![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In terms of language, what should an infant be able to do by a year of age? By one and half years?
|
One year: Speak in jargons and say "mama" or "dada"
One and half years: Ability to point to desired objects and gain of several words |
|
|
**If there is a language delay, what are the four most likely (general) causes?
|
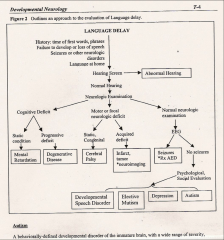
1. Hearing Disorder
2. Motor Disorder 3. Cognitive Disorder 4. Social Disorder |
|
|
**True or False: You should always test a child with a suspected language delay for a hearing disorder
|
True
|
|
|
What are two motor disorders associated with language delay?
|
1. congenital: cerebral palsy
2. acquired: lesion in the brain *identify through localizing exams or neuroimaging |
|
|
What are two cognitive disorders associated with language delay?
|
1. Mental retardation
2. Progressive degenerative diseases |
|
|
If the child has a language delay and a hearing, motor, and cognitive disorder have all been ruled out, what might be suspected?
|
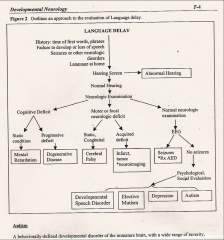
Social Disorder
|
|
|
**What is autism?
|
Behaviorally defined disorder that results in:
1. Impaired communication 2. Impaired sociability 3. Rigidity: desire for sameness, stereotypic behaviors, perseveration |
|
|
**What is a simple way to test/help identify if a child might be autistic?
|
Simple test of pointing and prosody
(Pointing is an important way children indicate joint interest/communicate and autistic children often have a flat or sing-song quality to their speech/cannot identify sarcasm) |
|
|
True or False: The ability to identify sarcasm relies on prosody.
|
True
|
|
|
What conditions can a social and psychological evaluation for a child with a language delay rule out?
|
1. Speech disorders
2. Elective mutism 3. Depression 4. Autism |
|
|
**What is the definition of aphasia?
|
Language disorder that affects the ability to understand and express spoken or written language (either or both)
|
|
|
**What are 3 examples of childhood epileptic syndromes associated with aphasia?
|
1. Rolandic Epilepsy/Benign Childhood Epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes
2. Landau-Kleffner Syndrome 3. Continuous Spikes and Waves during slow Sleep (CSWS) |
|
|
Rolandic Epilepsy:
1. Where is the region of epileptic activity? 2. What will the EEG show? 3. Does it affect expressive or perceptive language? 4. Is good recovery likely? |
1 & 2.) Centrotemporal spikes during sleep
3. Affects expressive language (vs. receptive); similar to Wernicke's Aphasia (language rarely involved, but if it is) 4. Good recovery likely |
|
|
Landau Kleffner Syndrome:
1. What does the EEG show? 2. True or false: Affects comprehension 3. Is it more or less severe than Rolandic epilepsy? |
1. Paroxysmal EEG, abnormal activity in one or both temporal lobes; no focal brain lesion
2. True (verbal and auditory recognition impaired) 3. More severe |
|
|
Continuous Spikes and Waves during slow sleep (CSWS):
1. What does the EEG show? 2. True or False: It is transitory. 3. What is the prognosis for epilepsy? 4. What other deficits are a concern with CSWS? |
1. Spike and wave discharges during 85% of non-REM sleep
2. True 3. Good 4. Neuropsychological deficits are a concern |
|
|
What is the definition of phonology?
|
The ability to discriminate and produce specific sounds of a given language (phonemes)
Prosody and stress are aspects of phonology |
|
|
True or False: Phonological receptivity is constant throughout life.
|
False. Receptivity starts to decline at around 10 months. (ex. pronouncing Hanukkah)
|
|
|
What is the definition of grammar?
|
Underlying rules that organize any specific lanaguage; morphology + syntax
|
|
|
What is the definition of semantics? When is the peak of its acquisition?
|
Vocabulary; maximally acquired during year 3 and 4
|
|
|
True or False: Vocabulary acquisition greatly affected by the environment
|
True
|
|
|
What is the definition of pragmatics?
|
Social use of language (ex. turn taking, politeness, conversational repair, a high cognitive function)
|
|
|
What does Noam Chomsky's theory of Pure Linguistics posit?
|
Phonology and grammar are the products of innate rules that are genetically imprinted and universal to languages. (ex. Grammar gene, KE family)
Environment activates genetic mechanism. (This also means that semantics and pragmatics are learned (vs. innate/genetic)) |

