![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

Deposition
|
eroded materials being dropped in a new location.
|
|
|

Erosion
|
soil and sediment are moved from place to place.
|
|
|

Weathering
|
breakdown of rock into smaller pieces by mechanical (physical) or chemical means.
|
|
|
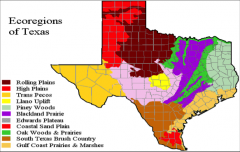
Ecoregion
|
an ecosystem that covers a large area
|
|
|

Sediment
|
tiny grains of broken down rock and minerals
|
|
|
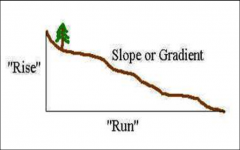
Gradient
|
measure of change in elevation over a certain distance—also known as slope.
|
|
|

Contour plowing
|
plowing and planting along the curves of the land to reduce soil erosion.
|
|
|
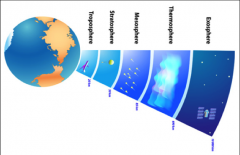
Atmosphere
|
A mixture of gasses that surround a planet, moon, or other space object.
|
|
|
Gravity
|
A force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses. Reason why planets revolve around the Sun.
|
|
|
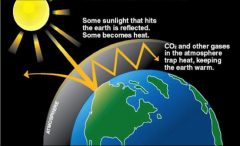
Greenhouse effect
|
A phenomenon in which the atmosphere of a planet traps radiation emitted by its sun, caused by gases such as CO2, H2O vapor, and CH4 that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but retain heat radiated back from the planet’s surface.
|
|
|
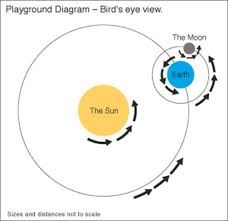
Revolution (Orbit)
|
The path that a body follows as it travels around another body in space.
|
|
|
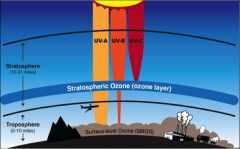
Ozone
|
gas molecule that is made up of three oxygen atoms (O3). The ozone layer in the atmosphere blocks most ultraviolet radiation from reaching the Earth’s surface.
|
|
|
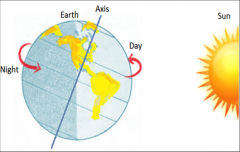
Rotation
|
circular movement around a body’s central axis, cause day and night
|
|
|
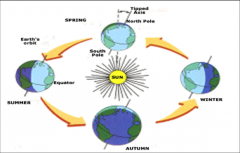
Seasons
|
caused by the earth tilted axis and its revolution around the sun
|
|
|

Solar system
|
a system of planets orbiting a single star due to its gravity. Our solar system’s star is referred to as the Sun.
|
|
|
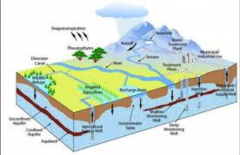
Ground water
|
the water that is beneath earth’s surface that’s is held in the soil and in porous rock (ex
|
Aquifer).
|
|

Surface water
|
all bodies of water collecting above the ground (freshwater, saltwater, brackish water, ice, or snow), such as river, lake, wetland, estuary, or ocean.
|
|
|
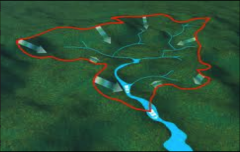
Watershed
|
The area of land that is drained, by a river system, into the same place.
|
|
|
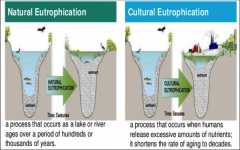
Eutrophication
|
an increases in the amount of nutrients, such as nitrates, in an aquatic ecosystem.
|
|
|

Reservoir
|
an artificial body of water that usually forms behind a dam.
|
|
|
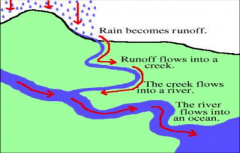
Runoff
|
water that flows over land and into streams and rivers.
|
|
|
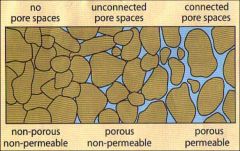
Permeable (porous)
|
having small spaces that liquid or air is able to pass through.
|
|
|
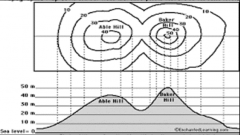
Topography
|
study of the size, shape, and elevation of Earth’s land features. Contour lines connect areas of equal elevation.
|
|
|

Pollution
|
contaminants (chemical materials or energy) in an environment that cause it to be unsafe. Point-source can be traced back to a single place whereas non-point source has multiple points of pollution
|
|

