![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
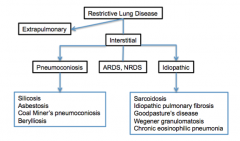
What are the two types of lung disease? What are the three types of interstitial lung disease? What are some examples of pneumoconiosis? What are some examples of idiopathic diseases? |
|
|
|
Illness: Silicosis
Describe inhaled substance and features:
|
Silica dust from quartz, sand, and other minerals. Seen in sand blasters, rock miners, quarry workers and stone cutters. |
|
|
Illness: Coal worker's pneumoconiosi
Describe inhaled substance and features: |
Coal dust (both carbon and silica) Anthracosis --> mild symptomatic build up of carbon commonly seen in city dwellers and smokers |
|
|
Illness: Asbestosis
Describe inhaled substance and features: |
Asbestos (amphibole fibers) seen in insulation, shipyard and construction workers, and mechanics |
|
|
Illness: Berylliosis
Describe inhaled substance and features: |
Beryllium dust seen in workers of aerospace, nuclear weapon, and electronic industries. |
|
|
Is there a curative treatment for deposited material? What should patients do? What are they at increased risk for? |

|
|
|
What are some causative agents of ARDS? Excessive doses of what? Idiosyncratic reactions of what? Does alcohol abuse INCREASE RISK or CAUSE ARDS? What is the treatment for ARDS? |

Drug treatment but none have really shown to be beneficial. |
|
|
Drug for ARDS: B-2 agonist (albuterol IV)
Give mechanism. |
Preferential vasodilation of pulmonary vessels that perfuse alveoli |
|
|
Drug for ARDS: Inhaled nitric oxide
Give mechanism. |
Preferential vasodilation of pulmonary vessels that perfuse alveoli |
|
|
Drug for ARDS: Inhaled prostacyclin (PGI2)
Give mechanism. |
Vasodilator |
|
|
Drug for ARDS: Corticosteroids
Give mechanism. |
Anti-inflammatory action |
|
|
Drug for ARDS: Dietary oil supplementation
Give mechanism. |
Anti-inflammatory action (modulation of arachidonic acid metabolism). |
|
|
What is the most common cause of respiratory failure in newborns and most common cause of death in premature infants? What is the cause and three things that it leads to? |

|
|
|
What is the treatment of NRDS? Who gets it? What does it do? |

|
|
|
Additional treatment? What are the products given? What are they composed of? Which one is the primary active component that lowers alveolar surface tension? |

|
|
|
What is the hallmark of sarcoidosis? Treatment? What does it depend on? |

|
|
|
Mechanism of action of the glucocorticoids? What do they inhibit production of? Increase production of? What do they do to macrophages and dendritic cells? |
Bind to glucocorticoid receptors and modulate transcriptional regulation in the nucleus. Inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines = IL-1B and TNF Promote anti-inflammatory cytokines = IL-10 by macrophages and dendritic cells. Apoptosis of macrophages and dendritic cells => inhibition of immune response. |
|
|
What axis is suppressed with glucocorticoid use (adverse effects of this)? |
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA)
Osteoporosis Pancreatitis Diabetes Cataracts/glaucoma Psychosis Oral candidiasis and other opportunistic infections w/ immunusuppression Weight gain, skin atrophy |
|
|
What is the mechanism of methotrexate? What type of immunsuppression does it lead to? |
DHFR inhibition and an antineoplastic action Leads to increase in adenosine-mediated immunosuppression. |
|
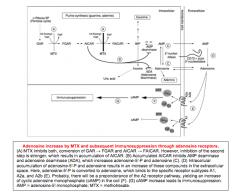
Draw out mechanism. |
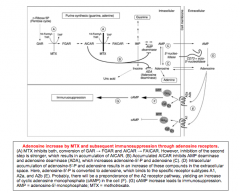
|
|
|
What is methotrexate not considered "front-line therapy" for anti-inflammatory effects? What are some issues? |
Side effects: Severe dermatological reactions Birth defects Malignant lymphoma Increased infection risk Acute/chronic interstitial pneumonitis Pulmonary fibrosis |
|
|
Is IPF a chronic inflammatory disease? Do anti-inflammatory medications work? |

|
|
|
What is the pathway of IPF? |
Normal situation: Short-lived inflammatory process --> fibrolysis --> apoptosis of repair cells --> return to normal
IPF: Altered mesenchymal cell phenotype and blockade of apoptosis --> altered stromal cell population and blockade of apoptosis --> TGF-B and PDGR --> interact w/ deposited matrix --> patchy areas of remodeling of BV walls --> PAH |
|
|
Is there clinical benefit to using drugs in IPF? |
None, some worsen No benefit from using same drugs as in other forms of PAH. |
|
|
Define Goodpasture's syndrome. How is it treated? |

|
|
|
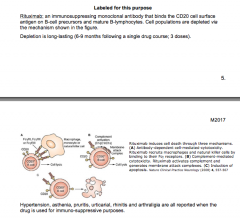
Define Wegener's Granulomatosis. What drugs are used to treat it? |

Rituximab, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, corticosteroids |
|
|
MOA of rituximab? LABELED for WEGENER'S |
|
|
|
Adverse effects of rituximab? |
Hypertension Asthenia Pruritis Urticarial Rhinitis Arthalgia
All when drug used for immuno-suppressive purposes |
|
|
MOA of Azathioprine? OFF-LABEL USE for Wegener's Adverse effects? |

|
|
|
MOA of cyclophosphamide? OFF-LABEL use for Wegener's Adverse effects? |

|
|
|
Draw the three pathways of pulmonary hypertension: |
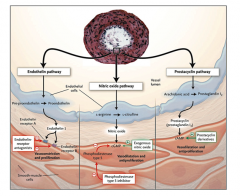
|
|

|

|
|
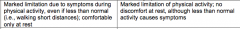
Identify the class of pulmonary hypertension: |
III |
|

Identify class of PAH: |
II |
|
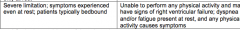
Identify class of PAH: |
IV |
|

Identify class of PAH: |
I |
|
|
What are the general effects of the prostanoids? |
Induce pulmonary artery vasodilation, retard smooth muscle growth, and disrupt platelet aggregation. |
|
|
Of the three drugs, which has the longest half life, shortest half life, which require IV infusion, which are inhaled, which is continuous SC or IV and more stable in solution?
Epoprostenol, Iloprost, Treprostinil |
Longest HL = treprostinil Shortest HL = Epoprostenol IV infusion = Epoprostenol Inhaled = Iloprost Continuous SC or IV/ more stable in solution = Treprostinil |
|
|
Adverse effects for Epoprostenol? |

|
|
|
Adverse effects of Iloprost? Why should you monitor? |

|
|
|
Adverse effects of Treprostinil? Which drug interactions possible? Decreased clearance with what drug? Increased clearance with what drug? |

|
|

|

|
|
|
What is the general mechanism of action of endothelin-1 receptor antagonist? Where is ETA located? Where is ETB located? What is the advantage over the prostacyclins? |

|
|
|
Disadvantages of endothelia-1 receptor antagonists (think dead babies and toxicities)? |

|
|
|
Which drug has a longer half-life? Which is less likely to cause elevated LFTs but still need to monitor? Which is likely to cause anemia, nasopharyngitis, and headaches? Which are metabolized by CYP2C9 and CYP3A4? Which are also metabolized by OATP and P-gp substrate? Which has drug-drug interactions? Which has potential but none recorded? Bosentan or Ambrisentan |
Bosentan Ambrisentan Bosentan Both Ambrisentan Bosentan Ambrisentan |
|
|
What is the mechanism of action of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors? What patients SHOULD NOT use them? Name the two drugs? |

Sildenafil and Tadalafil |
|
|
Which drug has the longer half life? Which drug has headache as the most common effect? Which drug has nosebleed? Backpain, dyspepsia? Flushing, insomnia, dyspepsia? Which one rarely has dizziness with sudden hearing loss? Which one has change in color vision (NAION)? Which one is a CYP3A4 substate with drug interactions with 3A substates/inducers/inhibitors?
Tadalafil, Sildenafil |
Tadalafil Both Sildenafil Tadalafil Sildenafil Silddenafil Tadalafil Both |
|
|
Mechanism of action of the calcium channel blockers:
Do all patients respond to these drugs? What do some fatally develop? |

|
|

Which patients are prescribed CCBs? |
Patients who respond positive to a vasodilator challenge. |
|
|
Diltiazem immediate release Nifedipine extended release Amlodipin
Which drug has longest half life, shortest half life? Which drugs is CYP3A4 substrate? Which drug has flushing, edema, hypotension, and heartburn? Bradycardia, hypotension, headache, and edema? Hypotension, fatigue, and edema? |
Amlodipine Nifedipine extended release All three
Nifedipine Diltiazem Amlodipine |
|
|
Why is verapamil avoided in PAH? |

|
|
|
What is the goal of calcium blocker therapy? What if not achieved? |

|

