![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Indirect taxes |
Taxes on expenditure |
|
|
|
Ad valorem taxes (type of indirect tax) |
% of the price of a product |
|
|
|
Specific taxes (type of indirect tax) |
Set amount per unit of the product |
|
|
|
Which direction do indirect taxes cause the supply curve to shift in? |
Left |
|
|
|
What will indirect tax allow the producer to do when demand is inelastic? |
Allow them to pass on some or all of this tax onto the consumer through a higher price
|
|
|
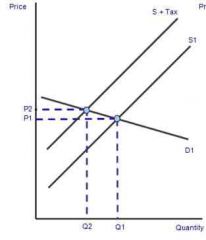
Indirect tax when demand is... |
Elastic |
|
|
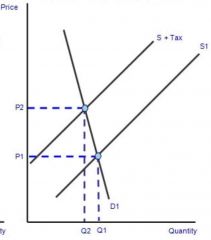
Indirect tax when demand is... |
Inelastic |
|
|
|
Incidence of tax |
How the burden of tax is distributed between different groups (eg producers and consumers) |
|
|
|
Grant from the government which has the effect of reducing the costs of production... |
Subsidy |
|
|
|
Which directors will subsidies cause the supply curve to shift in? |
Right |
|
|
|
Wage rate |
Amount paid per hour/day/week/month for working |
|
|
|
Derived demand |
Demand dependant on the demand for the final product |
|
|
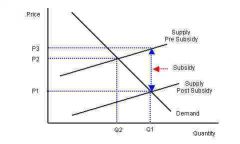
What effect does a subsidy have? |
Price will fall and quantity will increase |
|
|
A decease in wage rates... |
Increase in demand for labour |
+ Add a hin |
|
|
3 factors which influence elasticity of demand for labour |
1) elasticity of demand for final product 2) wage area high proportion of total costs, demand elastic 3) replacing labour with machinery, hard to replace - inelastic |
|
|
|
3 factors which influence demand for labour to particular industry |
1) if labour costs rise relative to cost of machinery, firms likely to replace labour with capital 2) productivity of labour 3) labour market regulations. |
|
|
|
What does the supply curve of labour show? |
How many people are willing to work given the wage rates |
|
|
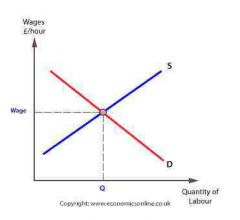
If wage rates drop... |
The supply of workers drop as the incentive to work drops |
|
|
|
2 influencing factors of the elasticity of supply of labour |
1) skills, qualifications are high, supply of labour inelastic 2) level of unemployment, high unemployment, supply elastic |
|
|
|
5 changes which could cause a shift in supply curve for labour in particular industry |
1) net migration - rise relative to emigration, > shift 2) real wage in other occupations 3) non-monetary factors - eg hours of work 4) income tax rates - reduction might encourage more to seek employment 5) qualifications and legal requirements - increase = decease supply of labour |
|
|
|
National Minimum Wage |
Rate set by government to specify the lowest legal amount workers can be paid |
|
|
|
What is the main aim of NMW? |
prevent exploitation of workers and reduce inequality |
|
|

Where is the surplus labour? (Unemployment) |
Q1 to Q2 |
|
|
|
Unemployment determined by 3 factors... |
1) how high NMW compared to equilibrium wage 2) price elasticity of demand for labour 3) price elasticity of supply of labour |
|

