![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Fault and force at a divergent boundary |
Normal and tension |
|
|
Fault force at a transform boundary |
Strike - slip and shearing |
|
|
Locating the earthquake epicenter by drawing three circles and finding where the three intersects is called |
Triangulation |
|
|
Scientists have been able to use earthquake waves to find out what about the Earth |
Composition and depth of each layer |
|
|
Vibrations caused by energy released when a break occurs at a fault is a |
Seismic wave |
|
|
Earthquake waves that arrive at the surface first |
Primary |
|
|
Earthquake waves that cause the ground to shake and make rocks roll like an ocean wave |
Surface |
|
|
The movement of rock particles duringthe passage of S waves |
Right angles |
|
|
The movement of rock particles during a P wave |
Back and forth motion |
|
|
The sequence of waves during an earthquake from first to last |
Primary, secondary, surface |
|
|
Force that causes plays to move sideways past each other |
Shearing |
|
|
Type of stress that produces reverse faults |
Compression |
|
|
What type of fault is created by tensional forces |
Normal |
|
|
A fault where rocks slip past each other sideways |
Strike-slip |
|
|
Type of force at a stroke-slip fault |
Shear |
|
|
Force that pushes rock in opposite directions |
Tension |
|
|
Changes in Earth's interior have been detected due to |
Seismic waves |
|
|
The force that squeezes rock together |
Compression |
|
|
When the force on rocks is great enough, they break, producing vibrations called |
Fault |
|
|
Measuring the time between the arrival of P and S determines the distance between the epicenter and the... |
Siesmograph |
|
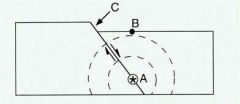
Point A where energy is initially released during the earthquake is called the |
Focus |
|
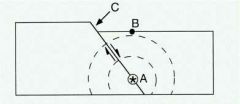
Point B is called the earthquake |
Epicenter |
|
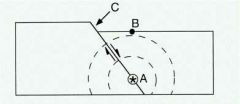
What type of fault is illustrated in this diagram |
Normal |
|
|
A layer of hot rock |
Mantle |
|
|
When arrows at plate boundaries are point towards each other is it a |
Convergent boundary |
|
|
When arrows at plate boundaries are pointed away from each other are |
Divergent |

