![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Note
|
Under both U.S. GAAP & IFRS, all public entities (or entities that have made a filing for a public offering) are required to present EPS on the face of the I/S.
|
|
|
Note
|
An entity's capital structure determines the manner in which EPS is disclosed.
|
|
|
What are the types of Capital structure forms in an entity?
|
1- Basic
2- Complex |
|
|
When does an entity is having a Simple capital structure?
|
If it has ONLY CS outstanding
|
|
|
What are the EPS presentation requirements in case of Simple capital structure?
|
The entity presents basic per share amounts on the face of the I/S for:
1- Income from continuing operations 2- NI |
|
|
What are the EPS presentation requirements in case of Complex capital structure?
|
The entity presents basic & diluted per share amounts on the face of the I/S (or statement of income & comprehensive income if the entity is using the one-statement approach) with equal prominence for:
1- Income from continuing operations 2- NI |
|
|
Note
|
In case of Complex capital structure, If the entity reports a discontinued operation , or an extraordinary item (U.S. GAAP only), the entity presents the basic & diluted (if applicable) per share amounts for those items either on the face of the I/S or in the notes to the FSs.
|
|
|
Note
|
An entity that issues only CS (or no other securities that can become CS, such as nonconvertible PS) is said to have a simple capital structure.
|
|
|
Note
|
The number of CSs outstanding (the denominator) used in the EPS calculation is arrived at by the weighted-average method.
|
|
|
Note
|

|
|
|
How did Income available to CS holders is determined?
|
By deducting from the line item income from continuing operations & NI the following:
1- Dividends declared in the period on non-cumulative PS (regardless of whether they have been paid) 2- Dividends accumulated in the period on cumulative PS (regardless of whether they have been declared). |
|
|
Note
|
If there is a loss from continuing operations (or a net loss), the amount of the loss should be increased by the PS holders' dividends or claims to determine income available to the CS holders.
|
|
|
What is meant by "Weighted average number of CS outstanding" (WACSO)?
|
It is the average of shares outstanding & assumed to be outstanding for EPS calculations.
|
|
|
Note
|
Shares sold or reacquired during the period (including T/S) should be weighted for the portion of the period they were outstanding.
|
|
|
How could WACSO be calculated?
|

|
|
|
Note
|
Stock dividends & stock splits (to the same class of shareholders in the same company) must be treated as though they occurred at the BEGINNING of the period.
|
|
|
Note
|
The shares outstanding before the stock dividend or stock split must be restated for the portion of the period before the stock dividend/split.
|
|
|
Note
|
If prior periods are presented, the effects of stock dividends & stock splits must be retroactively adjusted for those periods.
|
|
|
Note
|
If a stock dividend or stock split occurs after the end of the period but before the FSs are issued, those shares should enter into the shares outstanding for the EPS calculation for all periods presented.
|
|
|
Note
|
Reverse stock splits would retroactively reduce shares outstanding for all periods presented.
|
|
|
Note
|
In case of stock issued in a business combination, If the acquisition method is used , the weighted-average is measured from the date of the combination.
|
|
|
What is the Complex capital structure of an entity?
|
An entity has a complex capital structure when it has securities that can potentially be converted to CS & would therefore dilute (reduce) EPS (of CS).
|
|
|
Note
|
In case of the complex capital structure, Both basic & diluted EPS must be presented.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of calculating diluted EPS?
|
To measure the performance of an entity over the reporting period while giving effect to all potentially dilutive CSs outstanding during the period.
|
|
|
What are the potentially dilutive securities that affect the diluted EPS?
|
1- Convertible securities (e.g., convertible PS, convertible bonds, etc.)
2- Warrants & other options 3- Contracts that may be settled in cash or stock 4- Contingent shares. |
|
|
How to calculate the diluted EPS?
|

|
|
|
Note
|
The dilutive effect of options & warrants & their equivalents is applied using the T/S method.
|
|
|
What does that T/S method assumes?
|
The T/S method assumes that the proceeds from the exercise of stock options, warrants, & their equivalents will be used by the company to repurchase T/Ss at the prevailing market price, resulting in an INCREMENTAL increase in shares outstanding, but not the full amount of shares that are issued on exercise of the CS equivalents.
|
|
|
What are the equivalents of options & warrants?
|
1- Non-vested stock granted to employees,
2- Stock purchase contracts, 3- Partially paid stock subscriptions. |
|
|
Note
|
Any canceled or issued options or warrants during the period shall be included in the denominator of diluted EPS for the period they were outstanding.
|
|
|
Note
|
Options & similar instruments are ONLY dilutive when the average market price of the underlying CS EXCEEDS the exercise price of the options or warrants because it is unlikely they would be exercised if the exercise price were higher than the market price.
|
|
|
Note
|
If the exercise price of the options & similar instruments is higher than the market price, then this options are considered Antidilutive.
|
|
|
Note
|
Previously reported EPS should not be adjusted retroactively in the case of options or similar instruments to reflect subsequent changes in market prices of the common stock.
|
|
|
Note
|
If the average market price of the stock is greater than the exercise price (called "in the money"), assume that the warrants or other options are exercised at the beginning of the period (or at the time of issue, if later).
|
|
|
Note
|
Under the T/S method, The difference between the number of shares assumed issued to satisfy the options or warrants & the number of shares assumed to be purchased with the proceeds should be included in the number of shares (denominator) for diluted EPS.
|
|
|
How to compute additional shares for options & similar instruments?
|
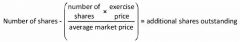
|
|
|
Note
|
The "if-converted" method should be used to determine the dilutive effects of the convertible securities.
|
|
|
Note
|
The "if-converted" method assumes that the securities were converted to common stock at the BEGINNING of the period (or at the time of issue, if later).
|
|
|
Note
|
If the convertible bonds were issued during the period, Add to the numerator of the diluted EPS calculation formula (i.e., income available to CS holders) the interest expense, net of tax, due to the assumed conversion of bonds to CS.
|
|
|
Note
|
If the convertible bonds were issued during the period, Add to the denominator of the diluted EPS calculation formula (i.e., weighted-average number of shares outstanding) the number of CSs associated with the assumed conversion.
|
|
|
Note
|
Use the results of each assumed conversion only if it results in dilution (i.e., reduces EPS).
|
|
|
Note
|
The tests for dilutive or antidilutive effects should be based on income from continuing operations, if available (otherwise use income before extraordinary items).
|
|
|
In case of convertible PS what are the procedures required to calculate the diluted EPS?
|
1- Adjust the numerator (as PS dividends do not affect net income)
2- Add to the denominator the number of shares associated with the assumed conversion. 3- Antidilution rules apply to convertible PS. |
|
|
Note
|
If a contract will be settled in CS, the resulting shares should be included in diluted EPS if the effect is more dilutive.
|
|
|
Note
|
Under IFRS, contracts that may be settled in cash or In stock are always presumed to be settled in CSs & included in diluted EPS.
|
|
|
What is meant by "Contingent shares"?
|
They are issuable shares do not require cash consideration & depend on some future event or on certain conditions being met.
|
|
|
Note
|
Contingent shares (that are dilutive) are also included in the calculation of basic EPS if all conditions for issuance are met.
|
|
|
Note
|
If the necessary conditions have been satisfied by the end of the period, contingent shares are included in basic EPS as of the beginning of the period in which the conditions were satisfied.
|
|
|
Note
|
If the necessary conditions have not been satisfied by the end of the period, contingent shares are included to diluted EPS denominator as of the beginning of the period (or as of the date of the contingent stock agreement, if later).
|
|
|
Note
|
If the contingency is due to attainment of future earnings &/or future prices of the shares, both earnings to date & current market price, are used.
|
|
|
Note
|
Under IFRS, contingently issuable ordinary shares are treated as outstanding & included in the calculation of diluted EPS only if the conditions are satisfied.
|
|
|
Note
|
Cash flow per share should not be reported.
|
|
|
What are the EPS disclosure requirements?
|
1- A reconciliation of the numerators & the denominators of the basic & diluted per-share computations for income from continuing operations.
2- The effect that has been given to preferred dividends in arriving at income available to CS holders in computing basic EPS. 3- Securities that could potentially dilute basic EPS in the future that were not included in the computation of diluted EPS because the effect was antidilutive for the period(s) presented. 4- Description of any transaction that occurred after the period end that would have materially affected the number of actual &/or potential CSs outstanding. |
|
|
Note
|
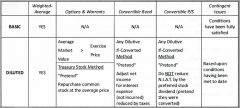
|

