![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
166 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are some causes of acute hepatitis ? |
- viral hepatitis A-E -Drugs -EtOH - Toxins - Autoimmune - Wilson's Diease |
|
|
What is the most common cause of acute hepatitis in the US ? |
- HAV - most common cause of acute hepatitis in US - fecal - oral route |
|
|
What is the 2nd most common cause of acute hepatitis in the US? |
- HBV -2nd most common cause in the US - Parenteral, sexual contact. |
|
|
which viral hepatitis is most prevalent world but rarely symptomatic ? |
- HCV - most common cause in IV rug users - previously designated non A non B - risk of sexual transmission - vertical transmission is lower than HBV |
|
|
HDV requires which viral hepatitis ? |
- requires HBsAG for transmission - can only be present with HBV |
|
|
HEV |
- young adults in East Asia, Middle East and Mexico - can lead to fulminant hepatitis in these endemic areas -fecal - oral route |
|
|
Name the phases of symptoms for viral hepatitis |
1.) prodromal phase - last several days 2.) icteric phase |
|
|
Prodromal phase of viral hepatitis |
- constitutional and GI symptoms - malaise -fatigue -HA -N/V -anorexia ** flu like symptoms ; possible low grade fever. |
|
|
Icteric phase of viral hepatitis |
- Jaundice with acholic stools - lever tender and enlarged
* icteric phase lasts days to weeks then resolution. |
|
|
how do pt's present with acute viral hepatitis ? |
- many patients asymptomatic or have symptoms without jaundice |
|
|
what labs for acute hepatitis |
- AST and ALT 20-100 x normal - bilirubin > 2.5-3 mg/dL ( >20mg/dL uncommon) - Alk phos no more than 3 x normal - mild leukopenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia |
|
|
Serodiagnosis for viral hepatitis |
- HAV - anti- HAV is antibody to HAV
|
|
|
serodiagnosis : IgM Anti-HAV |
- documents acute infection - disappears after several months |
|
|
serodiagnosis: IgG Anti- HAV |
- demonstrates someone has been infected with HAV sometime in the past - appears to offer lifelong immunity against HAV |
|
|
If you are looking for an acute infection which immunoglobulin will you look at ? |
- IgM |
|
|
what is the first serum maker seen in a HBV acute self-limiting infection? |
- HBsAG is the first marker seen in a HBV acute self limiting infection. - Usually disappears 4-6 months after infection in patients who clear HBV.
|
|
|
the presence of HBsAG means ? |
- the presence of HBsAG does not indicate whether it is acute or chronic infection. |
|
|
What is believed to offer immunity to HBV ? |
- Anti - HBs - may persist life of patient.
|
|
|
what antibody is seen in recovery of acute HBV and vaccination ? |
- Anti-HBs |
|
|
HBeAG |
transiently positive in acute hep B |
|
|
Anti Hbe |
- may persist for years
|
|
|
Anti- Hbc |
- first antibody to appear - IgM anti-HBc diagnostic for acute HBV |
|
|
will you see IgM anti-HBc in chronic infection? |
- no. no IgM in chronic infections. |
|
|
Anti- HBc assay |
- detects IgM and IgG - demonstrates history of infection with HBV at some point |
|
|
HBV chronic infection:
Carrier of HBV |
- HBsAg is a positive finding for carriers or chronic
|
|
|
HBV DNA levels |
- typically low or absent in inactive carriers - higher in patients with chronic hepatitis B - High levels are associated with increased infectivity |
|
|
what are the markers for vaccination to HBV ? |
1.) >90% of recipients develop protective anti-HBs 2.) vaccine recipients are not positive for anti-HBc unless they were previously infected with HBV. |
|
|
Anti- HCV |
- appears several months after infection -remains present for the life of the patient, even without chronic infection |
|
|
HCV RNA |
- aids in diagnosis of early HCV infection - before anti HCV and elevated ALT - predicts response to treatment |
|
|
What marker will predict response to treatment of HCV ? |
- HCV RNA will predict response to treatment |
|
|
a liver biopsy is also important for diagnosis of ? |
HCV - liver biopsy is also important for diagnosis and determining level of fibrosis |
|
|
Acute viral hepatitis - Diagnostic approach |
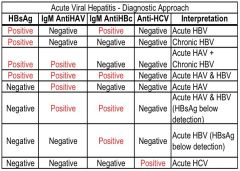
|
|
|
HDV |
-IgM anti- HDV positive with confection = acute - IgG anti- HDV persist in chronic infection |
|
|
HEV |
- IgM anti-HEV acute -IgG anti- HEV chronic |
|
|
what are some complications of acute viral hepatitis ? |
1.) Cholestatic hepatitis 2.) Fulminant hepatitis 3.) HeptoCellular Carcinoma with HBV/ HCV |
|
|
cholestatic hepatitis is most common in? |
- HAV |
|
|
What must you rule out before diagnosing Cholestatic Hepatitis ? |
- must rule out obstructive jaundice |
|
|
What labs will you have for cholestatic hepatitis ? |
- Marked elevated conjugated bilirubin - Marked elevated alk phos and pruritis |
|
|
Fulminant Hepatitis |
- massive hepatic necrosis <1 % of patients |
|
|
Hepatocellular Carinoma HCC |
- seen with HBV/ HCV |
|
|
How do you manage acute self-limited HAV, HBV, and HEV ? |
- Supportive care - unless complicated by fulminant hepatitis |
|
|
Acute HCV management |
- treated within 12 weeks of diagnosis with interferon |
|
|
Chronic HBV management |
- Pegylated IFN- alpha-2a and nucleoside or nucleotide analogues * lamivudine |
|
|
Chronic HCV managment |
- interferon often with riboflavin |
|
|
HBV and HDV management |
- less responsive to IFN therapy |
|
|
Prevention of HAV/ HEV |
- improved sanitation - Vaccine for traveling to endemic areas for HAV - men who have sex with men and users or illicit drugs
|
|
|
Is there a vaccine for HEV? |
- no vaccine for HEV |
|
|
HBV prevention |
1.) vaccine - infants and adults at high-risk 2.) condom use and not sharing needles |
|
|
HCV prevention |
1.) no vaccine 2.) condom use and not sharing needles |
|
|
HDV prevention |
- effective immunization against HBV |
|
|
Alcohol fatty liver is a precursor to ? |
- Alcoholic hepatitis |
|
|
What are the symptoms of alcohol fatty liver ? |
- tender hepatomegaly - RUQ pain - Jaundice rare - AST/ALT mildly elevated <5x normal - liver biopsy - diffuse or centrilobular fat occupying most of the hepatocyte |
|
|
Alcoholic hepatitis |
- progressive inflammatory liver injury due to long term heavy alcohol use |
|
|
what does alcoholic hepatitis progress to ? |
- progresses to : 1.) cirrhosis 2.) hepatic failure 3.) death if heavy alcohol consumption continues |
|
|
how does alcoholic hepatitis resolve ? |
- resolves slowly over weeks to months if alcohol use stopped - residual cirrhosis does occur |
|
|
who does alcoholic hepatitis present? |
- anorexia - N/V - Malaise -Fever -abdominal pain -tender hepatomegaly - leukocytosis - jaundice 1. itchy skin, yellow sclera, brown urine 2. unconjugated bili, PT + INR prolong - coagulopathy -mild forms may be asymptomatic |
|
|
what lab test would you order if you suspect your patient is a lying bastard about alcohol use ? |
-gGGT; could be positive if someone has heavy alcohol use. |
|
|
Severe forms of alcoholic hepatitis may include cutaneous signs of chronic liver disease |
- palmer erythema - spider angioma |
|
|
if your pt has alcoholic hepatitis what should you counsel them on ? |
- cessation and abstnence of alcohol. |
|
|
Severe forms of alcoholic hepatitis may also have portal HTN |
-esophageal varices - caput medusa -portal systemic shunting -encephalopathy - ascites |
|
|
What is ratio of AST/ALT for alcoholic hepatitis ? |
AST:ALT > 2:1 |
|
|
Alcoholic hepatitis biopsy |
- may need to establish diagnosis -determine presence or absence of cirrhosis, and to exclude other causes of liver disease |
|
|
what might you see on a biopsy for alcoholic hepatitis ? |
- mallory bodies; intracellular eosinophilic aggregates of cytokeratins - focal acccumulation of polymophonuclear leukocytes - intralobular connective tissue surrounding hepatocytes and central veins. |
|
|
how do you treat alcoholic hepatitis ? |
- **abstinence from alcohol - high calorie diet with vitamin * folate and thiamine - protein; except in renal failure pt. - Parenteral vitamin K if coagulopathic |
|
|
how do you treat severe alcoholic hepatitis |
- hospitalization ICU is necessary - long term goals= improvement of liver function, prevention of progression to cirrhosis, and reduction of mortality - glucocorticosteroids to suppress inflammation. |
|
|
What is the leading cause of acute liver failure in the U.S. |
- Acetaminophen
|
|
|
what type of hepatic failure will you see with acetaminophen ? |
- fulminant hepatic failure |
|
|
Acetaminophen |
- hepatotoxicity can occur with misuse and overdose - Occurs with dose > 10 g in adults - N/V 1/2 hour to 24 hours after ingestion - followed by RUQ pain/tenderness - then hepatic necrosis and dysfunction- jaundice, coagulopathy, hypoglycemia and encephalopathy. |
|
|
Acetaminophen induced acute hepatitis: critically ill pt |
- present with : renal failure mulitorgan failure death |
|
|
how long is recover from acetaminophen induced acute hepatitis |
4 days to 3 weeks after ingestion - for those who don't die; full complete recovery. |
|
|
how is diagnosis of acute hepatitis via acetaminophen made |
- serum acetaminophen concentration - also check LFTs, PT/ INR, renal function studies |
|
|
how is acute hepatitis via acetaminophen treated? |
- activated charcoal if in the immediate post-ingestion time - Nacetylcystein NAC loading dose of 140 mg/kg. 17 doses of 70 mg/kg given every 4 hours -total treatment duration is 72 hours. |
|
|
what is the antidote for acetaminophen overdose ? |
N-acetylcystein; NAC |
|
|
NSAIDS and hepatitis |
- dose dependent hepatocellular injury that is milder and more easily reversible than acetaminophen |
|
|
Herbs and hepatitis |
- many are hepatotoxic and can cause massive necrosis and fulminant hepatic failure and death. |
|
|
which Herbs do what |
- Chaparral : Arthritis, colds, stomach problems - Germander: GB problems, diarrhea, wt loss -Pennyroyal: colds, pneumonia, stomach pain - Mistletoe: epilepsy, HTN, arthritis -Vaerian root: sleep -Comfrey: upset stomach, angina, cough -Ma Haung: wt loss and appetite supression |
|
|
drug induced hepatits |
- acetaminophen -amoxicillin - Amiodarone - chlorpromazine -ciprofloxacin - diclofenac - Erythromycin -Fluconazole - Isoniazid -meythyldopa -oral contraceptives -statins****** -rifampin -valproic acid and divalpoex sodium - esctasy and cocaine |
|
|
what is the critieria for chronic hepatitis ? |
- hepatic inflammation that does not resolve after 6 months |
|
|
What is chronic hepatitis caused by |
- Acute viral hepatitis- mostly HBV, HCV, and HEV -nonalcoholic steatohepatitis NASH -several drugs |
|
|
What is the most common type of chronic hepatitis in the US |
- NASH; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis |
|
|
chronic hepatitis B |
- 5-15% of the time of diagnosis of hep B will be chronic - Those in high replicative phase are at high risk of developing cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
How do you treat chronic hepatitis B |
- interferion A - oral nucleoside or nucleotide analogues |
|
|
Chronic hepatitis C |
- 75% of the time will be chronic at the time of diagnosis - 20% will develop cirrhosis |
|
|
how do you treat chronic hepatitis C |
- Interferon A -oral Riboflavin |
|
|
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD |
-steatosis (fatty liver) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis secondary to NASH |
|
|
What is the most common cause of abnormal LFT's in adult in the US? |
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
|
|
NAFLD is associated with |
- most common with overweight, DM and hyperlipidema |
|
|
NASH histology |
- macrovesicular fatty inflitration - inflammation - hepatocyte injury with or without fibrosis
|
|
|
what can improve NASH liver histology ? |
- weight loss and exercise improves liver histology |
|
|
What are the causes of fulminant hepatic failure ? |
- viral hepatits ( HAV, HBV, HEV) -hepatotoxins * acetaminophen -Wilson's disease |
|
|
Fulminant hepatic failure |
- development of encephalopathy within 8 weeks of the onset of symptoms in a patient with a previously healthy liver |
|
|
fulminant hepatic failure short term survival rate |
20% without liver transplant |
|
|
What is the survival rate after a liver transplant for fulminant hepatic failure |
- 1 year survival rate after liver transplant is 80-90% |
|
|
what is prognosis for fulminant hepatic failure for someone that survives without a liver transplant ? |
- those who survive without a liver transplant have a good long term prognosis |
|
|
what are some signs and symptoms of fulminant hepatic failure |
-encephalopathy -cerebral edema - jaundice: often present but not always - ascites - RUQ tenderness -Hematemesis of melena - hypotension and tachycardia - hypoglycemia -coagulopathy |
|
|
what must you have in order to be diagnosed with fulminant hepatic failure |
- must have encephalopathy - No encephalopathy then no fulminant hepatic failure |
|
|
explain the change in liver spain in fulminant hepatic failure |
- may be small due to hepatic necrosis or may be enlarged due to heart failure, viral heaptitis or Budd-chiari syndrome |
|
|
Diagnosis of fulminant hepatic failure |
- presence of hepatic encephalopathy - liver failure : elevated bilirubin and transaminases, and prolonged PT/INR -Thrombocytopenia may be present -Hypoglycemia -serum ammonia level may be very elevated |
|
|
how do you treat fulminant hepatic failure |
- ICU support -ABCs -monitor metabolic parameters -asses for infection -maintain nutrition -promptly recognize GI bleeding |
|
|
What do you do for hepatic encephalopathy ? |
- lactulose |
|
|
fulminant hepatic failure : cerebral edema management |
- measure ICP and try to keep <20 mmHg -mannitol, barbiturate coma, liver transplant |
|
|
fulminant hepatic failure: hypoglycemia management |
- 10% glucose |
|
|
fulminant hepatic failure: coagulopathy management |
- vitamin K and prophylactic gastric acid suppression |
|
|
Cirrhosis of the liver |
- diffuse hepatic process characterized by fibrosis and the conversion of normal liver architecture into structurally abnormal nodules. |
|
|
Progression of liver injury |
Progression of liver injury to cirrhosis may occur over week to years. |
|
|
is cirrhosis reversible ? |
- no. cirrhosis is irreversible damage. |
|
|
Clinical features and complication of cirrhosis of the liver are from |
- portal HTN -decreased hepatic function -decreased detoxification abilities of the liver |
|
|
What are some of the most common causes of cirrhosis of the liver in the US ? |
1. alcohol consumption 2. HCV 3. nonalcoholic liver disease |
|

|
* just pay attention to the most common cause of cirrhosis of the liver in the US |
|
|
what are signs and symptoms of cirrhosis of the liver ? |
-fatigue, malaise, weakness, wt gain or loss, anorexia, nausea, increased abdominal girth, abdominal discomfort |
|
|
What will you see on physical exam for cirrhosis of the liver ? |
- jaundice -abnormal liver span -splenomegaly -ascites -lower extremity edema -spider angiomas -palmar erythema -gynecomastia -caput medusa -asterixis testicular atrophy |
|
|
how will the liver be in cirrhosis verses hepatitis |
cirrhosis - fibrotic and small hepatitis -inflamed and big |
|
|
lab findings for cirrhosis of the liver |
- hypoalbuminemia -prolonged PT/INR -hyperbilirubinemia - low blood BUN -elevated serum ammonia levels - thrombocytopenia - leukopenia -anemia -hyponatremia |
|
|
what are the radiological findings for cirrhosis of the liver ? |
- US of the portal and hepatic venous vasculature - CT/MR : hepatic atrophy Ascites Intra-abdominal varices - liver biopsy if diagnosis in doubt |
|
|
what are complications of cirrhosis of the liver ? |
1.) Portal HTN 2.) Hepatocellular dysfunction 3.) HCC
|
|
|
Cirrhosis of the liver complications : Portal HTN |
1.) variceal heorrhage 2.) ascites 3.) spontaneous bacterial peritonitis 4.) hepatorenal syndrome 5.) encephalopahty |
|
|
Cirrhosis of the liver complications: Hepatocellular dysfunciton |
- jaundice - coagulopathy - hpyoalbuminemia |
|
|
what is the name of the scale that is used to determine severity of cirrhosis ? |
- Child-Turcotte Pugh Class scale |
|
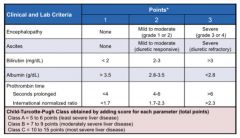
what is this used for? |
- Child-Turcotte Pugh Class Scale used for determination of severity of cirrhosis |
|
|
What criteria is on the Child Turcotte Pugh Class Scale ? |
- Encephalopathy -Ascites - Bilirubin - Albumin - Prothrombin Time PT - International normalized ration INR |
|
|
Child Turcotte Pugh Class A |
- the least severe liver disease |
|
|
Child Turcotte Pugh Class C |
- the most severe liver disease |
|
|
Cirrhosis of the liver complications:
Portal HTN - Esophageal varices |
- portal pressure gradient > 10 mm Hg will create esophageal varices -portal pressure gradient > 12mmHg gastroesophageal variceal bleed - bleeding occurs in 10-30% of pt with mortality rate of 15-30% |
|
|
how do you diagnose an esophageal varice? |
- upper endoscopy |
|
|
how do you treat acute esophageal varices ? |
- acutely - ABCs and resuscitation- blood, FFP, vit k -Somatostatin or analogues * octreotide AND - endoscopy with ligation and/or sclerotherapy. - if all fails- then balloon tampanade - portal decompression- surgical shunt or transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt TIPS |
|
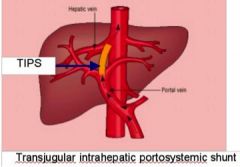
what is this showing |
- TIPS for treatment of acute esophageal varices |
|
|
How do you treat esophageal varices after the first bleed ? |
- prophylaxis - non-selective Beta Blocker - Propanolol -Banding |
|
|
how do you treat esophageal varices prior to first bleed ? |
- primary prophylaxis - large varices or advanced liver disease (Child-Tourcotte Class B or C ) . ** Non-selective Beta Blockers |
|
|
Cirrhosis of the liver complication:
Portal HTN - Ascites |
- detectable on PE with > 500mL fluid - abdominal distention, bulging flanks, shifting dulness - ultrasound |
|
|
how do you treat ascites ? |
- Na restriction < 2g per day - Fluid restriction if hyponatremia present -Spironolactone (aldosterone antagonist) and a loop diuretic; too aggressive - renal failure. |
|
|
Refractory ascites |
- repeated large volume paracentesis with colloid volume expansion ( albumin), TIPS, liver transplant. |
|
|
Cirrhosis of the liver complications:
Portal HTN- Hepatorenal syndrome |
- concurrent liver disease and renal failure - most often occurs with significant hepatic synthetic dysfunction and ascites -kidneys are normal and can regain normal function if recovery of liver function. |
|
|
Hepatorenal syndrome type I |
- rapid and more severe |
|
|
Hepatorenal syndrome type II |
- more slowly and better prognosis |
|
|
what is hepatorenal syndrome provoked by ? |
- usually provoked by : 1.) infection 2.) over-diuresis 3.) large volume paracentesis |
|
|
Cirrhosis of the liver complications:
Portal HTN: Hepatic Encephalopathy |
- personality changes -intellectual impairment -depressed level of consciousness
|
|
|
What seems to be a prerequisite for Hepatic encephalopathy ? |
- The diversion of portal blood into the systemic circulation appear to be a prerequisite for the syndrome. |
|
|
Explain the increased levels ammonia with Hepatic encephalopathy |
- Ammonia is produced in GI tract. - detoxified in the liver by conversion to urea and glutamine. - in liver disease or portosystemic shunting, portal blood ammonia is not converted efficiently to urea. - increased level of ammonia may enter the systemic circulation because of portosystemic shunting. - multiple neurotoxic effects |
|
|
what are some symptoms of hepatic encephalopathy ? |
- range from mild to severe and may be observed in as many as 70% of patients with cirrhosis. |
|
|
Hepatic encephalopathy Grade 0 |
- subclinical; normal mental status but minimal changes in memory, concentration, intellectual function, coordination. |
|
|
hepatic encephalopathy Grade 1 |
- mild confusion, euphoria or depression -decreased attention -slowing of ability to perform mental tasks -irritability -disorder of sleep patter * inverted sleep cycle. |
|
|
hepatic encephalopathy grade 2 |
- drowsiness -lethargy -gross deficit in ability to perform mental tasks - obvious personality changes -inappropriate behavior -intermittent disorientation- usually with regard to time |
|
|
hepatic encephalopathy grade 3 |
-somnolent; but arousable state - inability to perform mental tasks -disorientation with regard to time and place -marked confusion -amnesia -occasional fits of rage - speech is present but incomprehensible |
|
|
hepatic encephalopathy grade 4 |
-coma -with or without response to painful stimuli |
|
|
laboratory diagnostics for hepatic encephalopathy |
- elevated serum ammonia |
|
|
you have a pt that has portal HTN and cirrhosis of the liver; list possible stressors/precipitating factors that can lead to hepatic encephalopathy |
- diuretics -hypovolemia -renal failure -infection -constipation -possibly high protein diet -some medication- opiates, benzos |
|
|
how do you manage hepatic encephalopathy ? |
1.) Lactulose- lowers stool pH, trapping ammonia in the colon. 2.) Neomycin; 2nd line therapy- decreases colonic concentration of ammoniagenic bacteria 3.) address precipitating factors / stressors. |
|
|
liver transplant |
- important treatment for patient with decompensated cirrhosis - approx. 12-15 % of patients listed as candidates die while waiting for a liver. |
|
|
What are some contraindication for a liver transplant ? |
- severe cardiovascular or pulmonary disease -active drug or alcohol abuse - malignancy outside the liver - sepsis -psychosocial problems that might jeopardize patient's ability to follow their medical regimens after transplant |
|
|
what is the most common primary malignancy of the liver ? |
- hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
what is the 3rd leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide |
- hepatcellular carcinoma |
|
|
- what is the fastest growing cause of cancer mortality in the US due to its link to HCV |
- hepatocellular carcinoma |
|
|
hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis shift |
- has shifted to being diagnosed in late stages to earlier stages due to screening of patients with known cirrhosis |
|
|
Hepatocellular carcinoma and resection |
- many patients are not candidates for resection due to advance degree of cancer at diagnosis or their degree of liver disease. |
|
|
who does hepatocellular carcinoma affect the most ? males or females ? |
- male preponderance |
|
|
what are the clinical and laboratory findings of HCC ? |
- hepatic bruit or friction rub - Serum alpha- fetoprotein > 400 ng/mL |
|

HCC |
know some stuff |
|
|
HCC ultrasonography |
- mass lesion with varying echogenicities but usually hypoechoic |
|
|
HCC on Dynamic CT |
- arterial phase: tumor enhances quickly -venous phase: quick de-enhacement of the tumor relative to the parenchyma . |
|
|
HCC MRI T1 |
- hypointense |
|
|
HCC MRI T2 |
-hyperintense - after gadolinium administration the tumor increases in intensity |
|
|
HCC treatment |
- resection if possible - liver transplantation - percutaneous ethanol injection, arterial chemoembolization, radiofrequency ablation. |
|
|
What is the most common malignant tumor to the liver ? |
- HCC |
|
|
What is the 2nd most common organ involved in metastatic disease - after lymph nodes |
- liver |
|
|
Metastasis to the liver can come from any primary cancer but most common are |
- colon, stomach, pancreas, breast, lung. |
|
|
Metastasis to the liver from colon cancer benefit from ? |
- resection; if possible- based on extra-hepatic disease, number, size and location of lesions. -lesions can be downsized with CT and ablation -10% 5-year survival rate. |

