![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Explicit costs
|
Costs that require an outlay of money by the firm
|
|
|
Implicit Costs
|
Costs that do not require
an outlay of money by the firm |
|
|
Fixed costs
|
Costs that do not vary with the
quantity of output produced or FC |
|
|
Variable costs
|
Costs that do vary with the
quantity of output produced or VC |
|
|
Total cost
|
The market value of all the inputs that a firm uses in production
VC + FC |
|
|
Average fixed cost
|
Fixed costs divided by
the quantity of output FC/Q |
|
|
Average variable cost
|
Variable costs divided by
the quantity of output VC/Q |
|
|
Average total cost
|
Variable costs divided by the quantity of output
VC/Q |
|
|
Marginal Cost
|
The increase in total cost that arises from an additional unit of production
Change in TC/ Change in Q |
|
|
Economies of scales
|
When increase in quantity decreases ATC
|
|
|
Dis-economies of scale
|
When increase in quantity decreases ATC
|
|
|
What happens at the point when average total cost = marginal costs?
|
The U shape of the ATC takes a turn and increased quantity increases costs rather than decreases them.
|
|
|
Explicit Costs
|
Costs that firms incur by buying items to produce their service or goods
|
|
|
Implicit Costs
|
Costs incurred by firms such as opportunity cost or other items that would not be see on a balance sheet
|
|
|
Diminishing Marginal Product
|
property that states that for each additional input the increase in output will become less and less per 1 increase.
|
|
|
What market has:
-Many buyers and sellers -The goods offered by the sellers are pretty much the same. -Firms can freely enter or exit a market |
A perfectly competitive market
|
|
|
What is a price taker?
|
Someone who takes the value of an item at the price for which the market as determined and has very little impact
|
|
|
Average revenue
|
Revenue/quantity
|
|
|
Marginal Revenue
|
Change in revenue for each additional unit sold
|
|
|
For competative firms, market revenue =
|
the price of goods.
|
|
|
Three general rules for profit maximization
|
1. If marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost, the firm should increase it's output.
2.If marginal cost is greater than marginal revenue, the firm should decrease its output 3. Optimum at point at which marginal cost and marginal revenue are equal |
|
|
Difference between the shutdown and exit of a firm
|
1. Shutdown is a period in which a firm will close due to market conditions
2. exit is when a firm leaves a market for good |
|
|
What are three features of a perfectly competitive market in the SHORT RUN?
|
-Large numbers of firms
-perfectly homogeneous products -perfect information ----firms have no ability to affect market price. |
|
|
In a perfectly competative market, firms will produce up to the point where...
|
...marginal cost equals marginal revenue... that determines the prices of a good.
|
|
|
What are the features of a perfectly competitive market in the long run?
|
-Large numbers of firms
-homogeneous products -perfect information -firm is A PRICE TAKER -NEW ---->no barrier to exit and entry of the market. |
|
|
A firm is a monopoly when...
|
It is the sole seller of a product and there are no close substitutes.
|
|
|
What is price discrimination?
|
Charging different prices to different users for the same good
|
|
|
Characteristics of a natural monopoly are:
|
-High fixed costs
-increasing returns of scale=constantly falling ATC -because efficient production is at such a large scale there is only room for one firm in a market -MC is always falling believe ATC because ATC is always falling |
|
|
Anti-trust laws are design too...
|
keep firms from colluding or merging to gain monopoly power
|
|
|
Characteristics that define monopolistic competetion
|
-many sellers
-product differentiation -free entry and exit from marketplace |
|
|
CDs, Books, Movies, Computer Games, Restaurants, Piano lessons are all examples of firms in...
|
Monopolistic competition
|
|
|
What is a main different between monopolistic competition and oligopoly?
|
Monopolistic competition features many sellers w/ different goods.
Oligopoly, few sellers with similar goods. |
|
|
In monopolistic competition, in the long run firms will enter/exit the market until:
|
there are zero ECONOMIC profits.
|
|
|
What are four criticisms of advertising?
|
1. Can be barrier to entry
2. Can manipulate tastes 3. Can impede competition by distracting from price or creating false difference 4."nonproductive" use of resources |
|
|
What are three benefits of advertising?
|
1. Can provide useful/important information
2. Can increase competition, especially on quality. 3. Can provide a signal of product quality or the stability of a firm. |
|
|
When do firms choose to advertise?
|
When firms sell different products and charge prices above marginal cost. In this case each firm has an incentive to attract more buyers to it's particular product.
|
|
|
Game theory is...
|
Study of how people behave in strategic situations
|
|
|
In game theory, a player's BEST strategy is the one that...
|
maximizes their payoff GIVEN the strategy chosen by the other player
|
|
|
In game theory, a player HAS a DOMINANT strategy when...
|
their best strategy is the same regardless of strategies chosen by other players.
|
|
|
A Nash equilibrium is a situation in which...
|
economic actors acting with one another each choose their best strategy given the strategies that all the others have chosen.
|
|
|
In game theory, why do firms cooperate?
|
Because of repeat games, outcomes will provide for an overall beneficial outcome versus one firm cheating in one game and jeopardizing their relationship with other firms.
|
|
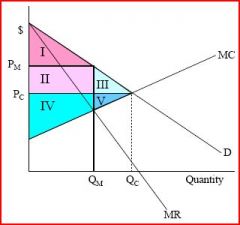
What does each section correspond too?
|
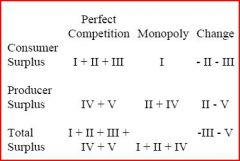
YES
|
|
|
Perfect competition
|
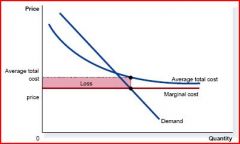
This is loss under what situation?
|
|
|
Shut down
|

In this situation a firm will:
|
|
|
a perfectly competitive market
|
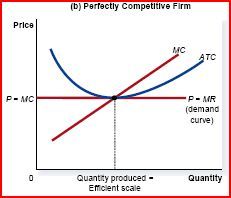
This is equilibrium in...
|
|
|
Monopolistic competition
|
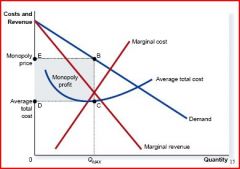
This is profit under...
|
|
|
LONG
|
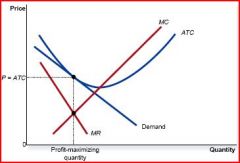
This is monopolistic comp's equilibrium under short or long run?
|
|
|
What is the difference between monopolistic profit and perfectly competitive profit?
|

this
|
|
|
Causes for monopolies to exist
|
-A key resource is owned by a single firm
-A government gives a single firm the exclusive right to produce some good -the cost of production make a single produce more efficient than large numbers of producers |
|
|
If the firm is a factor-price taker,
a. the marginal factor cost (MFC) will be constant. b. the value marginal product (VMP) will equal the marginal factor product (MRP). c. the VMP will equal the MFC. d. the MFC will equal the MRP. |
1. a
|
|
|
2. If the wage in an alternative occupation to insurance salesperson increases,
a. supply of insurance salespeople will increase. b. supply of insurance salespeople will decrease. c. demand for insurance salespeople will increase. d. demand for insurance salespeople will decrease. |
2. B
|
|
|
3. If the price of cars increases,
a. supply of autoworkers will increase. b. supply of autoworkers will decrease. c. demand for autoworkers will increase. d. demand for autoworkers will decrease. |
3. C
|
|
|
4. If the substitution effect for a person’s labor supply decision dominates her income effect,
a. her labor supply curve is positively sloped. b. her labor supply curve is negatively sloped. c. her labor supply curve has a zero slope. d. her labor supply curve has an infinite slope. |
4. A
|
|
|
5. Which of the following is a reason that labor demand would be highly elastic?
a. high price elasticity of demand b. low labor cost relative to total cost c. few substitutes for labor d. high marginal product of labor |
5. A
|
|
|
• Demand Supply
○ |
§ Shift is caused by exogenous factors…
If price changes, that’s not gonna cause a shift in the curve its going to make you go up or down the curve |
|
|
in the long run, supply side elasticity is...
|
greater because they are able to respond to changes
|

