![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Database
|
A structured collection of data stored for use by one or more applications.
Also contains the relationships between data items and groups of data items |
|
|
Database Mgmt System
|
DBMS
A suite of programs for contructing and maintaining the database and for offering ad hoc query facilities to multiple users and applications |
|
|
Structured Query Language
|
SQL
Provides uniform interface to the database for users and applications Developed by IBM in mid 1970's Used to define schema, manipulate,a nd query data in a relational database |
|
|
Relational Database
|
A relation is a flat table.
A database of them uses multiple tables related to one another by a designed key |
|
|
Table of Data consisting of rows
|
Tuples
|
|
|
Table of Data consisting of columns
|
Attributes
|
|
|
Primary Keys
|
A portion of a row used to uniquely identify a row on a table
Consists of 1 or more column names Must be unique to each Tuple |
|
|
Foreign Keys
|
Creates a relationship between two tables, the attributes that define the primary key in one table must appear as attributes in another table.
Can appear multiple times in a table |
|
|
View
|
A virtual table
|
|
|
Database Access Control
|
DAC
Centralized Admin Ownership-based Admin Decentralized Admin |
|
|
Centralized Admin
|
A small number of privileged users may grant and revoke access rights
|
|
|
Ownership-based Admin
|
The owner (creator) of the table may grant and revoke access rights to the table
|
|
|
Decentralized Admin
|
In addition to granting and revoking access rights to the table, the owner of the table may grant and revoke authorization rights to other users, allowing them to grant and revoke access rights to the table
|
|
|
SIEM
|
Security Intrusion and Event Mgmt
Writing a cybersecurity plan to protect a DB |
|
|
Types of malicious software
|
Malware
A program that is inserted into a system, usually covertly, with the intent of compromising the CIA of the victim's data, applications, or operating system or otherwise annoying or disrupting the victim. |
|
|
Viruses
|
Malware that, when executed, tries to replicate itself into other executable machine or script code
When it succeeds, the code is said to be infected. When the infected code is executed, so is the virus. |
|
|
Infection Mechanism
|
The means by which a virus spreads or propagates, enabling it to replicate.
The mechanism is also referred to as the Infection Vector. |
|
|
Trigger
|
The event or condition that determines when the payload is activated or delivered, sometimes know as a Logic Bomb.
System events, a date, the presence of another program, the capacity of the disk exceeding some limit, the number of times a virus has cloned itself to propogate |
|
|
Payload
|
The variety of actions executed by malware
What the virus does besides spreading. May involve damage benign but noticeable activity |
|
|
Dormant
|
The virus is Idle
Will eventually be activated by a trigger Not all viruses have this stage |
|
|
Propagation
|
The means the malware uses to spread
Virus places a copy of itself into other programs or into certain system areas on the disk. Copy may not be identical to the propagating version Viruses often morph to avoid detection Repeat procedure. |
|
|
Triggering
|
The virus is activated to preform the function for which it was intended. As with the dormant phase, the triggering phase can be caused by a variety of triggers (s
|
|
|
Execution Phases
|
The function is preformed. The function may be harmless, such as a message on the screen, or damaging, such as the destruction of programs and data files.
|
|
|
Boot Sector Infector
|
Infects a master boot record or boot record and spreads when a system is booted from the disk containing the virus.
|
|
|
Polymorphic Virus
|
A virus that mutates with every infection, making detection by the "signature" of the virus impossible.
Creates copies during replication that are functionally equivalent but have distinctly different bit patterns, in order to defeat programs that scan for viruses. |
|
|
Metamorphic Virus
|
As with a polymorphic virus, a metamorphic virus mutates with every infection. The difference is that a metamorphic virus rewrites itself completely at each iteration, increasing the difficulty of detection. Metamorphic viruses may change their behavior as well as their appearance.
|
|
|
Worms
|
A computer program that can run independently and can propagate a complete wroking version of itself onto other hosts on a network, usually by exploiting software vulnerabilities in the target system.
|
|
|
Scanning and Fingerprinting
|
The first function in the propagation phase for a network worm
Searching and for other systems to infect. Identifies potential systems running the vulnerable service and then infects them |
|
|
Spam emails/Trojans
|
Social Engineering
A computer program that appears to have a useful function, but also has a hidden and potentially malicious function that evades security mechanisms, sometimes by exploiting legitimate authorizations of a system entity that invokes the Trojan Horse Program. |
|
|
System Corruption
|
s
|
|
|
Bots
|
Program activated to an infected machine that is activated to launch attacks on other machines.
|
|
|
Remote Control
|
Command and Control
|
|
|
Phishing
|
Given sufficient details, the attacker can "assume" the user's identity for the purpose for obtaining credit, or sensitive access to other resources.
Exploits social engineering to leverage user's trust my masquerading as communications from a trusted source. |
|
|
Backdoor/Trapdoor
|
Any mechanism that bypasses a normal security check
it may allow unauthorized access to functionality in a program, or onto a compromised system. Secret entry point int a program that allows someone who is aware for the backdoor to gain access without going through the usual security access procedures. |
|
|
Rootkit
|
Set of hacker tools used after attacker has broken into a computer system and gained root-level access.
|
|
|
Countermeasures
|
Anti-virus
Detection, Identification, and Removal Host-based Scanners |
|
|
Stuxnet Lecture
|
Megavirus
A thing of beauty |
|
|
Adware
|
Advertising that is integrated into software.
Can result in pop-up ads or redirection of a browser to a commercial site |
|
|
Attack Kit
|
Set of tools for generating new malware automatically using a variety of supplied propagation and payload mechanisms.
|
|
|
Auto-rooter
|
Malicious hacker tools wised to break into new machines remotely
|
|
|
Downloader
|
Code that installs other items on a machine that is under attack. It is normally included in the malware code first inserted on to a compromised systems to then import a larger malware package.
|
|
|
Drive-by-Download
|
An attack using code in a compromised Web site that exploits a browser vulnerability to attack a client system when the site is viewed.
|
|
|
Exploits
|
Code specific to a single vulnerability or set of vulnerabilities
|
|
|
Floders (DoS client)
|
Used to generate a large volume of data to attack networked computer systems, by carrying out some form of denial-of-service (DoS) attack
|
|
|
Key Loggers
|
Captures keystrokes on a compromised system
|
|
|
Macro virus
|
A type of virus that uses macro or scripting code, typically embedded in a document, and triggered when the document is viewed or edited, to run and replicate itself into other such documents.
|
|
|
Mobile code
|
Software (e.g. script, macro, or other portable instruction) tha can be shipped unchanged to a heterogenous collection of platforms and execute with identical semantics
|
|
|
Spammer Programs
|
Used to send large volumes of unwanted e-mail
|
|
|
Spyware
|
Software that collects information from a computer and transmits it to another system by monitoring keystrokes, screen data, and/or network traffic; or by scanning files on the system for sensitive info
|
|
|
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
|
An action that prevents or impairs the authorized use of networks, systems, or applications by exhausting resources such as central processing units (CPU), memory, bandwidth, and disk space
|
|
|
Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
|
The use of multiple systems to generate an attack.
Typically compromised user workstations or PCs. |
|
|
Reflection Attacks
|
The attacker sends packets to a known service on the intermediary with a spoofed souce address of the actual target system. When the intermediary responds, the response is sent to the target. Effectively this reflects the attack off the intermediary, which is termed the reflector.
|
|
|
Amplification Attacks
|
A variant of reflector attacks and also involve sending a packet with a spoofed source address for the target system to intermediaries.
Difference: they generate multiple response packets for each original packet sent |
|
|
DNS Amplification Attacks
|
Uses packets directed at a legitimate DNS server as the intermediary system. Attackers gain attack amplification by exploiting the behavior of the DNS protocol to convert a small request into a much larger response.
|
|
|
Application-based Bandwidth Attacks
|
Attempt to take advantage of the disproportionally large resource consumption at a server.
|
|
|
SIP Flood
|
SIP - Session Initiation Protocol
Exploits the fact that |
|
|
HTTP-based Attacks
|
Flood
-an attack that bombards Web servers with HTTP requests Slowloris -exploits the common server technique of using multiple threads to support multiple requests to the same server application |
|
|
Defenses against DoS Attacks
|
-Enforcing policies of resource consumption
-Providing backup resources available on demand -Modify systems and protocols on the internet to reduce the possibility of an attack -Look for suspicious behavior patterns -Track the attack back to its source to prevent it from happening again |
|
|
Intruder
|
Hacker or Cracker
|
|
|
Masquerader
|
An individual who is not authorized to use the computer and who penetrates a system's access controls to exploit a legitimate user's account.
|
|
|
Misfeasor
|
A legitimate user who accesses data, programs, or resources for which such access is not authorized, or who is authorized for such access but misuses his or her privileges.
|
|
|
Clandestine User
|
An individual who seizes supervisory control of the system and uses this control to evade auditing and access controls or to suppress audit collection.
|
|
|
Criminal Enterprise
|
$$$
Pattern of Behavior: -Act quickly and precisely to make their activities harder to detect -Exploit perimeter through vulnerable ports -Use Trojan horses (hidden software) to leave back doors for reentry -Use sniffers to capture passwords -Do not stick around until noticed -Make few or no mistakes |
|
|
Internal Threat
|
Pattern of Behavior:
-Create network accounts for themselves and their friends. -Access accounts and applications they wouldn't normally use for their daily jobs. -E-mail former and prospective employers. -Conduct furtive instant-messaging chats. -Visit Web sites that cater to disgruntled employees, such as f*dcompany.com. -Perform large downloads and file copying. -Access the network during off hours. |
|
|
Security Intrusion
|
A security event, or combo of multiple security events, that constitutes a security incident in which an intruder gains, or attempts to gain, access to a system (or system resource) without having authorization to do so.
|
|
|
Intrusion Detection
|
A security service that monitors and analyzes system events for the purpose of finding, and providing real-time or near real-time warning of, attempts to access system resources in an unauthorized manner.
|
|
|
SIEM Software
|
Security Intrusion and Event Management
Writing cyber security plan to protect DB |
|
|
Intrusion Detection Systems
|
IDS
|
|
|
Host-based IDS
|
Monitors the characteristics of a single host and the events occurring within that host for suspicious activity.
|
|
|
Network-based IDS
|
Monitors network traffic for particular network segments or devices and analyzes network, transport, and application protocols to identify suspicious activity.
|
|
|
Honeypots
|
Divert an attacker from accessing critical systems
Collect info about the attacker's activity Encourage the attacker to stay on the system long enough for admin to respond. |
|
|
Sensors
|
Responsible for collecting data.
May be any part of a system that could contain evidence of an intrusion. EX: -Network Packets -Log Files -System Call Traces |
|
|
Analyzers
|
Receive input from one or more sensors or from other analyzers.
Responsible for determining if an intrusion has occurred. Output = an indication that an intrusion has occurred. |
|
|
User Interface
|
Enables a user to view output from the system or control the behavior for the system
Can equate to a manager, director, or console component. |
|
|
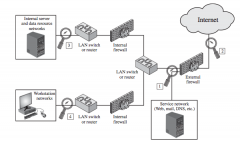
NIDS Sensor Deployment
Probably the Essay MEMORIZE THIS!!! |
|
|
Firewall Types and Locations and Configurations
|
Packet Filtering
Stateful Inspection Application Level Gateway Circuit Level Gateway Host-Based Personal |
|
|
Packet Filtering
|
Applies a set of rules to each incoming and outgoing IP packet and then forwards or discards the packet
2 way firewall |
|
|
Stateful Inspection
|
Reviews the same packet info as a packet filtering firewall, but also records info about TCP connections
|
|
|
Circuit Level Gateway
|
Circuit-level Proxy
Can be a stand alone system or can be a specialized function performed by an application-level gateway for certain applications. Does not permit end-to-end TCP connection Sets up 2 with it as a middle man |
|
|
Application Level Gateway
|
Application Proxy
Acts as a relay of application level traffic STATEFUL |
|
|
Virtual Private Networks
|
VPN
Consists of a set of computers that interconnect by means of a relatively unsecured network and that makes use of encryption and special protocols to provide security. Linked by LANS |
|
|
Firewall Restrictions (External vs Internal)
|
External
-Placed at the edge of a local or enterprise network, just inside the boundary router that connects to the Internet or some wide are network (WAN) Internal -Protect the bulk of the enterprise network |

