![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
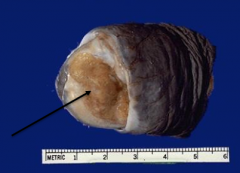
|
Penile Carcinoma (erythroplasia of queyrat)
*red rash leison on glans |
|
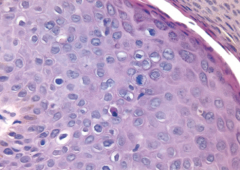
Taken from shaft of penis |
Penile Carcinoma in situ (Bowen Disease)
*atypical squamous cell that do NOT break through basement membrane |
|
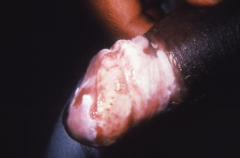
|
Could be either Balantitis (benign) or penile carcinoma in situ ... requires biopsy! |
|

|
Penile Carcinoma in situ (bowenoid papulosis)
*can present as non-healing warts *associated with HPV type 16 |
|
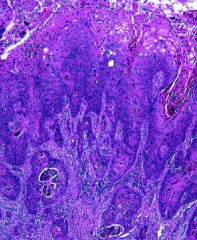
Take from glans of penis |
Invasive Penile Carcinoma
*broke through basement membrane *spreads quickly to inguinal LN |
|
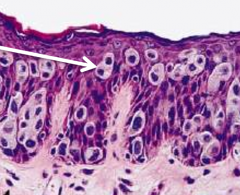
Taken from scrotum |
Extramammary Paget's Disease
*intraepidermal adenocarcinoma w/ clear cytoplasm cells *often occurs with other underlying malignancy |
|
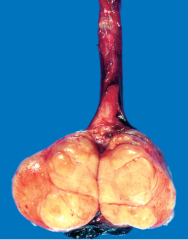
Pt complained of one testis feeling heavier |
Seminoma
*"Fish-flesh" appearance with no hemorrhage or necrosis *most common germ cell tumor of testis |
|
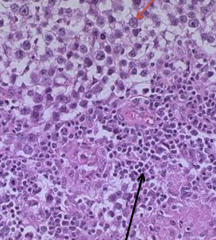
Stained + for placental Alk. Phos. |
Seminoma
*sheets of uniform cells with large central nuclei with 1-2 nucleoli (red) *area infiltrated with non-tumor lymphocytes (black) |
|
taken from testis |
Intratubular Germ Cell Neoplasia (ITGCN)
*carcinoma in situ that most germ cell tumors arise from (50% progress to tumor in 5yrs) *associated with infertility |
|
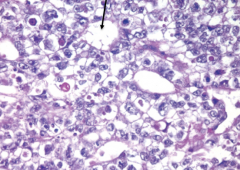
taken from testis |
Embryonal Carcinoma
*small tumor usually occuring in mixed germ cell tumors *Alveolar/Tubular (black arrow) appearance |
|
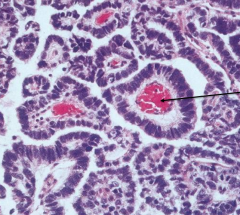
Taken from testis of a toddler with elevated AFP levels |
Yolk Sac (Endodermal Sinus) Tumor
*Yellow mucinoid tumor that often occurs in a mixed germ cell tumor *"Schiller-Duval Bodies" (arrow - endodermal sinuses) |
|
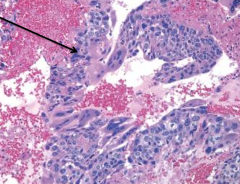
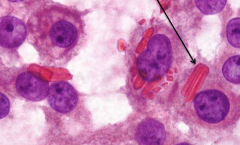
Taken from testis of man with high levels of hCG |
Choriocarcinoma
*malignant tumor usually part of mixed germ cell tumor *composed of cytotrophoblastic and syncytiotrophoblastic cells (arrow) with hemorrhage and necrosis |
|
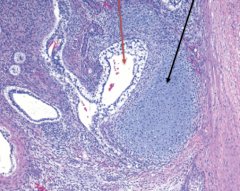
taken from testis |
Teratoma
*composed of many germ cell types -- this one has glandular (red) and cartilage (black) tissue *more common as part of mixed tumor type -- especially if it occurs in an adult |
|
taken from testis |
Sertolli Cell Tumor
*rare, benign, derived from sex cords |
|
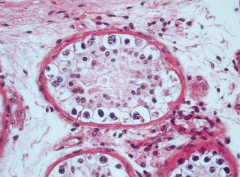
taken from testis in pt with precosious puberty |
Leydig Cell Tumor
*rare, benign, stromal cell tumor that secretes testosterone causing early puberty *characterized by "Crystalloid of Reinke" (arrow) |
|
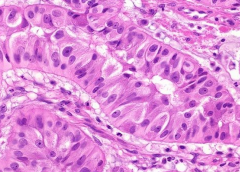
taken from prostate |
Prostate Cancer
*simple glandular appearance occurring in peripheral zone of prostate *can spread via LN to bone to cause OsteoBLASTIC lesions |
|
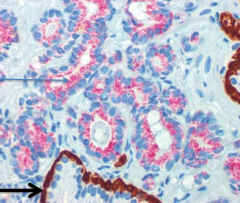
taken from prostate |
Prostate Cancer
*staining shows cancer cell in pink (upper arrow) with a lack of basal cells (bottom arrow) |
|
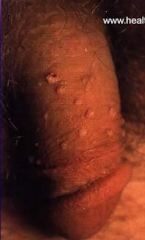
|
Condyloma Accumulatnum (genital warts)
*HPV 6 or 11 *Koilocytic change, not malignant |
|
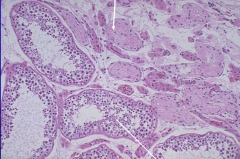
|
Testricular Atrophy
*Causes: Iliac atherosclerosis (most common), orchitism, cryptorchidism, Estrogen *Normal & Sclerosed tubules w/ Leydig hypertrophy |
|
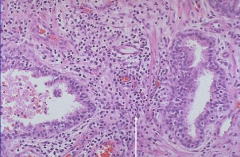
Pt has dysuria, frequeny, low-back pain, and Increased PSA |
Prostatitis
*Acute commonly bacterial (E. coli) *Chronic commonly abacterial (Chlamydia, Uroplasma) *Arrow shows leukocyte infiltrate |
|
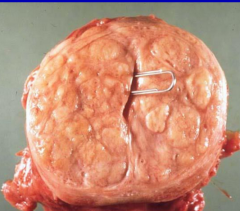
|
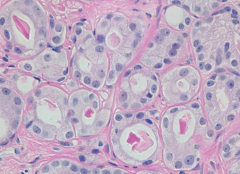
BPH (Nodular Hyperplasia)
*Obstructive LUDS (can cause bladder dilation/hypertrophy and stones), slightly elevated PSA (<10) |
|
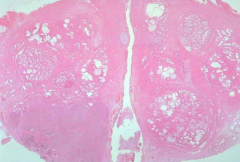
|
BPH (Nodular Hyperplasia)
*Distinct nodules in Periurethral & Transitional zones due to increased DHT sensitivity |
|
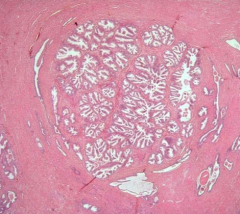
|
BPH (Nodular Hyperplasia)
*complex gland hyperplasia |

