![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
trace a piece of food through the GI tract from the mouth to the anal canal
|
1. mouth
2. pharynx 3. esophagus 4. stomach 5. small intestine 6. large intestine 7. anal canal |
|
|
list 3 similarities found throughout the GI tract
|
1. movement of food
2. innervation (nerves controlling things) 3. wall structure |
|
|
what is the peritoneum?
|
the membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity [below diaphragm]
|
|
|
how many layers does the peritoneum have?
|
2 layers
|
|
|
what are the layers of the peritoneum?
|
1- parietal: lines inner wall of abdominal and pelvic cavities
2- visceral (serosa): covers visceral organs |
|
|
what is located between the layers of the peritoneum?
|
peritoneal cavity -- contains peritoneal fluid
|
|
|
what is found between the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches of the oral cavity?
|
palatine tonsil
|
|
|
list the locations of the 4 different types of taste receptors on the tongue
|
1. bitter - toward the back
2. sour - toward sides 3. salt - tip and upper front portion of tongue 4. sweet - tip of tongue |
|
|
list the teeth found in deciduous VS permanent dentitions
|
deciduous: 4 incisors, 2 cuspids, 4 molars
permanent: 4 incisors, 2 cuspids, 4 premolars, 6 molars (last 2 molars are wisdom teeth) |
|
|
list the layers of a tooth
|
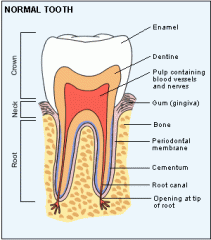
enamel
dentin cementum pulp root canals periodontal ligament |
|
|
list the 3 pairs of salivary glands
|
1. sublingual
2. submandibular 3. parotid |
|
|
list the 2 cell types found in the salivary glands
|
serous & mucous
|
|
|
what is each type of salivary gland cell type composed of?
|
serous: water; produces salivary amylase, bicarbonate (neutralize acids)
mucous: thick; mucous secretion for lubrication |
|
|
what is each type of salivary gland stimulated by?
|
serous: parasympathetic (speeds it up)
mucous: sympathetic (fight or flight: slows down) |
|
|
list 4 functions of saliva
|
1. solvent for taste
2. lubrication for swallowing 3. digestion of carbohydrates - due to amylase 4. cleanser - lysozyme breaks up cell walls of bacteria |
|
|
state the function of the eustacian tube
|
connects nasopharynx to middle ear to equalize pressure
|
|
|
list/describe the 3 stages of swallowing
|
1. voluntary -- tongue moves bolus into oropharynx
2. pharyngeal -- involuntary; peristalsis through pharynx; epiglottis closes over glottis (lets food into esophagus and not into trachea) 3. esophageal -- peristalsis into stomach |
|
|
list 3 functions of the stomach
|
1. digestion
2. food reservoir (*MAIN FUNCTION*) 3. limited absorption... not of nutrients though |
|
|
list and describe the location of the 4 regions of the stomach
|
1. cardiac -- upper region, located near heart, comes off espohagus
2. fundus -- upper left portion of stomach 3. body -- main, middle part of stomach 4. pyloric -- part of stomach between body and duodenum of small intestine |
|
|
state how the wall of the stomach is different from the rest of the GI tract
|
the muscularis layer of stomach has three layers: longitudinal, circular, oblique
the mucosa has lots of folds (rugae) that allow for expansion of stomach as food comes in the mucosa contains gastric pits and gastric glands |
|
|
state the name for the folds of the stomach mucosa
|
rugae
|
|
|
list the 4 types of cells lining a gastric gland
|
1. mucous
2. parietal 3. chief (zymogenic) 4. enteroendocrine |
|
|
list the secretions from each type of the cells lining the gastric gland
|
1. mucous -- mucus
2. parietal -- hydrochloric acid & intrinsic factor 3. chief (zymogenic) -- enzymes [pepsinogen & gastric lipase] 4. enteroendrocrine -- hormone [gastrin] |
|
|
list the 3 phases of gastric secretion
|
1. cephalic
2. gastric 3. enteric (intestinal) |
|
|
describe the 3 phases of gastric secretion
|
1. cephalic -- sight, smell, taste, or thought of food; caused by parasympathetic reflexes
2. gastric -- food in stomach; caused by stomach distention, secretagogues, gastrin, parasympathetic reflexes 3. enteric (intestinal) -- chyme in small intestine; caused by intestinal gastrin |
|
|
list 2 ways in which stomach secretion is inhibited
|
1. hormones from small intestine
[CCK-PZ, secretin, GIP] 2. enterogastric reflex [A. chyme stretches duodenum; B. receptors signal CNS; C. motor signals inhibit secretion, peristalsis] |
|
|
list 3 functions of the small intestine
|
1. major site of digestion
2. absorption of nutrients 3. moves residue to large intestine |
|
|
list the structural modifications of the small intestine mucosa adapted for absorption
|
1. simple columnar epithelium
2. plicae 3. villi 4. microvilli |
|
|
list the 3 sources of secretion from the small intestine
|
1. goblet cells
2. crypts of Lieberkuhn 3. paneth cells |
|
|
what is secreted by the goblet cells?
|
mucus -- to protect wall of small intestine
|
|
|
what secretes the hormones? which hormones are they?
|
crypts of Liberkuhn; GIP, secretin, CCK-PZ
|
|
|
what secretes the enzymes? what enzymes are secreted?
|
Paneth cells; lysozyme
|
|
|
list 6 classes of nutrients absorbed by the small intestine
|
1. monosaccharides
2. amino acids 3. triglycerides 4. electrolytes 5. vitamins 6. water |
|
|
what is unique about fatty acid absorption?
|
triglycerides combine with protein --> chylomicrons.
chylomicrons are absorbed in the lacteal [lymphatic system] and then get dumped in the subclavian veins. |
|
|
list 4 classes of enzymes secreted by the pancreas
|
1. pancreatic amylase
2. lipases 3. nucleases 4. proteases |
|
|
what does each pancreatic enzyme catalyze?
|
pancreatic amylase: digests starch [polysaccharide] down to maltose [disaccharide]
lipases: breaks down fats into fatty acids + alcohol nucleases: digests nucleic acids proteases: digests proteins [these enzymes are inactive until they hit the small intestine] |
|
|
list the 3 proteolytic enzymes secreted by the pancreas
|
trypsinogen
chymotrypsin carboxypeptidase |
|
|
how is each proteolytic enzyme (released by pancreas) activated?
|
trypsinogen: activated by enterokinase
chymotrypsin & carboxypeptidase: activated by trypsin |
|
|
what is the effect on the pancreas of the hormones secretin and CCK-PZ?
|
secretin: stimulates pancreas to produce a high volume of weak juice with a low concentration of enzymes; high bicarbonate (HCO3-) to buffer the acid coming out of the stomach
CCK-PZ: stimulates pancreas to produce a low volume of strong juice with a high concentration of enzymes |
|
|
list 3 functions of the cell membrane
|
1. functions as a boundary separating the internal environment of the cell from the external environment of the cell
2. functions as a semipermeable barrier, only permitting passage of selected materials into or out of the cell 3. contains protein receptors that enable the cell to communicate via chemicals with the exterior of the cell |
|
|
describe the electrical polarity of the cell membrane
|
the inner surface is slightly more negatively charged as compared to the outer surface
|
|
|
describe the Singer-Nicholson fluid mosaic model of membrane structure
|
there are 2 layers of molecules (phospholipids) that consist of many copies of the "polar head" and 2 lines projecting inward called the "fatty acid tails"
|
|
|
state which end of the phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic and which is hydrophobic
|
the polar head is hydrophilic
the fatty acid tails are hydrophobic |
|
|
list 6 functions of cell membrane proteins
|
1. channel proteins
2. carrier proteins 3. receptor proteins 4. enzymes 5. anchor proteins 6. cell identity or marker proteins |
|
|
state the difference between passive and active methods of transport
|
in passive [physical] transport, the cell moves material through the cell membrane without using energy to do so
in active [physiological] transport, materials are moved through the cell membrane accompanied by an expenditure of energy mediated by breaking of bonds within ATP |
|
|
list the 4 passive (physical) methods of transport
|
1. simple diffusion
2. facilitated diffusion 3. filtration 4. osmosis |
|
|
describe the 4 passive (physical) methods of transport
|
simple diffusion: materials are moved from an area of HIGH concentration to an area of LOW concentration [down its concentration gradient]
facilitated diffusion: refers to the movement of substances down their concentration gradient with the aid of carrier proteins embedded within the cell membrane filtration: materials are moved from an area of HIGH PRESSURE to one of LOWER PRESSURE [down a pressure gradient] osmosis: DIFFUSION OF WATER through a SEMIPERMEABLE MEMBRANE |
|
|
define the term "osmotic pressure"
|
the force that drives osmosis; measure by applying equal downward pressure, which prevents the fluid level from rising
|
|
|
contrast the terms: "isotonic", "hypertonic", and "hypotonic"
|
isotonic: EQUAL concentration of solutes [and therefore water] on both sides of the cell membrane
hypertonic: cell will shrivel as water leaves the cell, flowing down its concentration gradient; the reason for this is that the hypertonic solution contains a higher concentration of solute [and therefore water] that they cytoplasm of the cell hypotonic: a cell will swell as water enters the cell, flowing down the concentration gradient; the reason for this is because the hypotonic solution contains a lower concentration of solute [therefore more water] than the cytoplasm |
|
|
list the 2 basic categories of active transport methods
|
1. active transport: materials are moved through the cell membrane from low to high concentration [against the concentration gradient]
2. bulk transport: involves movement of a relatively large amount of material through the cell membrane |
|
|
contrast primary and secondary active transport
|
primary active transport involves SPLITTING of the molecule ATP [thus releasing energy] with an accompanying change in the shape of a membrane protein; this change of shape results in movement of some material through the cell membrane [ie. sodium/potassium pump]]
secondary active transport: depends on ION GRADIENTS [differences in ion concentrations across the cell membrane] established by means of primary active transport |
|
|
contrast the terms "symport" and "antiport"
|
symport: movement in same direction
antiport: movement in opposite direction |
|
|
list 3 methods of endocytosis
|
phagocytosis: literally means "cell eating"
pinocytosis: literally means "cell drinking" receptor-mediated endocytosis: occurs when ligand molecules bind to specific receptor proteins in the cell membrane |
|
|
list 8 functions of the liver
|
1. carbohydrate metabolism
2. fat metabolism 3. protein metabolism 4. detoxification 5. storage [vitamins] 6. activate vitamin D so calcium can be absorbed in sm intestine 7. phagocytosis by Kupffer cells 8. synthesize bile |
|
|
list the components of bile
|
bile salts & bile pigments
|
|
|
state the function of bile salts
|
emulsify fats
|
|
|
list the function of the gallbladder
|
it's a sac that stores bile
|
|
|
trace the pathway of bile from the liver to the gallbladder to the duodenum
|
liver
hepatic ducts common hepatic duct cystic duct gallbladder cystic duct common bile duct duodenum |
|
|
what are the effects on the biliary apparatus of the hormone secretin?
|
secretin comes from crypts of Lieberkuhn in small intestine; it stimulates the liver to produce bile
|
|
|
what are the effects on the biliary apparatus of the hormone CCK-PZ?
|
CCK-PZ comes from crypts of Lieberkuhn in small intestine; it stimulates the gallbladder to contract
|
|
|
state the name of the pouches present in the large intestine
|
haustra
|
|
|
list 3 functions associated with the large intestine
|
1. water/electrolyte reabsorption
2. eliminate waste as feces 3. bacteria ferment waste to synthesize vitamins **no enzyme secretion or digestion happens in large intestine** |
|
|
list the names and locations of the 2 flexures in the color
|
hepatic flexure --- between ascending and transverse colon; located by the liver
splenic flexure --- between transverse and descending colon; located by the spleen |
|
|
list the 2 sphincters located in the anal canal. what kind of muscle is each?
|
internal -- smooth muscle [involuntary]
external -- skeletal muscle [voluntary] |

