![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What HPV strains cause skin warts? What strains cause genital warts? |
Strains 1 - 4 cause skin warts Strains 6 & 11 cause non-cancerous genital warts |
|
|
What organisms cause tinea infections? How is it diagnosed? What is the trx? |
Causes - Microsporum, Trichophyton, Epidermophyton Dx - KOH addition shows hyphae Trx - Body → Topical clotrimazole, terbinafine, nystatins - Scalp → Oral Griseofulvin - Nails → Oral Terbinafine for prolonged time |
|
|
What is intertrigo? How is it diagnosed? What is the trx? |
Candida infxn in skin creases with satellite leisons Dx = KOH shows pseudohyphae Trx = Topical clotrimazole or terbinafine |
|
|
What is the treatment for Scabies, lice, or crabs? What is the treatment for pinworms? |
Permethrin cream Pyrantel or Me/Albendazole |
|
|
What is the difference between Erythema Multiforme, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)? |
Erythema Multiforme - target like lesions usually on hands/forearms that often spares mucous membranes SJS - more severe, always involves mucous membranes, involves < 10% of body TEN - Full thickness severe lesions involving >30% of body |
|
|
What are the common causes of Erythema Multiforme? |
HSV Mycoplasma Penicillin Sulfa NSAIDS OCPs Anticonvulsants |
|
|
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis? What is the trx? |
Red plaques with greasy-looking yellow scales (craddle cap if on infants head) Trx: Scalp → ketaconazole or SeS shampoo Body → topical steroids |
|
|
What is Seborrheic Keratosis? What is the treatment? |
Noncancerous warty "pasted-on" nodules No trx needed |
|
|
What infections are associated with Lichen planus? |
HIV Hep C |
|
|
What are the different stages of decubitis ulcers? |
Stage I - skin intanct, change in color only Stage II - superficial Stage III - full-thickness skin loss with damage to sub-Q tissues Stage IV - destruction/necrosis of mm, bone, supporting structures |
|
|
What is the difference between Pemphigus vulgaris and Bullous pemphigoid? How are each treated? |
Pemphigus vulgaris - flaccid bullae w/ + Nickoslky sign, + oral lesions, Anti-desmosome ab's in epidermis. Trx w/ High dose steroids Bullous pemphigoid - Tense bullae w/ - Nickoslky sign, no oral lesions, Anti-hemidesmosome antibodies in BM, Trx w/ Topical steroids |
|
|
What causes chronic blistering of sun-exposed skin and possible pseudoscleroderma? What causes this disease? RF? Dx? Trx? |
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda - Def in uroporphyringen decarboxylase - RF = Hep C, EtOH, excess Fe - Dx = ↑ plasma porphyrins - Trx = Phlebotomy + Hydroxychloroquine |
|
|
What are the 4 types of melanoma? |
Superficial Spreading - MC, grows laterally then vertically later Nodular - vertical growth, rapidly invasive Acral Lentiginous - least common, on palms/soles/nailbeds Lentigo Maligna - very slow vertical growth |
|
|
What is the treatment for melanoma |
Surgical Excision - If "In situ" → ½ cm margin - If < 2 cm in size → 1 cm margin - If > 2 cm in size → 2 cm margin w/ LN dissection |
|
|
What is trx for vitiligo? What conditions is it associated with? |
Topical Steroids (1st line) & avoid tanning Tacrolimus (or other calcineurin inhibitors) if severe or resistant Associated with hypothyroidism and autoimmune disorders |
|
|
What is the name of the following lesions? - Blue, compressible mass that does not regress - Red-pink nodule on a child that is often confused w/ melanoma - Diffuse stress-related hair loss |
Cavernous Hemangioma Spit Nevus Telogen Effuvium |
|
|
What is the USPSTF recommendations for Cholesterol screen in patients without CAD risk factors? |
Start at age 35 in men age 45 in females Q 5 yrs |
|
|
What are the following vitamins described? - Niacin - Ribofalvin - Def causes ↑ RBC fragility - Def causes peripherial neuropathy, angular cheliosis, and glositis |
- Vit B₃ = Niacin - Vit B₂ = Riboflavin - Vit E - Vit B₁₂ |
|
|
What is the order of default surrogate decision-maker in most states? |
1) Patient's Spouse 2) Patient's Adult Children 3) Patient's Parents 4) Patient's Siblings
|
|
|
What are the 4 elements of a malpractice claim? |
1) Duty of Care - Dr.'s obligation to conform to a reasonable standard of care 2) Breach of Duty - failure to conform to standard of care 3) Harm 4) Causation - breach of duty deemed to cause of harm |
|
|
What is "Vicarious Liability?" |
Supervisors are legally responsible for the actions of their those under their direct supervision |
|
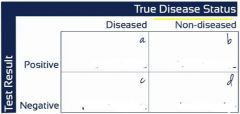
What are the formulas for sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV? |
Sensitivity = A / A + C Specificity = D / D + B PPV = A / A + B NPV = D / D + C |
|
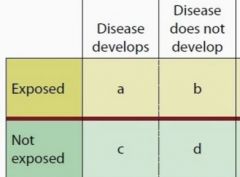
What is the formula for RR? What do its values mean? What study is it associated with? |
RR = (A / A+B) / (C / C+D) RR > 1 = exposure ↑ risk of developing disease RR = 1 = no association RR < 1 = exposure ↓ risk of developing disease *Used in Cohort Study |
|
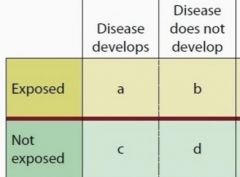
What is the formula for OR? When does it estimate RR? What study is it associated with? |
OR = (A/B) / (C/D) Estimates RR when disease prevalence is low *Used in Case-Control Study |
|
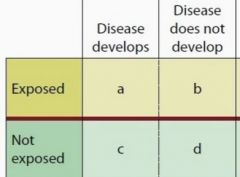
What is the formula for AR? ARR? NNT? |
AR = (A / A+B) - (C / C+D) ARR = (C / C+D) - (A / A+B) NNT = 1/ ARR |
|
|
What is the formula for confidence interval? |
CI = mean +/- (Z x SEM) - If 90% CI, Z = 1.5 - If 95% CI, Z = 2 - If 99% CI, Z = 2.5 |
|
|
What percent of the study population falls within 1 SD, 2 SD's, 3 SD's of the mean if it assumed to have normal distribution? |
1 SD = 68% of population 2 SD = 95% of population 3 SD = 99% of population |
|
|
What is the difference between a Case-control and a Cohort Study? |
Case-Control Study - Looks retrospectively at a group w/ disease (cases) and group w/out disease (controls) to ID risk factors. OR Cohort Study - Usually prospectively looks at a group with risk factor exposure (cohort) to see if they develop disease. RR calculated |
|
|
What are the following types of Biases? - Screening detects slowly progressive cases of a disease and misses rapidly progressive diseases - Subject's awareness of observation alters their reporting of subjective findings - Study groups are not treated the same - Pts with a certain med hx are more likely to participated in a study related to condition even though they don't represent pop |
- Length Bias - Observation Bias - Procedure Bias - Self-Selection Bias |

