![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
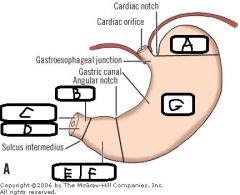
h. What is contained within (G)? |
a. Fundus b. Pylorus c. Pyloric Sphincter d. Pyloric Canal e. Antrum f. Pyloric Gland area g. Body h. Oxyntic Mucosa |
|
|
a. What are the sections of the Stomach? b. What are the Sphincters of the Stomach? c. The luminal surface of the Stomach has deep folds. Name 3 things found on the luminal surface |
a. - Fundus - Body (Oxyntic Mucosa) - Antrum (Pyloric area) b. - Pyloric - Gastroeosophageal c. - Gastric Pits - Gastric Glands - Variety of secretory cells |
|
|
Describe the 2 types of motility in the stomach + how they are made |
- Normal Peristaltic action: Basic Electrical Rhythm (BER) - Strong Contractions: From the Antrum |
|
|
Name 3 functions of the Stomach |
1. Stores ingested food until emptied ---> SI 2. Secretes HCL and digestive enzymes 3. Converts contents into Chyme |
|
|
a. Where are Gastric Glands found? b. What kind of cells are found in Gastric Glands? c. Give 3 Examples of cells which are found in Gastric Glands d. What do Exocrine secretions collectively make up? |
a. - Pyloric Glands - Oxyntic Mucosa b. Exocrine cells c. - Chief cells - Parietal cells - Mucous cells d. Gastric Juice |
|
|
a. What do Chief cells produce? (once activated) b. What is the stimulus for Chief cells? c. What do Parietal cells produce? d. What is the stimulus for Parietal cells? e. Give 3 functions of HCL |
a. Pepsinogen b. Ach + Gastrin c. HCL + Intrinsic Factor d. ACh + Gastrin + Histamine e. 1. Activate Pepsinogen 2. Kill Microorganisms 3. Destroy Connective Tissue |
|
|
a. Name the 3 sections of the SI b. How long is the SI c. The SI is the primary site for what 2 thing? d. How does Chyme move through the SI? e. How long does it take for contents to move through SI? |
a. - Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum b. 8-10 feet c. - Digestion - Absorption d. Via Segmentation e. 3-5 hours |
|
|
a. What is the difference between Segmentation and Peristalsis? b. Apart from Motility, give 2 functions of Segmentation c. Apart from Segmentation, what facilitates movement along SI |
a. Segmentation: Circular muscle (Back and forth) Peristalsis: Longitudinal Muscle b. - Mixing Chyme - Facilitates Absorption c. BER (Basic Electrical Rhythm) |
|
|
Name 3 things which increase the SA of the epithelium of the SI (+ by how much) |
- Circular folds (^ SA 3 fold) - Villi (^ SA 10 fold) - Microvilli (^ SA 20 fold) |
|
|
Name the 3 membrane bound enzymes found on Microvilli (of SI) |
1. Enterokinase 2. Disaccaridases 3. Aminopeptidases |
|
|
Name 3 substances which are secreted into the Duodenum |
1. Bile 2. Pancreatic Juice 3. Intestinal Juice |
|
|
a. Name the 3 areas where digestion occurs b. Name 3 digestion enzymes and which structures they are secreted in (for digestion) |
a. - Mouth - Stomach - Small Intestine b. - Salivary Amylase: Mouth - Pancreatic Amylase: Small Intestine - Disaccharidase: |
|
|
- In the mouth, what are the following broken down into?: a. Glycogen b. Starch c. Cellulose d. Disaccharides |
a. Glycogen + Oligosaccharides b. Starch + Oligosaccharides c. Not broken down d. Not broken down |
|
|
- In the SI, what are the following (FIRSTLY) broken down into? (+ by which enzyme) a. Oligosaccharides b. Glycogen c. Starch - (d.) after these substances are broken down, what is the product broken down into (+ by which enzyme) |
a. Disaccharides (Pancreatic Amylase) b. Disaccharides (Pancreatic Amylase) c.Disaccharides (Pancreatic Amylase) d. Monosaccharides (Disaccharidase) |
|
|
a. Name the structures in which protein digestion occurs b. Name 4 protein digestion enzymes |
a. - Stomach - Small Intestine b. - Gastric Pepsin - Aminopeptidases - Intracellular Peptidases - Pancreatic Proteolytic Enzymes |
|
|
a. Describe protein digestion in the Stomach b. Describe protein digestion in the SI |
a. - Proteins are broken down into large Polypeptides - Using enzyme (Gastric) Pepsin b. - Large Polypeptides are broken down into Dipeptides - Enzymes include: Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxypeptidases - Dipeptides are then broken into Amino Acids - Enzymes involved are Dipeptidases |

