![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Earth is composed up of several layers based on _______ and _______ ________. |
Composition Physical properties |
|
|
Earth's Compositional Layers |
Crust Mantle Core |
|
|
Earth's Physical Property Layers |
Lithosphere Asthenosphere Lower mantle Outer core Inner core |
|
|
Lithosphere |
Rigid 100-250 km thick Includes crust + uppermost solid mantle |
|
|
Asthenosphere |
Weak due to high temperature |
|
|
Lower mantle |
Strong Rigid due to high pressure |
|
|
Outer Core |
Liquid Iron and Nickel |
|
|
Inner Core |
Solid Iron and Nickel |
|
|
S waves travel only through _____? Solids / liquids / gases |
Solids |
|
|
P waves travel _______ than S waves? Faster / slower |
Faster |
|
|
Seismic wave velocities depends on the _______ properties (I.e. density, elasticity..) |
Material |
|
|
The velocity of seismic waves generally ______ with depth for a given layer.
Decreases / increases |
Increases |
|
|
When seismic waves pass from one material to another they both __________ and ___________. |
Refracted (bent)
Reflected |
|
|
Seismic refraction |
The bending of waves as their velocity changes |
|
|
Refracted waves will bend |
Upward |
|

Which model is more earth-like? (I.e. will waves typically bend up or down?) |
Model A Velocity of seismic waves increases with depth Refracted waves will bend upward |
|
|
The MoHo (mohorovicic discontinuity) At ~_____ km there is abrupt increase in wave speed. |
~50 km |
|
|
MoHo Is the boundary between ________ and _______. It seperates rocks above and below with very different ________ _________. |
Crust Mantle Seismic Velocities |
|
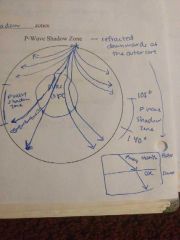
P wave shadow zone |
P |
|
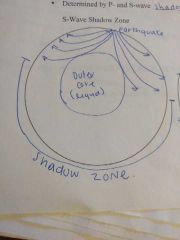
S wave shadow zone |
S wave shadow zone |
|
|
Core mantle boundary |
2900 km |
|
|
Inner core- Some p waves are _________ _________ as they pass through the inner portions of the core. |
Strongly refracted |
|
|
Velocity changes in the mantle are due to _____ ______ related to increases in pressure. |
Phase changes |
|
|
Olivine to spinel |
~440 km |
|
|
Spinel to perovskite |
~660 km |
|
|
Geothermal heat sources |
- heat emitted by radio active decay - iron crystallization - colliding particles |
|
|
Heat is transported in earth by two mechanisms |
Conduction and convection |
|
|
What mechanism do different layers in the Earth transport heat by? Crust - Mantle- |
Crust - dominated by conduction Mantle- convention heat rises, cool sink |
|
|
Convection in the outer core is what creates the ______ ______ |
Magnetic field |

