![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
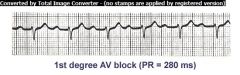
|
1st degree AV Block
PR interval > 0.20; There is 1 P wave before each QRS complex indicating the impulse from SA node passes through to ventricles but is delayed in AV node or Bundle of His |
|
|
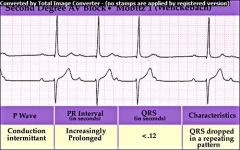
|
2nd Degree AV Block
Type I Wenckebach or Type I Mobitz Seen as a prolongation of RR intervals until a QRS complex is completely missing, then sequence begins again |
|
|
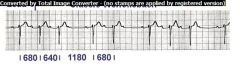
|
2nd degree AV Block a.k.a
Type I Wenckebach or Mobtiz Seen as prolongation of the PR intervals until a complete QRS interval is missing, cycle then begins again |
|
|
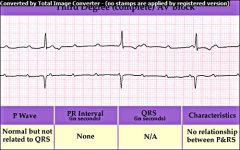
|
3rd Degree Block
atria & ventricles are paced by independant sources. Recognized by the establishment of a nonexistant relationship between the P waves and QRS complexes |
|
|
|
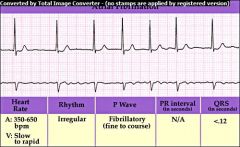
Atrial Fibrillation
atrium quivers w/no coordinated contraction; No true P waves and ventricular rate may be irregular & result in an abnormal RR interval |
|
|
|
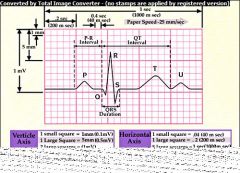
ECG Component Diagram
|
|
|
|
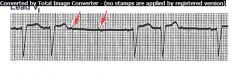
Mobitz 2nd Degree AV Block
Seen as a series of nonconducted P waves followed by a P wave that is conducted to the ventricles |
Sometimes ratio of nonconducted to conducted P waves is fixed at 3:1 or 4:1
Result from MI or ischemia |
|
|
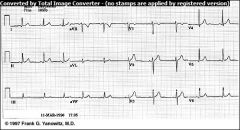
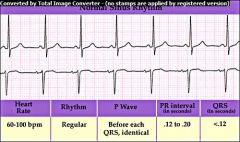
Normal ECG
begins w/upright P wave; PR interval of 0.12-0.20 consistently; QRS identical and no longer then 0.12; ST segment is flat; RR interval regular doesn't vary more than 0.12 between QRS complexes. Heart rate between 60-100 |
|
|
|
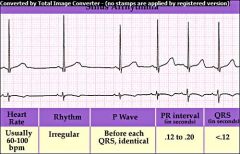
Normal Sinus Rhythm
60-100 bpm Identical P waves, PR interval of .12-.20 & consistent; QRS complex no longer than .12 seconds; ST segment is flat; R-R interval regular & don't vary more than .12 seconds between QRS complexes |
|
|
|
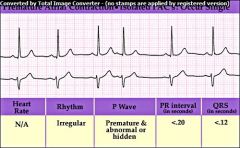
Sinus Arrhythmia
recognized by irregular spacing between QRS complexes. RR interval varies by more than 0.12 seconds |
|
|
|
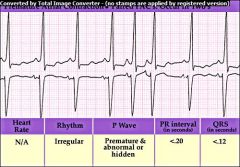
Premature Atrial Complex (PAC) P wave may be hidden or partially hidden in preceeding T wave; results when abnormal electrical activity in the atria causes the atria to depolarize before the SA node fires.
|
|
|
|
Paired PAC
P wave may be hidden in preceeding T wave; |
|
|
|
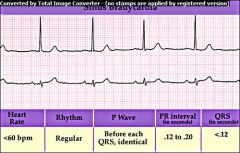
Sinus Bradycardia
Heart rate less than 60 bpm Other than the rate being too slow, sinus bradycardia does not differ from a normal sinus rhythm |
|
|

Type I versus Type II AV Block
|
In type I 2nd degree AV block the PR progressively lengthens until a non-conducted P wave occurs. The PR gets longer by smaller and smaller increments; this results in gradual shortening of the RR intervals. The RR interval of the pause is usually less than the two preceding RR intervals. The RR interval after the pause is longer than the RR interval just before the pause.
In type II AV block, the PR is constant until the nonconducted P wave occurs. The RR interval of the pause is usually 2x the basic RR interval |
|
|
|
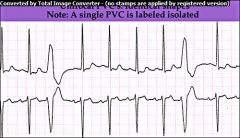
Unifocal PVC
unique & bizarre QRS complex which is much wider than normal; No P wave preceeding them |
Sources for impulse outside the SA node are called ectopic foci; PVCs are an example of ectopic foci that originate in the ventricles
|
|
|
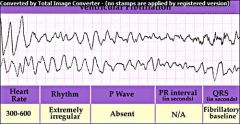
Ventricular Fibrillation - defined as erratic quivering of the ventricles; No CO present;
VF shows grossly irregular fluctuations w/zig zag pattern; |
|
|
|
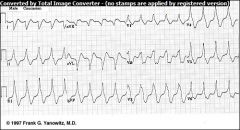
Ventricular Tachycardia - rates range from 140-220 bpm
run of 3 or more PVCs; recognized as a series of wide, bizzarre QRS complexes that have no preceeding P wave. |
|
|
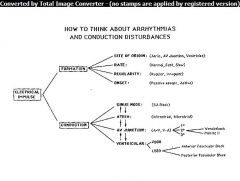
|
Conceptual Framework
|
|
|
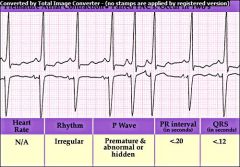
|
Paired PAC
|
|
|
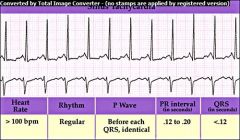
|
Sinus Tachycardia
|
|
|
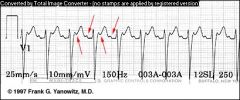
|
Atrial Flutter
Normal P wave is absent & replaced by 2 or more regular sawtooth like waves called flutter or ff waves. |
|
|
|
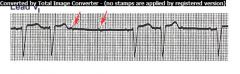
2nd degree AV Block
a.k.a. Mobitz Type II |
|
|
|
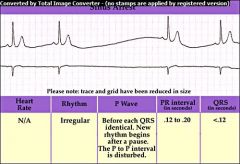
Sinus Arrest (SA Node Arrest)
sudden failure of SA node to initiate an impulse (NO P wave) 2-4 P-QRS-T complexes missing |
|
|
|
What is the term supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) commonly used to describe?
|
SVT describes any tachycardia that is not of ventricular origin
|
|
|
|
What arrhythmias are included in the general term SVT?
|
sinus tachycardia
atrial tachycardia junctional tachycardia atrial flutter atrial fibrillation (w/rates >100 bpm) |
|
|
|
What is the difference between Type I 2nd degree Wenkebach or Mobitz Blocks and Type II 2nd degree Mobitz Block?
|
Type I 2nd degree blocks the PR progressively lengthens until a non-conducted P wave occurs; Type II 2nd degree blocks the PR is constant until the nonconducted P wave occurs
|
|
|
|
In which two ventricular arrhythmias is ther no P wave present?
|
No P wave is present in:
VF & VT |
|
|
|
What drug is used to manage VT in stable patients?
|
Amiodarone
|
|
|
|
In which ventricular arrhythmia is there no cardiac output present?
|
Ventricular Fibrillation
|
|
|
|
What are some common causes of VF?
|
electrical shock, anesthesia, mechanical irritation of the heart, severe hypoxia, MI and large doses of digitalis or epinephrine
|
|
|
|
What are some serious signs and symptoms due to tachycardia (heart rate > 150)
|
Hypotension, pulmonary congestion, dizziness, shock, ongoing chest pain, SOB, CHF, weakness/fatique, acute altered mental status
|
|
|
|
What are some contributing causes to tachycardia?
|
pulmonary embolism, acidosis, tension pneumothorax, cardiac tamponade, hypovolemia, hypoxia, hypo/hyperalkalemia, MI, OD
|
|
|
|
What is the ideal route for med. admin in emergency situations if a central vein is not cannulated?
|
peripheral IV line
|
|
|
|
What arrhythmias is cardioversion indicated for?
|
SVT, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation, and VT
|
|
|
|
What drug is commonly used for bradycardia in ACLS situations?
|
Atropine
|
|
|
|
What drug(s) are commonly used for ventricular arrhythmias in ACLS situations?
|
epinephrine, amiodarone or lidocaine
|
|
|
|
What drug(s) are commonly used for hypotension or cardiac arrest in ACLS situations?
|
epinephrine or vasopressin
|
|

