety Planning permission |
|
|
3 Pricing Strategies by oligopolies |
Collusion Predatory Pricing Price Leadership |
|
|
Where are S-Normal Profits, Max revenue and productive/ allocative efficiency for a monopolist? |
S-Normal Profits » MC=MR Max revenue» MR intersects x-axis Allocative efficiency» MC= AR Productive efficiency» Lowest point of AC Curve |
|
|
First degree price discrimination |

Charging the highest price a consumer would be willing to pay |
|
|
Second degree price discrimination |
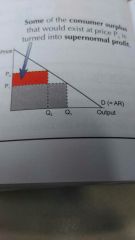
Lower prices charged to people who buy in bigger quantities |
|
|
Third degree price discrimination |

Charging different amounts to different groups of consumers |
|
|
Indicate the deadweight loss traingle for a monopolist |
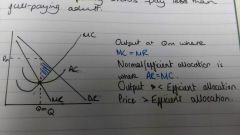
|
|
|
How do Monopolies come about? |
Few competitors Barriers to entry Advertising and product differentiation Natural monopolist through economies of scale |
|
|
What is the excess profits for a monopolist? |
The difference between ACm and Pm |
|
|
Why can a monopolist make supernormal profits but firms in a perfectly competitive market cannot? |
For a monopolist, the barriers to entry are total therefore the profits cannot get competed away. |
|
|
What does the deadweight loss represent for a monopolist? |
The potential revenue that the producer isn't earning but that the consumers would be willing to pay |

