![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
dendrites |
receives initial singal |
|
|
|
skeletal muscle |
striated, voluntary, function: body movement and heat production |
|
|
|
hyaline cartliage |
found at end of long bone, most commonly found |
type of cartilage |
|
|
fibrocartilage |
abundance of collagen fibers in the matrix, found in invertebral disks |
type of cartilage |
|
|
cardiac muscle |
striated, involuntary, function: blood movement |
|
|
|
elastic cartilage |
abundance in the matrix, found in external EAR |
|
|
|
smooth muscle |
non striated, involuntary, moves products internally |
|
|
|
axons |
move message away from cell body |
|
|
|
osteocytes |
cells in bone |
|
|
|
loose connective tissue |
fills in space in body and binds structures together |
loose network of fibers and cells |
|
|
dense fibrous connective tissue |
poor vascular supply, forms tendons and ligaments |
|
|
|
adipose |
forms protective cushion around certain organs, provides insulin |
|
|
|
heparin |
anticoagulant |
think of blood clots |
|
|
histamine |
promotes inflammation |
|
|
|
neuroglia/ myelin sheath |
on the axons of neurons |
|
|
|
steroid hormones |
diffuse through the plasma membrane of target cells and binds to DNA |
|
|
|
non steroid hormones |
binds to membrane receptor, doesnt enter cell |
|
|
|
squamous |
body cavities, blood vessels, air sacs of lungs, line the mouth |
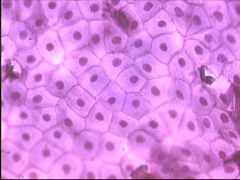
type of epithelial |
|
|
cuboidal |
cubelike, kidney tubes, glands |
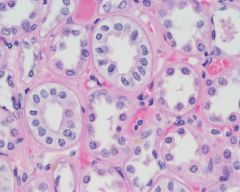
type of epithelial |
|
|
columar |
tall, narrow like |
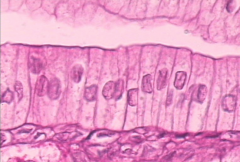
type of epithlial |
|
|
simple |
made of one layer |
type of epithelial |
|
|
stratified |
made of multiple layers |
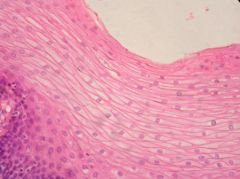
type of epithelial |
|
|
goblet cells |
located in simple columnar which secretes mucous |
|
|
|
Cilliated Pseudostratified Epithelial |
single layer of uneven cells that contains cilia |
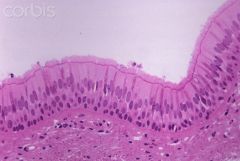
|
|
|
Transitional |
specialized for stretching; urinary bladder |
|
|
|
tubular |
shape of exocrine gland with no change in diameter |
|
|
|
acinar |
shape of exocrine gland when duct expands to form a sac-like structure |
|
|
|
merocrine |
secrete a fluid that is released through a cell membrane by exocytosis with no loss of cytoplasm |
|
|
|
Aprocrine |
product accumulates and then that portion pinches off so that a small part of the cell is lost with the secreation |
think of an Acorn falling off of a tree |
|
|
Holocrine |
the cell becomes filled with the product and then ruptures; oil glands |
when you rupture; you die; go to Heaven |
|
|
Negative feedback |
hormone levels in the blood are maintained by |
when your girlfriend is on her period she is always grumpy |
|
|
Hypothalamus |
synthesizes and secretes neurohormones which controls and regulates the secretion of pituitary hormones |
|
|
|
Pituitary Gland |
Hangs by a stalk from the hypothalamus |
|
|
|
Thyroid- Stimulating Hormone |
type of hormone that influences growth and activity of the thyroid |
a pituitary hormone |
|
|
Gonadotropic hormone |
type of hormonal activity of the gonads |
literally has the word GONDA in it |
|
|
Thyroid Gland |
found at the base of the throat |
starts with a T |
|
|
Parathyroid Glands |
tiny masses next to the thyroid |
has the word thyroid in it |
|
|
adrenal gland |
sits on top of the kidneys |
|
|
|
Pancreas |
produces insulin and glucagon |
|
|
|
Pineal gland |
found in the brain; secretes melatonin - sleep cycle |
|
|
|
Thymus |
largest in infants and children |
important to develop an immune system |
|
|
Estrogen and Progestrone |
hormones of the ovaries |
|
|
|
testosterone |
hormone of the testes |
|

