![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a rotary valve, and what are some examples? |
90 Degree rotation yields full open - Ball - Butterfly - Plug valves |
|
|
What is a linear valve, and what are some examples? |
Multiple turns of a threaded shaft moves valve - Gate valve - Globe valve - Diaphragm valve |
|

What type of valve is this? |
Plug valve |
|
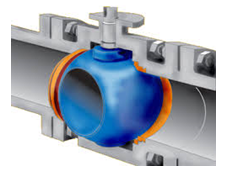
What type of valve is this? |
Ball valve |
|

What type of valve is this? |
Butterfly valve |
|

What type of valve is this? |
Gate valve |
|
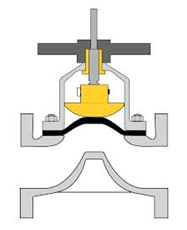
What type of valve is this? |
Diaphragm valve |
|
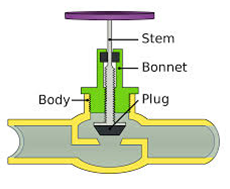
What type of valve is this? |
Globe valve |
|
|
What are pressure regulating valves? |
Valves that control water pressure. They operate by restricting flows. |
|
|
What are pressure regulating valves used for? |
They are used to deliver water from a high pressure system to a low pressure system. |
|
|
Air relief valves combine what 3 functions? |
1) Allow air to escape when filling a main 2) Permit air to enter when draining a main 3) Allow entrained air to escape when a line is operating under pressure
Note: can't be installed in areas that flood |
|
|
How does a pressure relief valve work? |
It provides surge control by venting excess pressure and prevents water hammer damage |
|
|
What does a backflow prevention valve do? |
It stops the flow of an unapproved and possibly contaminated supply into the domestic system. |
|
|
What is a dry barrel hydrant? |
A hydrant that is drained and is dry when not in use. Operating valve is at the bottom of the hydrant. Good in areas that freeze. |
|
|
What is a wet barrel hydrant? |
A hydrant that always has water in it. Only good in areas where the temperature never gets below freezing. |
|
|
What is the primary function of a water meter? |
To measure and display the amount of water passing through it. |
|
|
What are some benefits of metering? |
- Accurate billing - Amount of water produced can be determined - Unaccounted for water can be determined - Capacities of pipelines can be determined - Billed usage prevents waste |
|
|
What are some factors that affect meter selection? |
- Accuracy of meter at your flows - Minimum head loss - Durability - Precision - Ease of repair - Spare parts availability - Price |
|
|
Low flow meters are: a) displacement type b) velocity type |
a) displacement type b) velocity type |
|
|
List 2 low flow meters. |
- Nutating-disc (nodding) - Piston |
|
|
High flow meters are: a) displacement type b) velocity type |
a) displacement type b) velocity type |
|
|
List some high flow meters. |
- Turbine - Propeller - Venturi - Electronic - Insertion |
|
|
Which type of meters are commonly used for customer services? |
Displacement type meters |
|
|
How do displacement type meters work? |
They measure the flow by registering the number of times the meter chamber is filled and emptied. |
|
|
How do velocity type meters work? |
They measure the velocity of flow passed across a section of a known area |
|
|
What is a compound meter? |
A compound meter is a combination of displacement and velocity meters in one housing |
|
|
How does a compound meter work? |
At low flows, flow is directed to displacement meter. At high flows, the valve to velocity meter opens and starts operating. |
|
|
Characteristics of good water quality include: |
- Free of pathogens - Free of toxic chemicals - Attractive taste and odor - Not corrosive to distribution system |
|
|
What do primary drinking water standards deal with? |
Potentially harmful (toxic or disease) constituents |
|
|
What do secondary drinking water standards deal with? |
Aesthetic concerns |
|
|
What contributes to water quality degradation in distribution systems? |
- Cross connections - Corrosion - Biological growth - High temperatures - Unusual flows - Time in system - Dead ends |
|
|
What is a cross connection? |
An unprotected connection between potable and non-potable waters. |
|
|
What causes more waterborne disease than any other factor? |
Cross Connections |
|
|
What is the most vulnerable part of the distribution system? |
Storage |
|
|
What are test coupons? |
Thin strips of metal into main, leave for a couple months, weigh it, determine corrosiveness in line. |
|
|
What is telemetering? |
Remotely reading a meter/station from a control room. Via phone lines/microwave/etc. |
|
|
What are the water quality parameters that are monitored in the distribution system? |
- Turbidity - Coliform - Chlorine (should be a residual) - Trihalomethanes - Lead & Copper (measured in home/business) |

