![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What drugs are used in the treatment of gout? |
Colchicine Indomethacin Allopurinol Probenicid Febuxostat Pegloticase |
|
|
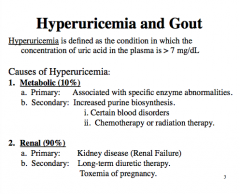
Define hyperuricemia. What does the plasma level have to be above?
What are two general causes of hyperuricemia? |
|
|
|
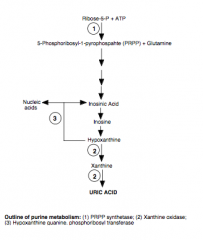
Draw the outline of purine metabolism. |
|
|
|
What are the therapeutic aims in the treatment of gout?
1. Terminate an __________ 2. Prevent recurrence of __________ ______ arthritis. 3. Reverse of prevent complications of ______________. 4. ________ other factors associated with the disease. 5. Prevent formation of ________ stones. |

|
|
|
What is cochicine effective against? Can it be used prophylactically? What is the mechanism of action?
What weird fever can it also be used in?
What are two major side effects (acute and chronic)? |

|
|
|
What type of drug is indomethacine? What does it inhibit? How is it like tylenol?
What is it therapeutically used for?
Describe the dose.
Any adverse effects? (CNS, blood)? |

|
|
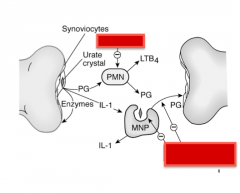
Identify where indomethacin and colchicine work. |
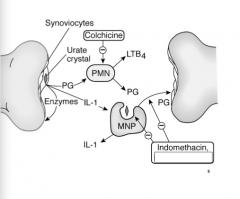
|
|
|
What is a drug that inhibits ureate synthesis? What is it a competitive inhibitor of? What is it metabolized to which is a non-competitive inhibitor of XO? |
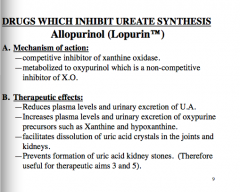
|
|
|
When is allopurinol used?
What are some adverse effects (think incidence, allergy, liver, interactions with a particular substance, any drug contraindications)? |
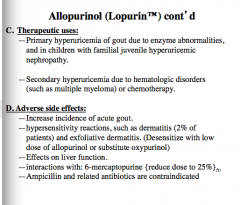
|
|
|
What enzyme does Febuxostat inhibit? What is the mechanism of action? What drug is it structurally related to? What does it lower by decreasing urate levels? |
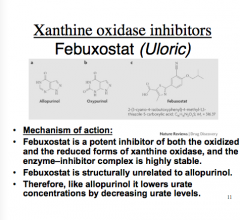
|
|
|
Is febuxostat more or less potent than allopurinol?
What is its main indication? If it works like allopurinol the only reason you would use it is if...
What is a limitation for the use of allopurinol?
What is the major side effect or febuxostat? |
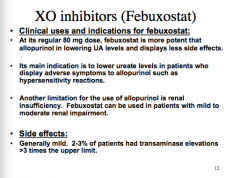
|
|
|
What are agents that increase the urinary excretion of uric acid? What are they called? |
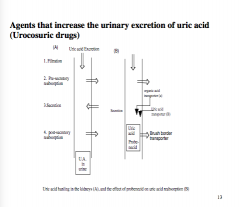
|
|
|
Where is uric acid filtered? Where is it reabsorbed?
Is it partially reabsorbed after secretion? |

|
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of probenecid? What does it inhibit the transport of? Where does it interfere with UA reabsorption?
What are the three clinical effects (you should always drink what?)
What is the major adverse effect of probenecid? |
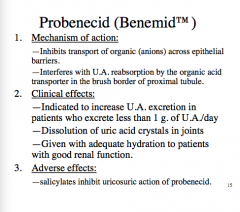
|
|
|
Where does probenecid act in the pathway? is urate oxidase present in most mammals? What about humans?
What is pegloticase? |
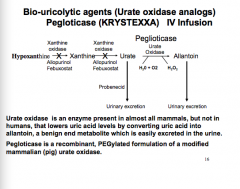
|
|
|
How does pegloticase work? What does it lower? What does it increase the serum levels of?
What are the clinical uses of pegloticase? |

|
|
|
What are the side effects of pegloticase? What does it cause a rapid drop in? What should pegloticase patients prophylactically receive?
Why is pegloticase pegylated?
What does the immune system develop against pegloticase? |
|
|
|
Is there a specific antidote agent for colchicine adverse reactions? |
No! |
|
|
How is colchicine metabolized? Where it is excreted?
What are the dose-related effects of colchicine?
What is chronic treatment associated with? |

|
|
|
Why is impaired renal function and hepatic function important with colchicine?
What has been reported in patients taking colchicine, especially in overdose situations?
What blood levels should you monitor in these patients? |

|
|
|
True or false.
The majority of hyperuricemia cases is the result of abnormal metabolism? |
False 90% due to EXCRETION 10% due to metabolism |
|
|
Which gout drug is most suitable to reduce urinary uric acid levels in patients with diminished renal function? |
Febuxostat |
|
|
Which drug inhibits the function of polymorphonuclear leukocytes? |
Colchicine (microtubule inhibitor => stops migration of inflammatory cells into joint) |
|
|
What is the most likely acute adverse effect for a physician declining to instigate the use of oral colchicine in her patient?
What if the drug were given chronically? |
Acute = GI distress (give until you get diarrhea)
Chronic = blood dyscrasias |
|
|
Which of the following drugs is the only one used in the treatment of gout that relives pain? |
Indomethacin |
|
|
Which of the following drugs can cause proximal weakness and elevated CPK? Think mechanism... |
Colchicine |
|
|
Probenecid works in the proximal convoluted tubule of the kidney to do what? |
Blocks post-secretory reabsorption |
|
|
The effects of probenecid would most likely be diminished in a patient who is also taking... |
A kidney drug
Hydrochlorothiazide (salicylates also) |
|
|
How does probenicid help with penicillin (increase efficacy)? |
Decreases renal elimination of penicillin, thereby increasing serum drug levels |

