![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Minerals |
a solid inorganic substance of natural occurrence
|

|
|
|
Ores |
A type of rock that has important minerals |

|
|
|
Fossil Fuels |
a natural gas formed from the geological past |
|
|
|
Physical Property |
Any property of an object or substance that is measurable |

|
|
|
Chemical Property |
characteristics of a substance that is observed during a reaction
|
|
|
|
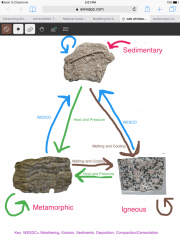
Rock Cycle |
The cycle of how rocks change and are created |
|
|
|
Sediments |
Rock that was weathered and eroded into crumbles |

|
|
|
Sedimentary Rock |
Rock formed from the deposition and compaction of sediments |

|
|
|
Metamorphic Rock |
Rock formed from extreme heat and pressure |
|
|
|
Extrusive Igneous Rock |
Rock made from lava on the outside of the volcano |

|
|
|
Intrusive Igneous Rock |
Rock made from lava on the inside of a volcano |

|
|
|
Mechanical Weathering |
Rock changed without any change in the chemical nature |

|
|
|
Chemical Weathering |
The breaking down of rock by chemical reactions |

|
|
|
Erosion |
The breaking down of any type of rock |

|
|
|
Deposition |
The natural taking away of sediments from place to place |

|
|
|
Density |
The degree of compactness of a substance
|
|
|
|
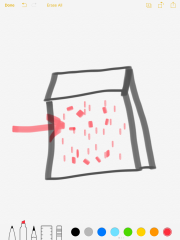
Continental Crust |
The outer layer of the Earth's surface |
|
|
|
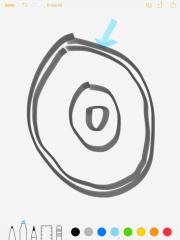
Oceanic Crust |
Thin part of the earth's crust that underlies the ocean
|

|
|
|
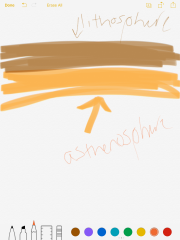
Lithosphere |
Solid part of the earths surface |

|
|
|
Asthenosphere |
Below the lithosphere; consists of tons of deformed rock |
|
|
|
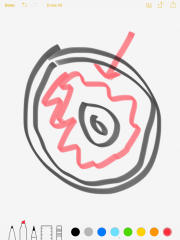
Mantle |
region of the interior of the Earth between the core
|
|
|
|
Outer Core |
Layer that is composed of mostly iron and nickel
|
|
|
|
Inner core |
a solid sphere in the middle of the fluid core
|
|
|
|
Tension |
the state of being stretched tight
|

|
|
|
Compression |
the reduction in volume and increase of pressure
|

|
|
|
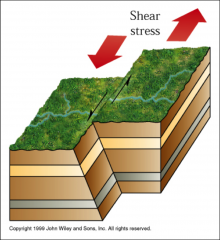
Shearing |
a distinct motion of two rock surfaces against each other
|
|
|
|
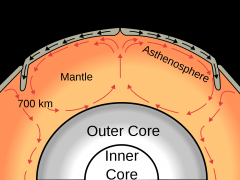
Convection Currents |
move a gas or fluid from one place to another
|
|
|
|
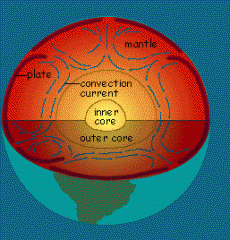
Theory of Plate Tectonics |
Crust is divided into several plates that glide over mantle |
|
|
|
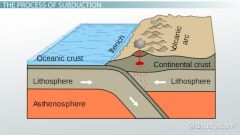
Subduction |
one plate moves under another and is forced down
|
|
|
|
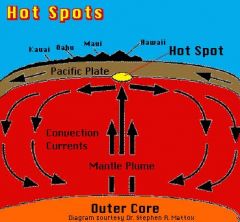
Hot Spots |
an area in the mantle from which heat rises
|
|
|
|
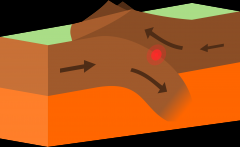
Convergent Plate Boundary |
A region where two or more plates collide |
|
|
|
Divergent Plate Boundary |
A region where two plates separate |

|
|
|
Transform Plate Boundary |
A region where two plates slide also eachother |
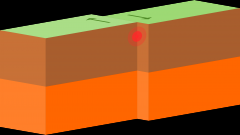
|
|
|
Mid-Ocean Ridges |
an underwater mountain system formed by plate tectonics
|

|
|
|
Pangaea |
The theory that all continents were once connected |
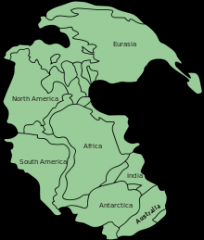
|
|
|
Island Arc's |
a curved chain of volcanic islands
|

|
|
|
Faults |
a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock
|
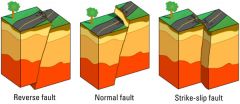
|
|
|
Trenches |
a long, narrow ditch
|

|
|
|
Folded Mountains |
two or more of Earth's tectonic plates are pushed together
|

|
|
|
Pacific Ring of Fire |
An area in the ocean where volcanoes and earthquakes occur |

|
|
|
Seismic Activity |
types, frequency and size of earthquakes that happen over time
|
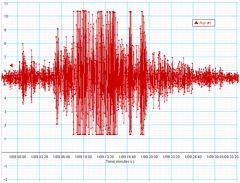
|
|
|
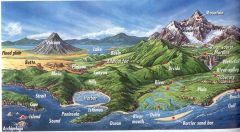
Landforms |
a natural feature of the earth's surface
|
|
|
|
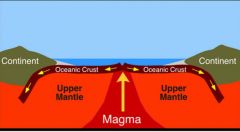
Sea-Floor Spreading |
the formation of new areas of oceanic crust
|
|
|
|
San Andreas Fault |
a continental transform fault that extends 800 miles through California
|

|
|
|
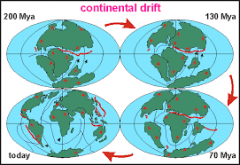
Continental Drift |
the gradual movement of the continents across the earth's surface
|
|

