![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
q: what type of stress pushes in two opposite directions |
a: shearing |
|
|
q:what is a force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume |
a:stress |
|
|
q:what is the lower part of a normal fault called |
a:footwall |
|
|
q:what type of stress produces reverse faults |
a: compression |
|
|
q: what is a large area of flat land that is elevated high above sea level |
a:plateau |
|
|
q:what is the point in earth where rock breaks under stress and triggers an earthquakes |
a:focus |
|
|
q:what type of seismic waves at the surface first and move by compressing and expanding the ground |
a:p waves |
|
|
q:what are s waves also known as |
a:secondary waves |
|
|
q:compared to p waves and s waves how do surface waves move |
a:slower |
|
|
q:in what direction do seismic waves carry energy |
a:away from the focus |
|
|
q:what type of waves can move through both liquid and soild |
a:p waves |
|
|
q:what does a seismograph |
a:the ground movement caused by semsic waves |
|
|
q:what do scientist measure the difference between to tell how far an earthquakes epicenter is from the seisograh |
arrive time of p waves and s waves |
|
|
q:what is the minimum number of seismograph required to determine the exact location of an seismograph |
a:3 |
|
|
q: in what order do the 3 types of waves arrive at a seismograph? |
a:P waves, S waves, surface waves |
|
|
q:What is lava called before it reaches Earth’s surface? |
a:magma |
|
|
q:What do volcanoes along converging oceanic plate boundaries form? |
a:island arc |
|
|
q:What is the long tube called that connects a magma chamber to Earth’s surface? |
a:pipe |
|
|
q:What provides the force that causes magma to erupt to the surface? |
a:dissolved gases trapped in the magma |
|
|
q:What will happen if a volcano’s magma is high in silica? |
a:erupt explosively |
|
|
q:What triggers the small earthquakes around a volcano right before it erupts? |
a:upward movement of magma |
|
|
q:What are tall, cone-shaped mountains called where layers of lava alternate with layers of ash? |
a:composite volcanoes |
|
|
q:What is formed when many layers of thin, runny lava build up a high, level area? |
a:lava plateau |
|
|
q:What is the huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain called? |
a:caldera |
|
|
q:What is formed when ash, cinders, and bombs build up in a steep pile around a volcano’s vent? |
a:cinder cone volcano |
|
|
q:What landform will eventually form when magma hardens in a volcano’s pipe? |
a:volcanic neck |
|
|
q:What is formed when groundwater heated by magma rises to the surface and collects in a pool? |
a:hot spring |
|
|
q:In volcanic areas, what is groundwater heated by magma a source of? |
a:geothermal energy |
|
|
q:What is the stress force that pulls on the crust where two plates are moving apart? |
a: tension |
|
|
q:What stress force causes a mass of rock to move in opposite directions? |
a:shearing |
|
|
q: What type of fault is formed when compression causes the hanging wall to move over the foot wall? |
a:reverse fault |
|
|
q: What is the block of rock that lies above a fault called? |
a:hanging wall |
|
|
q:What type of fault does shearing create? |
a:strike-slip |
|
|
q:What are the vibrations that move through the ground carrying the energy released during an earthquake? |
a:seismic waves |
|
|
q: When scientists draw circles on a map around seismograph stations, what are they looking for? |
a:epicenter |
|
|
q:What type of stress pulls on the crust and stretches rock so it is thinner in the middle? |
a:compression |
|
|
q: What is the major volcanic belt known as that circles the Pacific Ocean? |
a: Ring of Fire |
|
|
q:What is molten material called when it leaves a volcano’s vent? |
a:lava |
|
|
q: What is the bowl-shaped area around a volcano’s central vent called? |
crater |
|
|
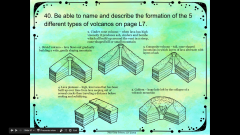
40. Be able to name and describe the formation of the 5 different types of volcanos on page L7. |
|

