![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define a circuit |
A never ending looped pathway for electrons and consists of sources, loads and conductors. |
|
|
Define current |
The continuous movement of free electrons through the conductors of a circuit |
|
|
Define voltage |
The potential energy difference between two points of Separated electric charge |
|
|
Define resistance |
A materials opposition to the flow of an electrical current |
|
|
Define resistance |
A materials opposition to the flow of an electrical current |
|
|
Define power |
Electric power is the rate at which work is done |
|
|
Define grounding |
A permanent and continuous conductive path to earth |
|
|
What is the main difference between an analog and a digital waveform? |
Analog quantity has a continuous set of values Digital quantity has a discrete set of values |
|
|
What are three advantages of digital technology |
-Compact storage -Less affected by noise -Ease of fabrication -Programmable operation -Data processed and transmitted more fission |
|
|
How can an analog waveform be converted to digital waveform |
Sampling and quantization using a analog to digital converter |
|
|
Digital electronics in____? |
Binary |
|
|
The voltages used to represent a 1 (high) and a 0(low) are called? |
Logic levels |
|
|
The interdisciplinary field the comprises both analogue and digital components are known as? |
Mechatronics |
|
|
Define binary
What is it comprised of? |
A two state number system
0’s & 1’s called bits |
|
|
What is positive logic |
1 is represented by the higher voltage |
|
|
In the conventional numbering system (decimal) We use how many digits? |
10
0-9 |
|
|
What kind of numbering system Do we use in a digital circuit? |
Binary (2 digits) |
|
|
How many bits in a byte?
How many bytes in a word? |
8 bits in a byte
2 bytes (16 bits) In a word |
|
|
In practical situations Binary digits are represented by ______ _______? |
Voltage levels |
|
|
If binary 1 is high between 2-5volts, and low is between 0-0.8v.
What does 0.8-2v represent? |
Invalid voltage |
|
|
A digital waveform is made up of a _________ ___ __________. |
Series of pulses |
|
|
What is the difference between An IDEAL PULSE and a NON-IDEAL PULSE |
- ideal pulse changes state instantaneously
- non ideal does not due to effects (droop, ringing etc) |
|
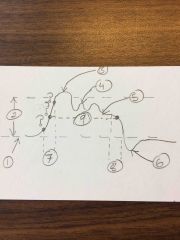
Label 1-9 |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Define a PERIOD (T)
What’s the formula in relation to frequency |
A periodic pulse waveform is one that repeats itself at a fixed interval
T(secs) = 1/f(Hz)
|
|
|
Define frequency (f) |
The rate at which it repeats it self and is measured in hertz |
|
|
Define duty cycle
Formula? |
The ratio of the pulse width(tw) to the period (T)
Duty cycle= (tw/T)*100% |
|
|
The time required for a post to go from low to high is called the_________.
When is this measured? |
Rise time (tr)
10% of pulse amplitude to 90% |
|
|
Fall time (tf) is measured from _______to________ of the pulse ________. |
90% to 10%. Amplitude |
|
|
What is the measure of the duration of the pulse?
How is it defined? |
Pulse width (tw)
Time interval between both 50% points of rising and falling edges |
|
|
Define amplitude |
The height from the baseline, 0 to 100% |
|
|
A waveform can be classified as either _________ or _________. |
Periodic or non-periodic |
|
|
Describe the characteristics of a digital waveform |
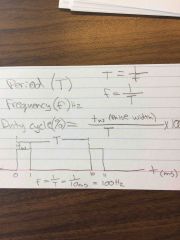
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Define a bit time |
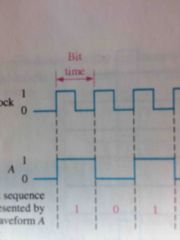
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Define data |
Groups of bits that convey some type of info |
|
|
What is a timing diagram |
A graph of the waveforms showing the actual time relationship between of two or more waveforms and how each waveform changes in relation to the others |
|
|
What is the difference between serial and parallel?
Advantage and disadvantage of each? |
Serial Data is sent one bit at a time along a single line Advantage- one line required Disadvantage- more time
Parallel Is sent in a group of bits on separate lines at the same time |
|
|
What are logic functions |
Building blocks for more complicated digital circuits like computers using gates |
|
|
How can logic functions be represented |
-symbols -truth table - algebraically( Boolean) -ladder logic -timing diagrams |
|
|
An inverter describes what gate |
NOT |
|
|
What is the uncommon condition of an AND gate |
1*1=1 ON |
|
|
What is the uncommon conditioning of an OR gate |
0+0=0 OFF |
|
|
What is the uncommon condition a NAND GATE |
1’*1’=0 OFF
|
|
|
What is the uncommon condition a NOR GATE |
0*0=1 ON |
|
|
What condition are you looking for a XOR GATE |
Opposites |
|
|
What condition are you looking for a XNOR GATE |
Same |
|
|
What within a gate compares the quantities indicating = or not= |
Comparator
Magnitude comparison |
|
|
What is the best way to analyze a circuit of logic gates |
Truth table |
|
|
Define encoder
Define decoder |
Decimal to binary conversion
Binary to hexadecimal conversion |
|
|
To broad types of digital integrated circuits are_______ & _________ |
Fix function and programmable |
|
|
2 examples of a data storage device are |
Register and a flip-flop |
|
|
Name an analog Quantity other than temperature and sound |
Speedometer |

