![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is DNA
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid
|
|
|
What is DNA made up of
|
nucleotides
|
|
|
3 parts of nucleotides
|
-5 Carbon sugar(ribose or deoxyribose)
-Phosphate Group -Nitrogenous Base (4 tyoes make up 4 types of nucleotides) |
|
|
4 Types of Nitrogenous Bases in DNA
|
Adenine(A)
Thymine(T) Cytosine(C) Guanine(G) |
|
|
4 Types of Nitrogenous Bases in RNA
|
-Adenine(A)
-Uracil(U) -Cytosine(C) -Guanine(G) same as in dna but uracil instead of thymine |
|
|
What are the base pairs of DNA
|
Adenine and Thynine (Uracil in RNA)
Cytosine and Guanine |
|
|
What type of bonds hold the complementary bases together
|
Hydrogen Bonds
|
|
|
Structure of DNA?
|
Double Helix
|
|
|
What encodes the vast Amounts of Information.
|
Order of the nitrogen bases
|
|
|
How many rings do each of the nitrogenous bases have
|
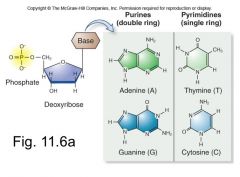
|
|
|
What is the backbone of DNA
|
Sugar-Phosphates
|
|
|
What is genome?
|
The entire DNA of an organism.
|
|
|
What makes each of us different?
|
Sequence of nirtogen bases
|
|
|
What is important for cell division & inheritance to work?
|
It is important for DNA to be replicated accurately
|
|
|
What affects how DNA is replicated?
|
Specific base-pairing and the double-helix structure affect how DNA is replicated
|
|
|
How is DNA replicated?
|
The double helix structure is unzipped then the new single strands are made to match the unzipped single strands. Following the rules of base pairing producing two identical daughter strands.
|
|
|
What unwinds the Double helix in DNA replication?
|
Enzymes-helicase
|
|
|
What acts as a template for making new DNA Strands?
|
The old single strands
|
|
|
What assembles the new strand of DNA?
|
DNA polymerase enzyme assembles new single strand with sequence of bases that complements the original strand
|
|
|
Where does the DNA replication begin
|
specific sites known ads the origins of replication.
|
|
|
How many strands are produced from replication?
|
2 TWO
|
|
|
What holds the base pairs together?
|
Hydrogen bonds
|
|
|
Sugar in DNA
|
Deoxyribose
|
|
|
Whar are rungs?
|
steps on the ladder of DNA
|
|
|
What can destroy DNA
|
Ultraviolet Radiation
|
|
|
Errors as a result of replication errors that change the DNA
|
Mutations
|
|
|
Mutations are rarely beneficial
|
Sickle cell disease to fight malaria CTT sequence mutated to CAT sequence
|

