![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a DNS Server?
|
Any computer providing domain name services is a DNS Server.
|
|
|
What is a DNS Client?
|
Any machine that issues queries to a DNS server.
Client issues DNS requests through processes called "Resolvers" example: IE, Firefox, etc |
|
|
What are Resolvers?
|
Resolvers are software processes, sometimes implemented in software libraries, that handle the actual process of finding the answers to queries for DNS data.
|
|
|
What is a Query?
|
A query is a request for information sent to a DNS server. Three types of queries can be made: Recursive, Inverse and Iterative.
|
|
|
What does the DDNS (Dynamic DNS Standard) do?
|
Allows clients to update information in the DNS Database files. Example- a DHCP server can automatically tell a DDNS server which IP addresses it has assigned to what machines.
|
|
|
What does the DDNS (Dynamic DNS Standard) do?
|
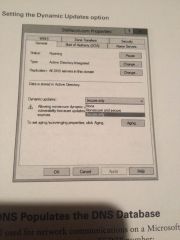
Allows clients to update information in the DNS Database files. Example- a DHCP server can automatically tell a DDNS server which IP addresses it has assigned to what machines.
|
|
|
What does Non DNS (NDDNS) do?
|
It does not automatically populate the DNS database. The clients don't have to ability to update to DNS. If you use 'Non Dynamic, the Admin will need to populate the DNS database manually.
|
|
|
Iterative Queries?
|
A client asks for the DNS server for an answer, and the server returns the best answer. This information most likely comes from the server's cache.
|
|
|
|
A client asks for the DNS server for an answer, and the server returns the best answer. This information most likely comes from the server's cache. |
|
|
Recursive Queries?
|
The client sends a query to a name server, asking it to respond either with the requested answer or with an error message.
|
|
|
Inverse Queries?
|
They use pointer (PTR) records. Instead of supplying a name and then asking for an IP address, the client first provides the IP address and then asks for the name.
|
|
|
What does TTL (Time To Live) specifies?
|
How long a record will be held in the local cache until it must be resolved again.
|
|
|
What does TTL (Time To Live) specifies?
|
How long a record will be held in the local cache until it must be resolved again.
|
|
|
When is the negative cache TTL used?
|
It's used when an authoritative server responds to a query indicating that the record queried doesn't exist and it indicates the amount of time that this negative answer may be held.
|
|
|
What is the Primary DNS zone responsible for?
|
Maintaining all of the records for the DNS zone. It contains the primary copy of the DNS database. All record updates occur on the primary zone.
|
|
|
What is the Primary DNS zone responsible for?
|
Maintaining all of the records for the DNS zone. It contains the primary copy of the DNS database. All record updates occur on the primary zone.
|
|
|
There are two types of Zones. What are they?
|
- Primary Zone
- Primary Zone with ADI (Active Directory DNS) |

