![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a SOA (Start of Authority) Record |
Indicates that the server is the best authoritative sourcefor data concerning the zone. |
|
|
How many SOA (Start of Authority) does a Zone must Have? |
Each zone must have an SOA record, and only one SOA record can be in a zone. |
|
|
What is a NS (Name Server) Record |
Identifies a DNS server functioning as an authority for the zone.Each DNS server in the zone (whether primary master or secondary) must be represented by an NS record. |
|
|
What is a A Record |
Provides a name-to-address mapping that supplies an IPv4 addressfor a specific DNS name. This record type performs the primary function of the DNS: converting names to addresses. |
|
|
What is a AAAA (Address) Record |
Provides a name-to-address mapping that supplies an IPv6 addressfor a specific DNS name. This record type performs the primary function of the DNS: converting names to addresses. |
|
|
What is a PTR (Pointer) Record |
Provides an address-to-name mapping that supplies a DNS name fora specific address in the in-addr.arpa domain. This is the functional opposite of an A record, used for reverse lookups only. |
|
|
What is a CNAME (Canonical Name) Record |
Creates an alias that points to the canonical name (thatis, the “real” name) of a host identified by an A record. Administrators use CNAME records to provide alternative names by which systems can be identified. |
|
|
What is a MX record |
Identifies a system that will direct email traffic sent to anaddress in the domain to the individual recipient, a mail gateway, or another mail server. |
|
|
What are the three elements DNS: |
-DNS namespace -Name servers -Resolvers |
|
|
What is a DNS namespace |
The DNS standards define a tree-structured namespace inwhich each branch of the tree identifies a domain. Each domain contains a collection of resource records that contain host names, IP addresses, and other information. Query operations are attempts to retrieve specific resource records from a particular domain. |
|
|
What is a Name servers |
A Name (DNS) server is an application running on a server computer thatmaintains information about the domain tree structure and (usually) contains authoritative information about one or more specific domains in that structure. The application is capable of responding to queries for information and forward queries about other domains to other name servers. |
|
|
What is a resolver? |
A resolver is a client program that generates DNS queries and sends themto a DNS server for fulfillment. A resolver has direct access to at least one DNS server and can also process referrals to direct its queries to other servers when necessary. |
|
|
How does DNS work? |
In its most basic form, the DNS name resolution process consists of a resolver submittinga name resolution request to its designated DNS server. When the server does not possess information about the requested name, it forwards the request to another DNS server on the network. The second server generates a response containing the IP address of the requested name and returns it to the first server, which relays the information to the resolver, |
|
|
What is DNS server caching? |
A DNS server that receives requests from clients, caches the addresses of therequested systems and the addresses for authoritative servers of particular domains. The nexttime a client requests the resolution of a previously resolved name, the server can respondimmediately with the cached information. |
|
|
What is time to live(TTL)? |
The amount of time that DNS data remains cached on a server |
|
|
What is DNS referrals? |
The process by which one DNS server sends a name resolution request to another DNS server |
|
|
What are the two types of name resolution requests? |
- Recursive query - Iterative query |
|
|
What is a Recursive query? |
In a recursive query, the DNS server receiving the name resolutionrequest takes full responsibility for resolving the name. If the server possesses information about the requested name, it replies immediately to the requestor. If the server has no information about the name, it sends referrals to other DNS servers until it obtains the information it needs. TCP/IP client resolvers always send recursive queries to their designated DNS servers. |
|
|
What is a Iterative query? |
In an iterative query, the server that receives the name resolutionrequest immediately responds with the best information it possesses at the time. DNS servers use iterative queries when communicating with each other. In most cases, it would be improper to configure one DNS server to send a recursive query to another DNS server. The only time a DNS server sends recursive queries to another server is in the case of a special type of server called a forwarder, which is specifically configured to interact with other servers in this way. |
|
|
What is a DNS Forwarder |
Anytime a server has to resolve the DNS name of an Internet system and fails to find the needed information in its cache, it transmits a recursive query to the forwarder, which is then responsible for sending its own iterative queries over the Internet connection. Once the forwarder resolves the name, it sends a reply back to the original DNS server, which relays it to the client. |
|
|
What is Reverse name resolution? |
Converts an IPaddress into a DNS name. |
|
|
What is a DNS Zone? |
A zone is an administrative entity you create on a DNS server to represent a discrete portion of the DNS namespace. |
|
|
How does a Zone work? |
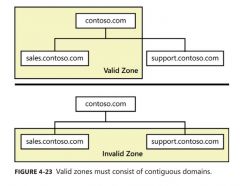
You can create a zone that containsmultiple domains as long as those domains are contiguous in the DNS namespace, I.e Parent-Child domains. But you cannot create a zone containing two child domains without their common parent, because the two children are not directly connected. |
|
|
What is a zone database? |
Every zone consists of a zone database, which contains the resource records for thedomains in that zone. |
|
|
What Zone types does Windows Server 2012 supports? |
*Primary zone - Creates a primary zone that contains the master copy of the zonedatabase, where administrators make all changes to the zone’s resource records. If the Store The Zone In Active Directory (Available Only If DNS Server Is A Domain Controller) check box is cleared, the server creates a primary master zone database file on the local drive. This is a simple text file that is compliant with most non-Windows DNS server implementations. *Secondary zone - Creates a duplicate of a primary zone on another server. The sec-ondary zone contains a backup copy of the primary master zone database file, stored as an identical text file on the server’s local drive. You can only update the resource records in a secondary zone by replicating the primary master zone database file, by using a process called a zone transfer. *Stub zone - Creates a copy of a primary zone that contains the key resource records that identify the authoritative servers for the zone. The stub zone forwards or refers requests. When you create a stub zone, you configure it with the IP address of the server that hosts the zone from which you created the stub. When the server hosting the stub zone receives a query for a name in that zone, it either forwards the request to the host of the zone or replies with a referral to that host, depending on whether the query is recursive or iterative. |
|
|
What is BIND? |
The most common DNS server Database implementation on the Internet is a UNIX program called BIND that uses text-based database files. |

