![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
compound stomach functions to
|
act as a fermentation chamber where fodder is broken down into usable metabolites by symbiotic micro-organisms
|
|
|
glandular compartment of the compound stomach
|
rumen
reticulum omasum |
|
|
non-glandular compartment of the compound stomach
|
proventiculus
|
|
|
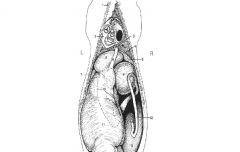
at birth the ____ chamber is the largest
|
abomasum
|
|
|
as an adult the ____chamber is the largest
|
rumen
|
|
|
|
|
|
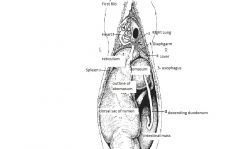
reticulum description
|
lies largely on left side
is most cranial compartment extends from cardia to most cranial part of diaphragm ventrally extends across midline to lie above the xiphiod esophagus empties into both reticulum and rumen at the cardia |
|
|
reticulum features and function
|
sieve for coarse material
forceful contraction fold form honeycomb structure wide ruminoreticular orifce medial walls form reticular groove |
|
|
fine material goes to
|
omasum
|
|
|
coarse material goes to
|
rumen
|
|
|
cardia
|
slit like opening of the esophagus, positioned at the junction of the rumen and reticulum and opens into both chambers
|
|
|
ruminoreticular orifce
|
wide opening between the rumen and reticulum which communicates over the ruminoreticular fold
|
|
|
reticulo-omasal orifice
|
round exit into the omasum at the lower end of the reticular groove
|
|
|
reticuloar groove
|
on the medial wall
extends from cardia to reticulo-omasal orifce mucosal surface lining it is pale and smooth |
|
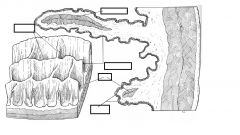
|
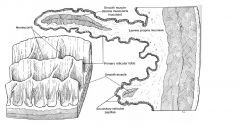
|
|
|
rumen description
|
fills left half of the abdominal cavity
extends across the midline especially caudally and ventrally |
|
|
dorsal sac
|
can be palpated via rectum
dorsal sac is in direct contact with upper park of left flank- auscultation, palpation and access |
|
|
rumen function
|
contractions mix ingesta
fermentation chamber absorption of volatile fatty acids, sodium, water etc papillae increase surface area, assist mixing and act as heating rods rumination eructation |
|
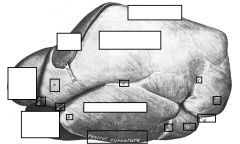
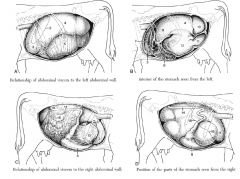
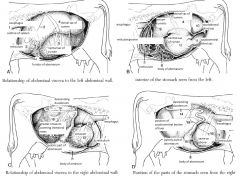
left side of ox
|
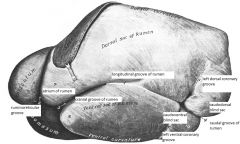
left side of ox
|
|
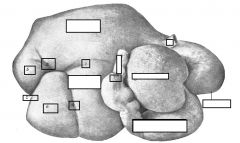
right side of ox
|
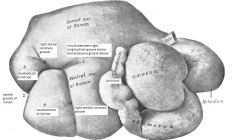
right side of ox
|
|
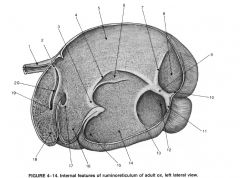
|
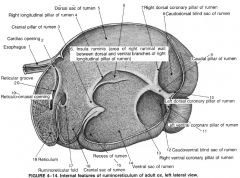
|
|
|
rumen papillae
|
mucosal projections covering the rumen surface
absorb fatty acid vary in height according to age, location, diet long/numerous- ventral and dorsal caudal blind sacs fewer and less prominent in ventral sac shorter or absent in roof of dorsal sac |
|
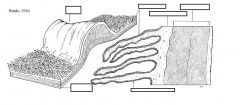
rumen wall
|
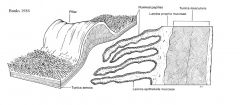
rumen wall
|
|
|
omasum
|
lies mainly on the right of the midline
left side faces the rumen and reticulum right side faces the liver and body wall |
|
|
omasum function
|
absorption of fatty acids, water
transfer of ingesta to abomasum sieve |
|
|
omasum external features
|
spherical to ellpsiodal in shape
has greater and lesser curvatures lower pole has extensive attachment to fundic region of the abomasum much of the right surface is covered by lesser omentum |
|
|
reticulo-omasal orifice
|
opening at the upper end of omasal canal
|
|
|
omaso-abomasal orifice
|
opening at the lower end of the omasal canal
is large and oval partly obscured by the prolapses of the abomasal folds |
|
|
omasal groove
|
runs between the two openings and is the floor of the omasal canal
mucosa is smooth except for a few longitudinal ridges |
|
|
omasal laminae
|
many parallel folds of four different sizes
arise from the greater curvature and sides and project towards the lesser curvature |
|

wall of omasum
|
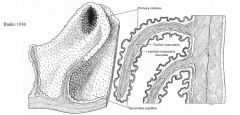
wall of omasum
|
|
|
abomasum
|
glandular stomach
elongated and lies on the abdominal floor proximal part lies between the central sac of the rumen and the reticlulm caudal end flexed around the lower pole of the omasum |
|
|
abomasum position varies with
|
age
pregnancy fullness of different compartment intrinsic abomasal activity contraction of the rumen and reticulum prone to dorso-lateral displacement |
|
|
pylorus
|
opens into duodenum from abomasum
|
|
|
abomasum wall
|
mucosa- rich in glands (fundic, pyloric)
thick muscularis mucosa submucosa muscularis externa (smooth muscle)- thick inner circular layer, thinner out longitudinal layer serosa |
|
|
gastric groove
|
muscular folds roll into a tube when the young animal drinks milk
serves as a conduit for conveying milk from esophagus to abomasum may be induced in adult |
|
|
spiral folds
|
serve to increase surface area
in the region of the omasal-abomasal orifice these folds help produce a plug to limit reflux of ingesta into omasum. |
|
|
torus
|
large swelling that projects from lesser curvature to narrow pyloric passage
|
|
|
reticular groove
|
cardia to reticulo-omasal orifice
bounded by 2 prominent muscular folds |
|
|
omasal groove
|
reticulo-omasal orifice to omaso-abomasal orifice
|
|
|
abomasal groove
|
area with gastric glands
|
|
|
nerve supply to compound stomach
|
branches from dorsal and ventral trunks of the vegus nerve
|
|
|
blood supply to compound stomach
|
branches of the celiac artery
veins drain into the portal vein |
|
|
small ruminant comparative anatomy reticlum
|
relatively larger
|
|
|
small ruminant comparative anatomy ventral sac of the rumen
|
relatively larger
|
|
|
small ruminant comparative anatomy caudoventral blind sac
|
extends more caudally than the dorsal
|
|
|
small ruminant comparative anatomy omasum
|
smallest compartment
|
|
|
small ruminant comparative anatomy abomasum
|
relatively larger
|

