![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Organism |
Any individual form of life |
|
|
Population |
A group of organisms of the same species living together |
|
|
Community |
Groups of different populations living together in same area at same time |
|
|
Ecosystem |
All biotic and abiotic factors in the same area at the same time |
|
|
Biosphere |
All ecosystems on earth |
|
|
Abiotic |
Nonliving |
|
|
Biotic |
Living |
|
|
Examples: Sunlight Soil Water Rocks |
Abiotic |
|
|
Examples: Predators Prey Disease Symbiosis |
Biotic |
|
|
Producer (______) = plants |
Autoroph |
|
|
Consumer (______) |
Heterotroph |
|
|
only eats plants |
Herbivore |
|
|
only eats meats |
Carnivore |
|
|
Eats plants and animals |
Omnivore |
|
|
Feeds on dead animals and plants |
Scavenger |
|
|
Organisms that break down dead or decaying organisms (ex: worm, bacteria, fungi) |
Decomposer |
|
|
Symbiosis |
Two different organisms living and interacting closely together |
|
|
Mutualism |
Both organisms benefit (+,+) |
|
|
Parasitism |
One organisms benefits while other suffers (+,-) |
|
|
Predator |
An individual that consumes another indi |
|
|
Predation |
The act of a predator capturing prey |
|
|
Producers |
Get their energy from the sun |
|
|
Consumers |
Get energy from other living things |
|
|
Decomposers |
Get their energy from dead/decaying things |
|
|
Energy transfer |
The movement of energy around an ecosystem by biotic and abiotic means organisms in a food chain provide energy for other organisms |
|

|
Food chain |
|
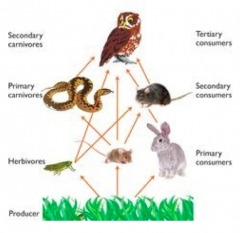
|
Food web |
|
|
Feeding position that an organism has in a food chain |
Trophic levels |
|
|
Shows relationship between organisms at different levels, their biomass, and energy transfer |
Pyramid |
|
|
____ is also greatest at bottom, only 10% is passed on each time |
Energy |
|
|
_____, at the bottom if the pyramid, have the most energy |
Producers |
|
|
Adds water as vapor (a gas) to the atmosphere, needs hear (like sweating, puddles disappearing) |
Evaporation |
|
|
Evaporation through plants |
Transpiration |
|
|
Water vapor cools in atmosphere, forming liquid water again (water droplets, forms clouds, or water on outside of your glass) |
Condensation |
|
|
Precipitation |
Liquid water leaves the atmosphere in the form of rain, snow, hail, or sleet |
|
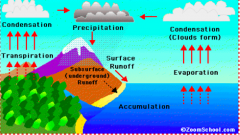
|
Water cycle |
|
|
______ absorb CO2 from atmosphere and water from soil to make the food they need. This process is ________. |
Plants & photosynthesis |
|
|
The food is C6H12O6, or ______ (sugar) |
Glucose |
|
|
________ eat the plants to get the C they need, then breathe it out as CO2 (or return to soil when die = decomposition). This process is ______. |
Animals & Respiration |
|
|
When a plant dies, the carbon can turn into _____ _______ (like coal and oil) over millions of years. Humans burn _____ _______ and release tons of carbon into the atmosphere. |
Fossil fuels |
|
|
_____ ______ is a Greenhouse Gas, and traps heat in the atmosphere. |
Carbon dioxide |
|
|
But, because of humans _____ _____ ______, there is much more carbon in the atmosphere than there should be. |
Burning fossil fuels |
|
|
When organic things are burned and give off carbon dioxide. |
Combusion |
|
|
A _____ _____ _____ in the earth's climate, especially due to an increase in the average atmosphere temperature. |
long time change |
|
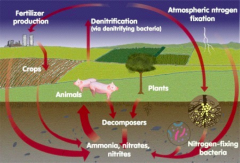
|
Nitrogen cycle |
|
|
Bacteria in soil change nitrogen from atmosphere into a form that plants can use call ammonia |
Nitrogen Fixation |
|
|
_____ get their nitrogen from eating plants and other animals that have eaten plants; get rid of nitrogen through waste. |
Animals |
|
|
Part of amino acids, which makes _______ (provide structure, enzymes) |
Protein |
|
|
Nitrogen is also a component of _____, which is our genetic material. |
DNA |

