![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ecology |
Part of the earth containing living organisms
|
|
|
Ecosystem |
Group of organisms that interact with each other and their environment |
|
|
Habitat |
Place where an organism lives and is adapted to |
|
|
Abiotic factors |
Non-living features → aspect = plants grow better on south facing slops → exposure = more organisms on south facing slopes → soil pH = suits different plants → climatic and edaphic factors |
|
|
Biotic Factors |
1) Food → more plants = more animals 2) Competition → reduce number of organisms 3) Predation → reduce number of prey 4) Parasitism → reduce number of hosts 5) Animals → needed for pollination and seed dispersal 6) Human influences |
|
|
Climatic Factors |
1) Temperature → higher temp = increased growth 2) Rainfall → water for growth 3) Light intensity → photosynthesis 4) Wind → damages plants, stunts growth and increases evaporation |
|
|
Edaphic Factors |
1) Soil pH 2) Soil type → sandy or clay 3) Humus content → increased growth of plants 4) Water, air and mineral content of the soil → + growth |
|
|
Aquatic factors |
1) Light 2) Currents → wash away algae, plants and animals 3) Wave action → physical damage 4) Oxygen concentration → less in water than air |
|
|
Food chain |
A sequence of organisms where each organism is eaten by the next one in the list |
|
|
Example food chain |
sessile oak→aphids→ladybird→blackbird→ sparrowhawk |
|
|
Trophic level |
Feeding stage in a food chain |
|
|
Lenght of food chains |
Short as huge energy loss (90%) between tropic levels |
|
|
Food web |
Two or more interlinked food chains |
|
|
Example of a food web |
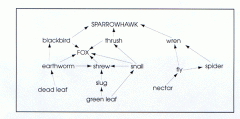
|
|
|
Pyramid of numbers |
Represents the number of organisms at each trophic level in a food chain |
|
|
Niche |
The functional role of an organism in an ecosystem or a habitat Eg swallows eat mice by day and bats eat mice by night |
|
|
Nutrient Recycling |
Way in which elements are exchanged between living and non-living components of an ecosystem (→ absorbed by organisms → released into the environment when the organisms decompose →absorbed by other organisms) |
|
|
The carbon cycle |
Plants and algae → remove CO2 from the atmosphere in photosynthesis and return it in respiration Animals → obtain carbon from eating plants and release it in respiration Fungi and bacteria → return CO2 when decomposing dead organisms |
|
|
Carbon cycle diagram |
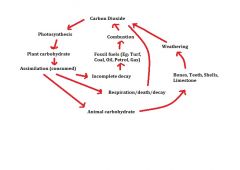
|
|
|
Causes of increased CO2 (Global warming) |
→ Increased burning of fossil fuels → Destruction of the world's forests |
|
|
The Nitrogen Cycle diagram |
See diagram in HB |
|
|
The nitrogen cycle theory |
→Plants need nitrogen to make proteins but can't use N2 as it is an inert gas
→Nitrogen fixing bacteria convert N2 into nitrate which plants can use.
→Transferred to animals when they eat and assimilate plant proteins
→When plants and animals die, they are decomposed by bacteria and fungi, and release nitrogen compounds such as ammonium salts
→Nitrifying bacteria convert theses to nitrites, then nitrates.
→Denitrifying bacteria convert nitrates to nitrogen gas |
|
|
Nitrogen fixation |
The conversion of nitrogen gas into ammonia, ammonium or nitrate |
|
|
Nitrification |
The conversion of ammonia and ammonium compounds to nitrite and then nitrate |
|
|
Denitrification |
The conversion of nitrates to nitrogen gas |
|
|
Population |
All the members of a species in an area |
|
|
Competition |
When two or more organisms actively struggle for a resource that is in scarce supply |
|
|
Contest competition |
An active, physical struggle between two organisms for a scarce resource with a winner and a loser |
|
|
Scramble competition |
All of the competing organisms get some of the scarce resource |
|
|
Predation |
The catching, killing and eating of another organism for food |
|
|
Adaptations of predators |
→colour of a fox's coat = camouflage →hawks excellent eyesight = see prey |
|
|
Adaptations of prey |
→rabbits have large hing legs = fast running →mice are flexible = hide in small places |
|
|
Parasitism |
When an organism benefits or takes food from a host and usually causes harm to it Eg: Aphids on oak trees |
|
|
Symbiosis |
When two organisms of different species live in close association where at least one of them benefits |
|
|
Predator-prey graph |
Predator peaks are smaller and slightly in front of prey peaks |
|
|
Factors affecting predator-prey |
→availability of food →migration |
|
|
Factors affecting human population numbers |
→War →Famine →Contraception →Disease |
|
|
Pollution |
Any harmful addition to the environment |
|
|
Effect of agricultural pollutant |
→Excessive fertiliser spread on grassland may be washed/leached into rivers/lakes →Minerals in fertiliser cause algae to grow faster = algae blooms →Algae decompose and use up all the oxygen →Death of living things →Eutrophication |
|
|
Control of pollutant |
→Limit use of fertilise so excess is not washed away →Avoid spreading on wet, frozen, or steeply sloping land near watercourses |
|
|
Conservation |
The wise management of our existing natural resources, in order to maintain a biodiversity, a wide range of habitats and prevent extinction of species. |
|
|
Conservation in agriculture |
→Mixed faming = arable and pastoral farming carried out, animals = manure to help soil fertility, increases nutrients, soil water holding capacity and structure
→Crop rotation = replenish soil nutrients and reduce soil erosion
→Gene Banks = preserve genetic material, freeze cuttings from plants, artificial insemination = better quality leather/meat |
|
|
Waste management |
The collection, transport, processing, recycling or disposal of waste materials, produced by human activity, or order to reduce their effect on human health, local aesthetics or amenity. |
|
|
Waste management in agriculture |
→Slurry is diluted and spread on dry days →Stored in water proof pits →Absorbed by plants = recycled
|
|
|
Problems with waste disposal |
1) availability of suitable landfill sites 2) toxic/polluting content of fumes from incineration 3) toxic substances may leak into groundwater supplies 4) may cause eutrophication |
|
|
Waste minimisation |
Reduce, reuse, recycle |

