![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Breast cancer incidence, lifetime, for women?
|
1/8
|
|
|
name of the structure that connects the mamary glands to the 20-40 lobules?
|
lactiferous ducts
|
|
|
2 blood sources for the breast?
-locations |
internal mammary artery: inner quadrants
lateral thoracic artery: outer quadrants |
|
|
Discuss how the following hormones are able to contribute to milk production
-estrogen -progesterone -prolactin -oxytocin |
-estrogen: ductal development, fat deposition
-progesterone: stromal development (lobule/alveolar( -prolactin: involved in milk production -oxytocin: milk letdown |
|
|
Describe discharge that is most concerning
|
bloody/serosanguinous, unilateral, spontaneous, from a single duct --> these are all associated with a mass
|
|
|
Compare:
bloody discharge vs. serous discharge vs. milky discharge vs. yellow-tinged vs, purulent discharge |
Bloody: intraductal papilloma, invasive papillary cancer
Milky: pregnancy, pituitary adenoma, hypothyroidism Serous: Normal menses, OCPs, fibrocystic change, early pregnancy Yellow-tinged: fibrocystic change, galactocele (tumor [benign] in the milk ducts) purulent: abscess |
|
|
Imaging modalities of breast cancer
-under 30 -over 30 |
-over 30: mammography
-under 30: ultrasound (highly dense breast tissue) |
|
|
What is the appropriate evaluation technique for a nonpalpable abnormal mammogram finding?
|
wire guided excision
|
|
|
what is the appropriate evaluation technique for a solid palpable mass
-under 30 -over 30 |
under 30: FNA
over 30: core needle biopsy |
|
|
If an FNA is nondiagnostic, the next step is to perform...
|
an excisional biopsy
|
|
|
Define: fibrocystic change
-overview -sx -epidemiology |
spectrum of findings related to an *exaggerated stromal response to hormones/growth factors*
-painful breast masses, multiple, bilateral, fluctuate rapidly in size -30-40 is peak age |
|
|
Define: fibroadenoma
|
benign tumors with glandular or stromal components
-rubbery, nontender -ages 20-35 |
|
|
Define: cystosarcoma phyllodes
|
rare variant of fibroadenoma --> epithelial and stromal proliferation
-rapid grwoth -large mass -most are benign, but have **agressive malignancies** |
|
|
Define: Intraductal papilloma
|
-benign solitary lesion that involves the epithelial lining of the lactiferous ducts
-most ocmmon cause of bloody nipple discharge w/out concurrent mass -tx by excising the duct |
|
|
Define: Mammary Duct Ectasia
|
subacute inflammation of ductal system, which dilates the mammary glands
benign |
|
|
BIggest risk factor for breast cancer?
|
increasing age
|
|
|
Define: Ligament of Cooper
-what is it -dimpling |
Supportive ligament that holds breast tissue in place. Skin dimpling occurs when tether of hte cooper ligament occrus from masses underneath it.
|
|
|
Define: Lobular Carcinoma in Situ
|
neoplastic epithelial cells w/in th ebreast lobule, no invasion into stroma
observe w/out therapy after biopsy confirmation |
|
|
Differentiate:
-DCIS -LCIS -infiltrating ductal carcinoma -infiltrating lobular carcinoma most common? |
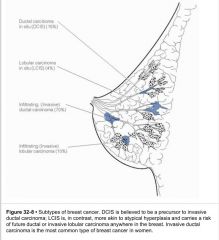
most common is infiltrating ductal carcinoma
|
|
|
DCIS vs. LCIS
-malignancy potential |
-DCIS has a higher invasive potential than LCIS
|
|
|
Define: DCIS
-compare to LCIS -detection? -tx? |
-malignant epithelial cells
-higher potential to progress to invasive carcinoma than LCIS -detected with mamography -tx with excision, mastectomy, radiation |
|
|
Name the four types of invasive breast cancer
|
-infiltrating ductal carcinoma (70% of breast cancer)
-infiltrating lobular carcinoma -Paget's disease of the nipple --> eczematous change, crusting, scaling, erosion -inflammatory breast carcinoma --> extremely aggressive, dermal lymphatic invasion, *peau d'orange* |
|
|
What are the 3 tumor receptors whose status we check regulalry?
|
--Estrogen
--Progesterone --Her2/neu |
|
|
when is adjuvant hormone therapy used?
|
in patients who have receptor positive cancers
--> tamoxifen is used, competitively binds estrogen receptors, inhibits the effect of estrogen on breast tissue |
|
|
Followup for breast cancer?
|
physical exam every...
-3-6 months until year 3 -6-12 months for years 4-5 -1 year for year 5+ |
|
|
When should women start getting mammograms?
|
q1-2 years @40
q1 year @ 50 |

