![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Fossil |
preserved remains or traces of an organism that usually lived more than 10,000 years ago |

|
|
|
Mold fossil |
Forms when sediments bury an organism, the sediments harden into rock, and the organism decays leaving a cavity |

|
|
|
Cast fossil |
Forms when sediments soak into a mold and it hardens into a rock |

|
|
|
Petrified/permineralized fossil |
Forms when minerals soak into the remains of decayed organisms and hardens |

|
|
|
Preserved fossil |
Forms when an organism is kept from decaying by being preserved in amber made from tree sap |

|
|
|
Carbonized fossil |
Forms an organism get compressed so much and the organism decays, leaving the carbon imprint of the organism |

|
|
|
Trace fossil |
When an imprint left by an animal is preserved, such as a footprint or a burrow |

|
|
|
Law of superposition |
The law that the further you go into Earth, the older it is |
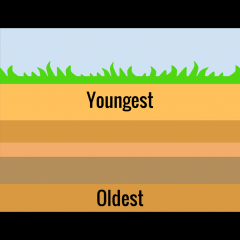
|
|
|
Relative Age |
an approximate age of a fossil or rock layer |

|
|
|
Absolute age |
the exact age of a fossil or layer of rock |
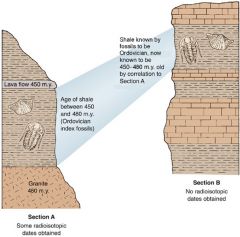
|
|
|
Index Fossil |
Fossils that are used to determine the relative age of layers of rock |
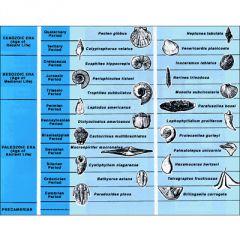
|
|
|
Trilobite |
A common prehistoric animal and a good index fossil |

|
|
|
Geologic Time Scale |
A record of every major event in Earth's history |
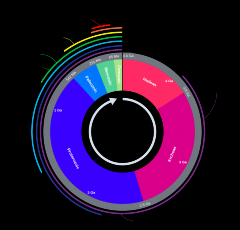
|
|
|
Era |
Second largest measure of geologic time. |
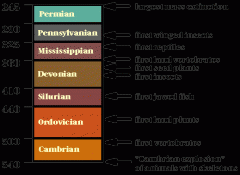
|
|
|
Period |
Second smallest measure of geologic time. |
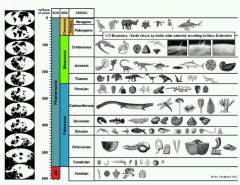
|
|
|
Epoch |
Smallest measure of geologic time. |

|
|
|
Precambrian Eon |
Beginning of Earth's history, taking up 87% of it |
|
|
|
Paleozoic Era |
The second era that began with an explosion of life and ended with a mass extinction |

|
|
|
Mesozoic Era |
The era in which reptiles were dominant and we begin to see the first mammals and birds |

|
|
|
Cenozoic Era |
Era after the dinosaurs and we live in it today |

|
|
|
Volcanic Activity |
when volcanoes erupt and release ash, gas, and lava |

|
|
|
Impact Events |
When an extra terrestrial object clashes into Earth |

|
|
|
Climate Change |
When the overall weather and temp. changes |

|
|
|
Natural Extinction Factors |
Factors that cause extinction that isn't man-made |

|
|
|
Man-made Extinction Factors |
Factors that cause extinction that is made by humans |

|
|
|
Adaptation |
something that an organism possesses that helps it survive and reproduce |

|
|
|
Physical Trait |
A part of an organism's body |
|
|
|
Behavior Adaptation |
How an organism acts |

|
|
|
Variation |
Different types of the same species |

|
|
|
Natural Selection |
The process that changes the population of an organism to fit its enviornment |
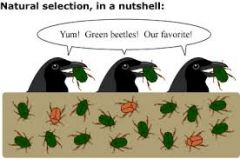
|

