![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
166 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Trim lines |
Lines that are light & continuous lines song which the tracing is trimmed to square the sheet. |
|
|
|
Main object lines |
Lines that are heavy, unbroken lines used to show visible outlines or edges that would be seen by people looking at the article, house, or building. Important because they outline the main wall lines on plans and sections. |
|
|
|
Dimension lines |
Light lines drawing outside the structure or serial to show the distance between two points. Drawn between extension lines with an arrow head on each end. Between the arrow heads, the distance will be given either at a break in the line or just above the line. |
|
|
|
Extension lines |
Lines that touch and are used with dimension lines. These lines extend out from the edge or the point at which the dimension is to be determined. |
|
|
|
Symbol section lines |
Generally solid, although, for certain conventions, dotted lines of the same weight may be used. |
|
|
|
Broke lines |
Lines that are lines with wavy breaks in it at intervals. They are used to indicate those parts that have been left out or to indicate that the full length of some part has now been drawn. Used in detail drawings where only a section of the object is to be shown. |
|
|
|
Invisible lines |
Lines that are made up of a series of short dashes and used to indicate and edge or edges hidden under some other part of the structure. |
|
|
|
Center lines |
Lines that are made up of alternating long and short dashes and used to indicate the center of an object. |
|
|
|
Break lines |
Are thin solid-ruled lines with freehand zigzags & used to reduce the size of a drawing required to delineate an object and reduce detial. |
|
|
|
Three categories of symbols |
Utility, electrical, and material |
|
|
|
Electrical symbols |
Identify power distribution. |
|
|
|
Material symbols |
Symbols for building material. Used in cross sections or cutaway views. They also label new or existing material. |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following disadvantages occur when the utility lines are ripped up?
A) loss of project time B) increased project cost C) people supported by the inconvenienced D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following disadvantages occur when the utility lines are ripped up?
A) loss of project time B) increased project cost C) people supported by the inconvenienced D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Earthwork computations |
Are the calculations of earth work volumes or quantities to determine final grades, to balance cut and full, & to plan the most economical movement of material. |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following disadvantages occur when the utility lines are ripped up?
A) loss of project time B) increased project cost C) people supported by the inconvenienced D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Earthwork computations |
Are the calculations of earth work volumes or quantities to determine final grades, to balance cut and full, & to plan the most economical movement of material. |
|
|
|
How are volumes of straight edged and circular shapes calculated? |
With an arithmetic formula based on length times width times height. (L x W x H) |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following disadvantages occur when the utility lines are ripped up?
A) loss of project time B) increased project cost C) people supported by the inconvenienced D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Earthwork computations |
Are the calculations of earth work volumes or quantities to determine final grades, to balance cut and full, & to plan the most economical movement of material. |
|
|
|
How are volumes of straight edged and circular shapes calculated? |
With an arithmetic formula based on length times width times height. (L x W x H) |
|
|
|
How is volume measured? |
In cubic units. Cubic inch: 1 inch X 1 inch X 1 inch (inch3) Cubic foot: 1 foot X 1 foot X 1 foot (foot3) Cubic yard: 1 yard X 1 yard X 1 yard (yard3) |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following disadvantages occur when the utility lines are ripped up?
A) loss of project time B) increased project cost C) people supported by the inconvenienced D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Earthwork computations |
Are the calculations of earth work volumes or quantities to determine final grades, to balance cut and full, & to plan the most economical movement of material. |
|
|
|
How are volumes of straight edged and circular shapes calculated? |
With an arithmetic formula based on length times width times height. (L x W x H) |
|
|
|
How is volume measured? |
In cubic units. Cubic inch: 1 inch X 1 inch X 1 inch (inch3) Cubic foot: 1 foot X 1 foot X 1 foot (foot3) Cubic yard: 1 yard X 1 yard X 1 yard (yard3) |
|
|
|
What is a cubic yard? |
A cube 3 ft long, 3 ft wide, and 3 ft high. |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following disadvantages occur when the utility lines are ripped up?
A) loss of project time B) increased project cost C) people supported by the inconvenienced D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Earthwork computations |
Are the calculations of earth work volumes or quantities to determine final grades, to balance cut and full, & to plan the most economical movement of material. |
|
|
|
How are volumes of straight edged and circular shapes calculated? |
With an arithmetic formula based on length times width times height. (L x W x H) |
|
|
|
How is volume measured? |
In cubic units. Cubic inch: 1 inch X 1 inch X 1 inch (inch3) Cubic foot: 1 foot X 1 foot X 1 foot (foot3) Cubic yard: 1 yard X 1 yard X 1 yard (yard3) |
|
|
|
What is a cubic yard? |
A cube 3 ft long, 3 ft wide, and 3 ft high. |
|
|
|
How many cubic feet are in one cubic yard? |
27 cubic feet in one cubic yard |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following disadvantages occur when the utility lines are ripped up?
A) loss of project time B) increased project cost C) people supported by the inconvenienced D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Earthwork computations |
Are the calculations of earth work volumes or quantities to determine final grades, to balance cut and full, & to plan the most economical movement of material. |
|
|
|
How are volumes of straight edged and circular shapes calculated? |
With an arithmetic formula based on length times width times height. (L x W x H) |
|
|
|
How is volume measured? |
In cubic units. Cubic inch: 1 inch X 1 inch X 1 inch (inch3) Cubic foot: 1 foot X 1 foot X 1 foot (foot3) Cubic yard: 1 yard X 1 yard X 1 yard (yard3) |
|
|
|
What is a cubic yard? |
A cube 3 ft long, 3 ft wide, and 3 ft high. |
|
|
|
How many cubic feet are in one cubic yard? |
27 cubic feet in one cubic yard |
|
|
|
existing grade |
The elevation of the project site before construction or the driving surface of an existing road that is to be replaced. |
|
|
|
Sketches |
Drawings made with out the use of mechanical aids or devices. May be used on graph paper, traced, or drawn with a straight edge. |
|
|
|
Which of the following construction phases are documented in the Seabee project package?
A) initial planning B) execution C) close out D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following disadvantages occur when the utility lines are ripped up?
A) loss of project time B) increased project cost C) people supported by the inconvenienced D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
Earthwork computations |
Are the calculations of earth work volumes or quantities to determine final grades, to balance cut and full, & to plan the most economical movement of material. |
|
|
|
How are volumes of straight edged and circular shapes calculated? |
With an arithmetic formula based on length times width times height. (L x W x H) |
|
|
|
How is volume measured? |
In cubic units. Cubic inch: 1 inch X 1 inch X 1 inch (inch3) Cubic foot: 1 foot X 1 foot X 1 foot (foot3) Cubic yard: 1 yard X 1 yard X 1 yard (yard3) |
|
|
|
What is a cubic yard? |
A cube 3 ft long, 3 ft wide, and 3 ft high. |
|
|
|
How many cubic feet are in one cubic yard? |
27 cubic feet in one cubic yard |
|
|
|
existing grade |
The elevation of the project site before construction or the driving surface of an existing road that is to be replaced. |
|
|
|
Sub grade |
Part of the road that is a prepared base for the placement of base-course materials. |
|
|
|
Base course |
Is a selected layer of well compacted soil placed in compacted lifts on top of the sub grade. This compaction can be by mechanical stabilization or chemical stabilization. May be composed of crushed of crushed stone, crushed slag, crushed or un rushed gravel and sand or combinations of these materials or may be bound with asphalt. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Travelway |
Is the surface course on which the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Travelway |
Is the surface course on which the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Crown |
Is an established slope from the center line of a roadbed to the outside of the shoulders and allows for excess water to drain from the surface into the ditches. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Travelway |
Is the surface course on which the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Crown |
Is an established slope from the center line of a roadbed to the outside of the shoulders and allows for excess water to drain from the surface into the ditches. |
|
|
|
How many types of ditches are there? And what are they? |
There are two. V-type ditch & flat bottomed ditch. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Travelway |
Is the surface course on which the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Crown |
Is an established slope from the center line of a roadbed to the outside of the shoulders and allows for excess water to drain from the surface into the ditches. |
|
|
|
How many types of ditches are there? And what are they? |
There are two. V-type ditch & flat bottomed ditch. |
|
|
|
How many parts are there to a ditch? What are they? |
There are three parts and they are an inslope, backslope, and bottom. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Travelway |
Is the surface course on which the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Crown |
Is an established slope from the center line of a roadbed to the outside of the shoulders and allows for excess water to drain from the surface into the ditches. |
|
|
|
How many types of ditches are there? And what are they? |
There are two. V-type ditch & flat bottomed ditch. |
|
|
|
How many parts are there to a ditch? What are they? |
There are three parts and they are an inslope, backslope, and bottom. |
|
|
|
V-type ditch |
A basic ditch that is usually used for unpaved roads or where the amount of water runoff water is minimal and space is limited. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Travelway |
Is the surface course on which the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Crown |
Is an established slope from the center line of a roadbed to the outside of the shoulders and allows for excess water to drain from the surface into the ditches. |
|
|
|
How many types of ditches are there? And what are they? |
There are two. V-type ditch & flat bottomed ditch. |
|
|
|
How many parts are there to a ditch? What are they? |
There are three parts and they are an inslope, backslope, and bottom. |
|
|
|
V-type ditch |
A basic ditch that is usually used for unpaved roads or where the amount of water runoff water is minimal and space is limited. |
|
|
|
Flat bottom ditch |
Also called trapezoid ditch, is difficult to construct. Usually for permanent roads with asphalt or concrete surfaces or where the amount of water runoff is great. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Travelway |
Is the surface course on which the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Crown |
Is an established slope from the center line of a roadbed to the outside of the shoulders and allows for excess water to drain from the surface into the ditches. |
|
|
|
How many types of ditches are there? And what are they? |
There are two. V-type ditch & flat bottomed ditch. |
|
|
|
How many parts are there to a ditch? What are they? |
There are three parts and they are an inslope, backslope, and bottom. |
|
|
|
V-type ditch |
A basic ditch that is usually used for unpaved roads or where the amount of water runoff water is minimal and space is limited. |
|
|
|
Flat bottom ditch |
Also called trapezoid ditch, is difficult to construct. Usually for permanent roads with asphalt or concrete surfaces or where the amount of water runoff is great. |
|
|
|
Inslope |
Or foreslope, extends from the outside of the shoulder to the bottom of the ditch. |
|
|
|
Surface course |
Completes the road. Usually made of asphalt, concrete, or crushed stone. It is the part of the road that the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Backslope |
Extends from the top of the cut at the existing grade to the bottom of the ditch. |
|
|
|
Shoulder |
Completes the road. This part of the road performs as a retainer on each side of the surface course and provides an emergency parking area. |
|
|
|
Roadbed |
Is the section that includes the surface course and both shoulders. |
|
|
|
Travelway |
Is the surface course on which the vehicle travels. |
|
|
|
Crown |
Is an established slope from the center line of a roadbed to the outside of the shoulders and allows for excess water to drain from the surface into the ditches. |
|
|
|
How many types of ditches are there? And what are they? |
There are two. V-type ditch & flat bottomed ditch. |
|
|
|
How many parts are there to a ditch? What are they? |
There are three parts and they are an inslope, backslope, and bottom. |
|
|
|
V-type ditch |
A basic ditch that is usually used for unpaved roads or where the amount of water runoff water is minimal and space is limited. |
|
|
|
Flat bottom ditch |
Also called trapezoid ditch, is difficult to construct. Usually for permanent roads with asphalt or concrete surfaces or where the amount of water runoff is great. |
|
|
|
Backslope |
Extends from the top of the cut at the existing grade to the bottom of the ditch. Is constructed to be steeper than the inslope, so that there will be minimal erosion. |
|
|
|
Roadway |
The area that covers the entire width of the road project, including the ditches. |
|
|
|
Earth work computations are the calculations of earth work volumes used to determine which of the following factors?
A) the final grade B) a balanced cut and fill C) a plan for the most economical movement of material D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
What term is used to describe a selected layer of well-compacted soil that is placed in compacted lifts on top of the subgrade? A) crown B) base course C) surface course D) backslope |
B) base course |
|
|
|
Earth work computations are the calculations of earth work volumes used to determine which of the following factors?
A) the final grade B) a balanced cut and fill C) a plan for the most economical movement of material D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
What term is used to describe a selected layer of well-compacted soil that is placed in compacted lifts on top of the subgrade? A) crown B) base course C) surface course D) backslope |
B) base course |
|
|
|
Grade work |
Is the plotting of irregularities of the ground (making cuts or fills) to a definite limit of grade and alignment. This is preformed by reading information placed on construction (grade) stakes. |
|
|
|
Earth work computations are the calculations of earth work volumes used to determine which of the following factors?
A) the final grade B) a balanced cut and fill C) a plan for the most economical movement of material D) all the above |
D) all the above |
|
|
|
What term is used to describe a selected layer of well-compacted soil that is placed in compacted lifts on top of the subgrade? A) crown B) base course C) surface course D) backslope |
B) base course |
|
|
|
Grade work |
Is the plotting of irregularities of the ground (making cuts or fills) to a definite limit of grade and alignment. This is preformed by reading information placed on construction (grade) stakes. |
|
|
|
Construction stakes |
Referred to as grade steaks, are the guides and reference markets for earth work operations to show cuts, fills, drainage, alignment, and boundaries of the construction area. |
|
|
|
Stake |
Any wooden lath, or hub. They are used primarily for well-defined surveyors' reference points, with red and blue tops used in finished grade work. |
|
|
|
Starting point |
Also called the starting station and is numbered starting at 0+00. The next station is 100 ft beyond the starting station and is numbered 1+00. |
|
|
|
Starting point |
Also called the starting station and is numbered starting at 0+00. The next station is 100 ft beyond the starting station and is numbered 1+00. |
|
|
|
All stations that end in 00 are called... |
Full stations |
|
|
|
Plus stations |
Stations located at a distance shorter than 100 ft from the preceding station. Ex: 3+25, 3+53, & 3+77. |
|
|
|
Plus stations |
Stations located at a distance shorter than 100 ft from the preceding station. Ex: 3+25, 3+53, & 3+77. |
|
|
|
Line stakes |
Mark the horizontal location of the earthwork to be completed & give the direction of the proposed construction. |
|
|
|
Plus stations |
Stations located at a distance shorter than 100 ft from the preceding station. Ex: 3+25, 3+53, & 3+77. |
|
|
|
Line stakes |
Mark the horizontal location of the earthwork to be completed & give the direction of the proposed construction. |
|
|
|
Rough alignment stakes |
Are placed far ahead of the clearing crew to make boundaries of the area to be cleared and grubbed. |
|
|
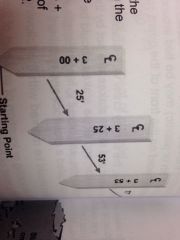
On the picture what does the symbol on the top of the stake mean? |
Center line |
|
|
|
Centerline stakes |
Stakes that are set along the centerline of a project. Most stakes are marked on both the front and back. |
|
|
|
The desires grade is always established at the _______ of the project. |
Centerline |
|
|
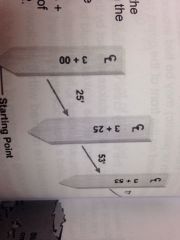
On the picture what does the symbol on the top of the stake mean? |
Center line |
|
|
|
Centerline stakes |
Stakes that are set along the centerline of a project. Most stakes are marked on both the front and back. |
|
|
|
The desires grade is always established at the _______ of the project. |
Centerline |
|
|
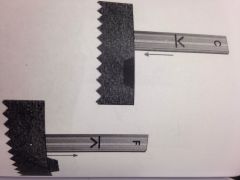
The top stake is indicating? The bottom stake is indicating? |
Top: cut Bottom: fill |
|
|
|
Shoulder stakes |
Stakes that are set on a line parallel (same direction and interval) with the centerline. They mark the outer edge of the shoulders and are set with the broad side facing the centerline of the road on the shoulder line. |

|
|

What does the symbol on the stake mean? |
Shoulder steak |
|
|
|
T/F: shoulder stakes carry different station numbers as the centerline stake. |
FALSE: the carry the same station # as the centerline stake to which they are set, but the station # is on the back of the stake. |
|
|
|
What is making a cut? |
Lowering the elevation of a grade. |
|
|
|
Raising the elevation of the ground is known as? |
A fill |
|

