![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Free market economy |
Where market forces of supply and demand determine how resources are allocated |
|
|
|
3 advantages of the free market economy |
1) flexibility - responds quickly to changes in consumer wants 2) increased choice - for consumers compared with a command economy 3) competition- and profit motive = efficient allocation of resources |
|
|
|
3 disadvantages of the free economy |
1) Imperfect information- unable to make rational choices 2) monopolies 3) externalities
|
|
|
|
What is used to overcome these problems, define |
Mixed economy- combination of free market and command economy |
|
|
|
Amount demanded by consumers at each price over a certain period of time... |
Demand |
|
|
|
What way does the demand curve slope and what does this indicate? |
From left to right, indicating more will be demanded as price falls |
|
|
|
What will a rise in price do to the quantity demanded? |
Decrease in quantity demanded |
|
|
|
What two effects is this based on? |
1) the substitution effect 2) the income effect |
|
|
|
The substitution effect |
Rise in price (income same) consumer tends to buy more of a lower priced good |
|
|
|
What are 5 factors affecting a shift in the demand curve? |
1) real incomes 2) size or age distribution of population 3) tastes, fashion or preferences 4) prices of substitutes or compliments 5) interest rates |
R S T P I |
|
|
Interest rate |
Cost of credit or reward for saving |
|
|
|
Supply |
How much is supplied by the producer at each price over a certain period of time |
|
|
|
Which way does the supply curve slope and what does that indicate? |
Right to left, indicating more will be supplied as the price increases |
|
|
|
What will a rise in price do to the quantity supplied? |
Cause it to increase |
|
|
|
5 shifts in the supply curve |
1) costs of production 2) productivity of the workforce 3) indirect taxes 4) subsidies 5) technology |
C P I S T |
|
|
Determined by the interaction of supply and demand curves. Equilibrium price doesn't change unless there's a change in the condition of supply or demand... |
The equilibrium (price and quantity) |
|
|
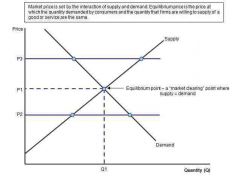
What does line P2 show? |
Excess demand |
|
|
|
means by which millions of decisions taken by consumers and businesses interact to determine the allocation of scarce resources between competing uses... |
Price mechanism |
|
|
|
3 main functions of the price mechanism |
1) signalling device - producers to increase or decrease amount supplied 2) transmission of preferences - change demand reflected by a change in price 3) rationing device - equates supply and demand eg When there is a shortage, the price is bid up – leaving only those with the willingness and ability to pay to purchase the product. |
|
|
|
When the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded... |
Excess supply |
|
|
|
If there is excess supply in the market what will the market forces do? |
allow the market price to fall, extension in demand and contraction in supply |
|
|
|
What are the 2 ways which cause a change in equilibrium? |
1) change in conditions of demand 2) change in conditions of supply |
|

