![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Economist as a scientist Economic Models |
1. Are objective/use scientific method Must observe economy to make theory --Stronger evidence=stronger theory --Can't experiment; must rely on data/history 2. Mostly diagrams/equations Omit details/make assumptions to make model more simple |
|
|
The role of assumptions -Challenges of them -Varriations of assumptions |
Simplify complexity--makes it more applicable Challenge: What assumptions to make -----------------What context to put assumptions in Different situations are more impacted by assumptions than others; use to answer different Qs |
|
|
First Model: |
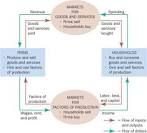
|
|
|
Positive v Normative -relation to personal beleifs |
Positive- How the world is --Often affects Normative --Science Normative- how it should be --Sci&values Good policy has P&N Both strongly intertwine with personal beleifs Differences of opinion here are why Econ disagree |
|
|
Economists in Washington -Why Econ advice is often wishy washy -Effect of ideas -Why Econ advice not always taken --Different prez advisers |
1. Advice often not straitforward; realize there's trade offs to everything Use economists all over Washington Ideas will often change history
2. Econ Advisers Communication advisers (how to present) Press advisers-how will it be in press? Legislative advisers-how will congress react Political-what groups will support Advice often not taken because it's only one part of many aspects of politics |

