![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
50 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
When was DNA unravelled? |
1953 |
|
|
Who unravelled DNA? |
Watson and Crick |
|
|
What does DNA stand for? |
Deoxyribonucleic acid |
|
|
What are the three nucleotides? |
Phosphate Deoxyribose One of 4 nitrogen-rich bases |
|
|
What are the upright of the ladder of DNA? |
Alternating phosphate and sugar groups |
|
|
What are the rungs of the DNA ladder? |
Nitrogen - rich bases |
|
|
What are the four bases? |
Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytosine |
|
|
What bases match up? |
A - T G - C |
|
|
What is complimentary base pairing? |
Bases that only pair up with certain bases |
|
|
What are chromosomes? |
Long, thin thread-like structures found in the nucleus of cells |
|
|
What are chromosomes made of? |
DNA and protein |
|
|
How many chromosomes are in each body cell (somatic)? |
46 |
|
|
How many chromosomes are in gametes? |
23 |
|
|
What are genes? |
Sections of DNA, found on chromosomes |
|
|
What is the difference between one gene and another? |
Order of bases and length of the strand |
|
|
What do genes code for? |
Specific protein; functions + characterisitcs |
|
|
What is DNA replication? |
Copying DNA |
|
|
What are the two different types of DNA replication? |
Mitosis & Meiosis |
|
|
What does mitosis produce? |
2 identical daughter cells, involved in growth and repair |
|
|
What does meiosis produce? |
Gametes (egg + sperm), have half the number of chromosomes |
|
|
What is the difference between meiosis and mitosis? |
Mitosis: produce two identical daughter cells, double the number of chromosomes. Meiosis: produce gametes, make four different daughter cells, half the number of chromosomes than mitosis |
|
|
What are the stages of mitosis? |
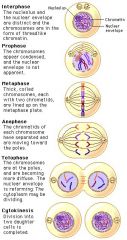
Interphase Prophase Metaphase (middle) Anaphase (apart) Telophase (end) |
|
|
What happens during prophase? |
Chromosomes in nucleus are copied |
|
|
What happens during metaphase (hint: middle) |
Chromosrallign to the middle |
|
|
What happens during anaphase? (hint: apart) |
Chromatids pulled apart and moved towards poles |
|
|
What happens during telophase? (hint: end) |
Chromosomes separate
|
|
|
What are chromatids? |
Each of the two thread-like strands of DNA |
|
|
What is the function of meiosis? |
Reproduction |
|
|
What is diploid number? |
Number of chromosomes in your body |
|
|
What does 2N mean? |
2 sets; only in body cells |
|
|
What are autosomes? |
Not sex chromosomes, a cell has 44 autosomes and 2 sex chromosomes |
|
|
What is asexual reproduction? |
Produced through mitosis; offspring inherit all genetic information from one parent only |
|
|
What are Mendel's conclusions? |
Each parent contributes one hereditary factor |
|
|
What are factors? |
Genes |
|
|
What is hereditary? |
The passing on of characteristics from parents to offspring |
|
|
What are characteristics inherited called? |
Traits |
|
|
Genes exist in alternative forms, what are these forms called? |
Alleles |
|
|
How is a dominant represented? |
Capital letter |
|
|
How is a recessive represented? |
Lower letter |
|
|
What are identical genes called? |
Homozygous |
|
|
What are different genes called? |
Heterozygous |
|
|
What is the genotype? |
Genetic composition for particular triats |
|
|
What is a phenotype? |
Characteristic shown |
|
|
What are punnette squares? |
Used to predict probability of possible genotypes |
|
|
What is co-dominance? |
Phenotype is combination of homozygous individuals, contributors of both alleles are visible |
|
|
What is incomplete dominance? |
The heterozygote is blended between two homozygous individuals |
|
|
What are the phenotypes of blood? |
A B O AB |
|
|
What are the genotypes of blood? |
A: AA AO B: BB BO O: OO AB: AB |
|
|
What is somatic? |
Not sperm or egg cells |
|
|
What is heredity |
Genes come in pairs |

