![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Three layers of the tympanic membrane?
|
1) Pars flaccida- upper portion, little support
2) Pars tensa- lower portion, taut 3) Umbo- center, attached to tip of malleus |
|
|
Auditory ossicles
|
Malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), stapes (stirrup)
|
|
|
Vestibule and Semicircular canal
|
maintain equilibrium
|
|
|
Semicircular canals contain
|
cristae- respond to body movement, control balance
|
|
|
Cochlea
|
organ of hearing
|
|
|
For position and symmetry of auricle
|
Tip of ear should line up with corner of eye.
|
|
|
Low set ears can =
|
congenital disorders
|
|
|
Pain while pulling the auricle back is a sign of?
|
otitis externa
|
|
|
Inspect opening of ear for?
|
* Discharge- color, consistency
* Redness * Odor * Nodules, masses, cysts, pimples * Foreign bodies |
|
|
The TM should look?
|
pearl gray, transparent
|
|
|
Decreased motion of the TM is a sign of?
|
* increased pressure in the inner ear
*as with otitis media, serous otitis, eustachian tube dysfunction |
|
|
Increased TM mobility is a sign of?
|
perforation
|
|
|
Blockage of EAC by cerumen - S/S
|
* decreases hearing
* causes discomfort * can affect equilibrium * pressure in ear canal |
|
|
Otitis Externa: “Swimmers Ear”(OM) - S/S
|
* Ear pain (especially with auricle tug)
* redness & inflammation of EAC * flaking or maceration of tissue * discharge from EAC |
|
|
Types of Acute Otitis Media: (AOM)
|
1) OM
2) Serous OM 3) Bullous Myringitis |
|
|
Acute Otitis Media - S/S
|
* Ear pain (not affected by auricle tug)
* sensation of fullness in the ear * decreased hearing * URI symptoms, fever * irritability in infants |
|
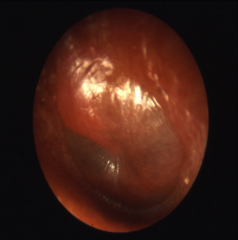
|
AOM
|
|
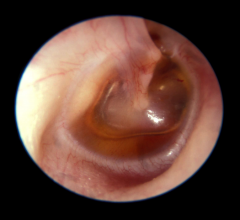
|
Serous OM
|
|
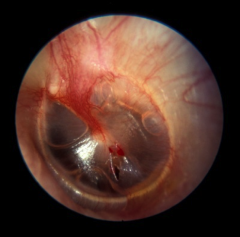
|
Serous OM
|
|

|
Bullous Myringitis
|
|

|
Bullous Myringitis
|
|
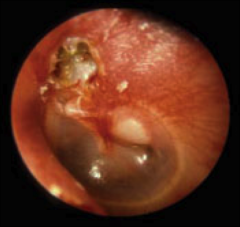
|
Cholesteotoma - A skin cyst of the middle ear that grows destructively and affects hearing
|
|
|
Describe the Auditory acuity-whisper test
|
1) Stand 2 ft behind the patient, have pt cover tragus of one ear with his finger
2) Whisper a number with 2-3 syllables (68, 100, 99 etc) 3) Repeat other ear |
|
|
Weber test
|
* Strike against your hand and place on top of patients head
|
|
|
Webber test results
|
* If lateralizes to impaired ear = conductive hearing loss
* If lateralized to good ear = sensorineural hearing loss |
|
|
Describe a normal weber’s test
|
hearing equal in both ears
|
|
|
Rinne test
|
1) Strike tuning fork and place on mastoid process
2) When patient tells you tone stops, move to front of ear * Normal is air 2x bone |
|
|
Rinne test results
|
* If in hearing loss ear
bone > air = conductive hearing loss * If in hearing loss ear air > bone = sensorineural hearing loss |
|
|
Most common area for epistaxis?
|
anterior and inferior septum in Kiesselbach's plexus
|
|
|
Angioedema - definition
|
rapidly developing, tense swelling of the lips, tongue and oral mucosa, usually allergic in origin
|
|
|
Angular cheilitis - definition
|
fissures at the corners of the mouth.
Causes: nutritional deficiency, over closure of mouth, infection |
|
|
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia - definition
|
* petechial red spots on the lips and oral mucosa.
* Areas may bleed with trauma/irritation. |
|
|
Protrusion of the tongue tests which CN?
|
* cranial nerve XII (hypoglossal)
* Tongue points toward muscular deficit. |
|
|
Torus palatinus - definition
|
midline bony growth on hard palate
|
|
|
Leukoplakia - definition
|
“white patch” thickened white patch on the oral mucosa or tongue, results from local irritant.
|
|
|
Aphthous Ulcer - definition
|
* (canker sore) a painful, round, ulcer.
* White ulcer on a red base. * Can occur on gums, tongue, and oral mucosa |
|
|
Koplick spots - definition
|
* small white specks against a red background, “grains of salt”.
* An early sign of measles |
|
|
Atrophic Glossitis - definition
|
* smooth and sore tongue, lacks papillae.
Causes: ribofalvin, niacin, folic acid, B12, pyridoxine, or iron deficiency, or recent chemotherapy. |
|
|
Peritonsillar Abscess - definition
|
* Complication of tonsillitis which results in collection of pus near the tonsil (abscess).
* Red, edematous tonsils and pharynx, exudates, mass like uvula deviation. |
|
|
Name the ten lymph nodes for the midterm
|
1) Preauricular
2) Posterior auricular 3) Occipital 4) Tonsillar 5) Submandibular 6) Submental 7) Superficial cervical 8) Posterior cervical 9) Deep cervical chain 10) Supraclavicular |
|
|
Which lymph node is a concern is swollen?
|
Supraclavicalar enlargement suggests metastasis
|
|
|
Diffuse lymphadenopathy suspect?
|
HIV/AIDs or Lymphoma
|
|
|
Posterior Cervical and Occipital adenopathy is seen with?
|
Mononucleosis
|
|
|
Anterior Cervical adenopathy is seen in?
|
URI and strep throat
|
|
|
Goiter - PE findings?
|
* thyroid enlargement
* soft enlargement, non-tender |
|
|
Thyroiditis - PE findings
|
tender enlargement of gland
|
|
|
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis - PE findings
|
firm enlargement
|
|
|
Malignant thyroid masses: PE findings
|
* firm, asymmetry of mass
* ill defined margins * non-tender |
|
|
Thyroglossal duct cyst - definition
|
* fibrous cyst that are due to persistent thyroglossal duct formed during embryonic development of the thyroid gland.
* Midline mass, non-tender |

